High echogenicity of the pancreas. Increased echo density of the pancreas
An ultrasound examination of the pancreas determines its characteristics, such as:
- The correctness of the geometric shape;
- Smoothness or tortuosity of contours;
- Dimensions - enlarged or normal;
- Echogenicity of the gland and the degree of its homogeneity.
In addition to the gland itself, the condition of the main pancreatic duct and nearby veins is examined along the way.
What is the echogenicity of the gland
A healthy pancreas on ultrasound looks homogeneous, in other words, homogeneous. The image consists of small, closely spaced echoes. The echogenicity of the parenchyma (gland tissue) is compared with the echogenicity of the liver, normally it should be equal to or higher than the latter. Moreover, the older the patient, the more significant the relative increase in echogenicity can be, and if the structure of the pancreas remains homogeneous, then there is no talk of pathology.
What is echogenicity, and what can decreased or increased echogenicity of the pancreas mean? This property of the dense tissue of the gland to reflect the sound signal of the apparatus for ultrasound. If cellular changes have occurred in it - for example, part of the gland tissue has been replaced by connective or fatty tissue, then the ability to reflect sound will also change. A short-term change in echogenicity can also be caused by a change in diet, temporary indigestion, and other external factors. Therefore, one value of echogenicity not enough to make a correct diagnosis.. To exclude an error, data on the size of the gland and its structure are required.
Possible diagnoses
What disease can a doctor suspect if ultrasound showed that the echogenicity of the pancreatic parenchyma is increased? Depending on whether there are changes in its size, whether the gland has retained a homogeneous structure, or inclusions are present, the diagnosis may be different.
As a rule, in most cases, this means that there is swelling in the gland associated with the inflammatory process. But on the basis of one sign of increased echogenicity, it is too early to immediately diagnose "chronic pancreatitis". If the size of the organ is not enlarged, then it is possible to suspect lipomatosis.
If ultrasound of the pancreas showed a decrease in its size, despite the fact that echogenicity is increased, it is possible that the parenchyma is replaced by connective tissue, and we will talk about fibrosis. Such changes in the tissues of the pancreas can occur as consequence of inflammation, or due to impaired metabolism caused by diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Sometimes this change in echogenicity is a direct consequence of diabetes mellitus, especially in the elderly. In addition to changes in the structure of the gland itself, portal hypertension - an increase in the blood pressure of the portal vein also leads to an increase in the echogenicity of the pancreatic parenchyma.
If the structure of the gland has lost its homogeneity, cysts or calcifications are traced, then the diagnosis of the disease is even more difficult.
Normally, pancreatic tissue produces up to a liter of pancreatic juice per day, which contains the most important enzymes for proper digestion of food. Whatever disease would cause increased echogenicity of the pancreas, need to be diagnosed as soon as possible and prescribe the necessary treatment.
The pancreas is a very important but very vulnerable organ. With belated treatment, tumor degeneration can begin in it, as well as tissue breakdown. It is very important, having revealed an increased echogenicity of the pancreas on an ultrasound examination, to undergo a set of additional diagnostic examinations in order to start treatment as quickly as possible.
If the ultrasound report indicates: the echogenicity of the pancreatic parenchyma is increased, do not panic and look for treatment methods on the Internet. This is not a diagnosis, but only a symptom. However, it should not be ignored. It may indicate a serious problem. After ultrasound diagnostics, a mandatory consultation with a gastroenterologist is required.
Echogenicity is a special term used to describe the results of ultrasound diagnostics. This is the ability of organ tissues to reflect high-frequency sound, which is the research method. Visually, this ability looks like a gray picture on the monitor. By shades of gray, the doctor determines the state of the organ. At the same time, it is impossible to establish an accurate diagnosis based on ultrasound alone.
Different organs are characterized by different indicators of echogenicity. Liquids, for example, do not reflect sound at all, but transmit it. Hollow organs - stomach bladder- echo-negative. For them, this is absolutely normal. In organs that are homogeneous in structure, dense in structure (liver, pancreas), echo density is an important indicator.
An increase in the echo density of the glandular tissue indicates the replacement of normal cells with fatty, scarring, or cells with a high water content. This is not the norm and requires more careful study.
In the pancreas, echogenicity increases due to a decrease in glandular cells in the tissue. This violation can be temporary or permanent, localized at one point or capture the entire organ.
Reasons for changing echo density
There are many reasons that affect the increase in echogenicity. It can be either a small inflammatory process, or the presence of a serious disease, neoplasms in the organ. The change in density may be a temporary phenomenon. For example, such a phenomenon is observed after suffering a cold, as a result of malnutrition.
The presence of an acute or chronic stage of pancreatitis invariably leads to heterogeneous structure organ density. If, during the collection of an anamnesis, the doctor finds symptoms of the disease, then treatment is prescribed. Pancreatitis requires inpatient treatment, constant medical supervision, and diet.
Hyperechogenicity may indicate the presence of neoplasms. If a malignant process in the pancreas is suspected, a puncture is additionally assigned, which will confirm or refute it.
Increased echogenicity of the parenchyma is also an age-related change. By old age, the cells of the organ are replaced by fibrous ones. This phenomenon does not require treatment. In some cases, supportive therapy is prescribed.
Diffuse echogenicity
If present, it may indicate the following pathologies:
- diabetes;
- the presence of a tumor (if other symptoms are present);
- pancreatitis with edema of the gland;
- organ necrosis;
- lipomatosis;
- fibrosis of the gland.
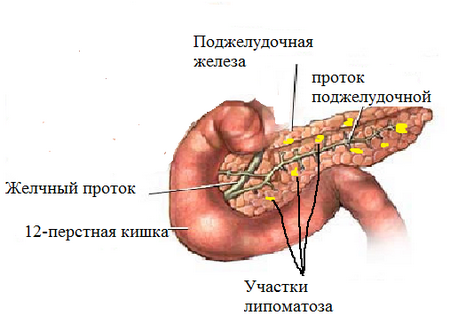
All these diseases require treatment and additional consultation with a doctor.
Violation does not always indicate the presence of the disease. It may indicate an altered condition that does not require specific treatment:
- after reactive inflammation;
- with climate change;
- seasonal changes;
- age-related changes;
- when eating fatty, spicy foods;
- when diagnosing immediately after eating.
The nature of the violation of the gland is determined by the degree of increase in echo density. In physiological conditions that do not require treatment, the echogenicity of the pancreatic parenchyma is moderately increased.
Local changes
The conclusion of the ultrasound may contain the following phrase: hyperechoic inclusions in the pancreas. In this case, we are talking about the presence of serious problems with the body.
The main reason for this conclusion is the appearance of neoplasms in the body of the gland. These may be pseudocysts. Such formations appear as a result of the transferred acute form of pancreatitis. They are characterized by an uneven outline, the contours of the pancreas become jagged. Stones in the ducts of the gland are another reason for the appearance of areas of increased echo density.
Tumors are also manifested by a local increase in echogenicity. Most often, these are metastases, secondary manifestations of cancer. They appear in the later stages of the disease and complicate therapy.
Lipomas appear as a result of the replacement of gland cells with adipose tissue. When fat cells accumulate in one part of the body, benign tumor. The process begins at the first stage of obesity, malnutrition.
After suffering pancreatic necrosis, the affected areas of the organ are replaced by scar tissue. Such fibrous areas ultrasound diagnostics are manifested by local changes in echogenicity.
Treatment
Treatment of hyperechogenicity is to find the cause of the changes. A single symptom identified by ultrasound cannot give a complete picture of the disease. Therefore, the doctor must necessarily collect an anamnesis and prescribe additional research methods.

First of all, you need to submit clinical analysis blood. A change in the main indicators will show the presence of an inflammatory process in the body. A blood sugar test is also required. It indicates that the patient has diabetes mellitus. With a local increase in the echo density of the parenchyma, a puncture of the formation is required. Biochemical analysis determine the malignancy of the tumor.
In the absence of serious problems, the state of the organ is normalized by following a diet, daily routine. The patient should avoid stressful situations, hypothermia.
When diagnosing severe disorders, serious therapy is required, aimed at the root cause of the disease.
Ultrasound examination of organs and tissues has become an integral part of everyday medical practice. Without ultrasound, it is difficult to imagine the diagnosis of a large number of various diseases. The study assesses the echogenicity of the organs: liver, pancreas and thyroid gland, gallbladder. When it is elevated - what could it be? We will talk about situations for which it is typical. Indeed, such a formulation can often be seen from the results of a study of the abdominal organs. So, the diagnostician in his conclusion described: the echogenicity of the pancreas is increased, what is it?
Gastroenterologist Mikhail Vasilyevich:
"It is known that for the treatment of the gastrointestinal tract (ulcers, gastritis, etc.) there are special drugs that are prescribed by doctors. But we will not talk about them, but about those medicines that you can use yourself and at home ..."
The essence of ultrasound examination
Ultrasound evaluates many different parameters that allow visualization of the organs under study. To diagnose changes in parenchymal organs (lungs, liver, pancreas), a parameter such as echogenicity is used.
This indicator is used to characterize how dense the tissue under study is. The principle on which ultrasound is based is known from such a branch of physics as acoustics. The impulse that the sensor sends reaches the organ. Depending on the structure, density, the signal is transformed, returning to the screen.
Echogenicity is the higher, the denser the parechymal tissue. This may mean that an increase in the echogenicity of the pancreas on ultrasound may be associated with diseases that affect its density.
Brief description of the pancreas
This organ is considered glandular. It is able to produce hormones and enzymes. The pancreas is therefore considered not only a digestive organ, but also an endocrine gland.
Hormones produced include insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin. It often affects carbohydrate metabolism and the risk of developing diabetes.
The exocrine function of the organ is the secretion of digestive enzymes. They take part in the digestion, catabolism of fats, carbohydrates and proteins. For this reason, a violation of the exocrine function of the organ affects the work of all digestive processes.
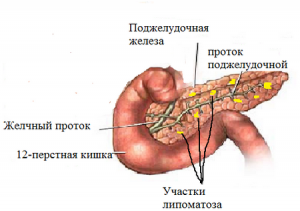
Increased echogenicity of the pancreas can be of two types:
- local zoom.
- Diffusely increased echogenicity of the organ.
Under what conditions can there be such an ultrasound picture?
pancreatitis
Inflammation of the tissues of the pancreas can be acute and chronic. Pancreatitis during exacerbation is very bright. There is a wide variety of symptoms. Here are some of them:
- pain in the epigastrium of a girdle character, resembling intercostal neuralgia;
- vomiting preceded by nausea;
- tachycardia;
- febrile temperature;
- severe weakness and headache.
An attack of pain is usually provoked by poor-quality food or an error in diet, alcohol intake. The picture of this disease is clear even without ultrasound, as it is very acute. But still, during this study, it is noted that the echogenicity of the pancreas is increased. There is a clear contour around it, especially in the edematous form of the disease. Pancreatic necrosis is accompanied by a parallel decrease in the size of the gland. Laboratory tests play an important role in diagnosis. Increasing blood amylase and urine diastasis, leukocytosis and accelerated ESR are typical for a complete blood count.

Chronic pancreatitis is a disease that occurs with remissions and exacerbations. The pain syndrome worries only at relapse. With remission, there may be a dyspeptic syndrome. It is known that a disease such as chronic pancreatitis occurs with indigestion and malabsorption. There is a lack of proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins in the body. The stool becomes irregular, there is a tendency to constipation, alternating with a diarrheal syndrome. The latter is caused by steatorrhea, as exocrine function is impaired and not enough enzymes are secreted for digestion.
When conducting ultrasound examination echogenicity of the pancreatic parenchyma is increased. With a long course of a chronic process, the size of the organ can be reduced, while early stages the pancreas is larger than usual. The ultrasound picture also demonstrates the heterogeneity of the structure of the pancreas. What does it mean? Against the background of increased organ density, calcified areas or cystic cavities (pseudocysts) may occur. It is possible that these are necrotic changes caused by frequent relapses.
Local increase in echogenicity
The clinical situations described above are accompanied by a diffuse increase in the density and intensity of the signal from the pancreatic tissues. There are situations like:
- malignant tumors;
- metastases in the parenchyma of the pancreas;
- benign neoplasia;
- lipomatosis.
These conditions are united by the fact that during ultrasound of the abdominal organs in the projection of the pancreas, foci of increased echogenicity will be visualized, while the rest of the tissue of the organ will have normal echo density.
Malignant neoplasms and metastases manifest themselves clinically at different stages in different ways. The first stages usually go unnoticed by clinicians.
- Weight loss for no apparent reason.
- Aversion to certain kinds of food.
- Pale skin.
- Unmotivated weakness and fatigue.
- Asthenia, anxiety.
Accession of pain and specific dyspeptic disorders is typical for the late stages of the disease. At the same time, the level of oncomarkers is increased, there are significant changes in the biochemical profile.
Other reasons
Among other factors that cause an increase in the intensity of the echo signal from pancreatic tissues, dystrophy in diabetes mellitus. This disease is characterized by impaired insulin secretion. It is impaired primarily in type 1 diabetes mellitus and secondarily in type 2 diabetes. In old age, the tissue of the organ undergoes sclerosis, fibrosis. Therefore, in the background increased echogenicity sizes are reduced.
What other conditions can cause increased echogenicity on ultrasound?
- non-compliance with the diet - the use of products that cause severe gas formation;
- systematic intake of alcohol;
- features of the chair, its multiplicity and regularity.
In any case, such a conclusion should be a reason to go to the doctor (therapist or gastroenterologist) and find out possible reasons. To do this, you will have to pass tests, against the necessary studies.
Published: October 15, 2014 at 10:28 amTired of pain in your stomach, stomach...?
- I have a stomachache;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- heartburn;
Have you forgotten when you were in a good mood, and even more so when you were feeling well?
Yes, digestive problems can seriously ruin your life!But there is a solution: a gastroenterologist, head of the gastroenterology department Arkhipov Mikhail Vasilyevich
When conducting an ultrasound of the pancreas, the doctor, first of all, evaluates its echo density and echogenic structure. A uniformly increased or decreased density of the gland allows us to conclude that there are diffuse changes in the organ. If the size of the pancreas is normal, the Wirsung duct is convoluted, and its edges are uneven, then most often it will be lowered.
But with fibrosis of the tissues of the gland, it will be increased, since the fibrous tissues have a denser structure than the tissues of the organ. Such a change in the structure during the growth fibrous tissue combined with a reduced volume of the pancreas. Usually, fibrous growths in the gland are associated with trauma, metabolic disorders, or chronic pancreatitis. And when acute form iron pancreatitis on ultrasonography will be displayed with fuzzy contours and reduced density. The echo density of the pancreas in acute pankeratitis can vary widely. With pancreatitis and other diseases of the gland, the density of the organ can be reduced not only diffusely, but also focally. In this case, the number of denser parts of the organ directly depends on the severity of the disease. These areas may have distinct or blurry contours, the shape of such less dense inclusions is usually irregular.
If during ultrasound there is an alternation of areas of increased echo density with a reduced one, then, most likely, the patient chronic form pancreatitis.
Areas of very low density of the pancreas are found on sonography of an organ prone to necrosis, while necrotic zones may have uneven contours with varying degrees of clarity.
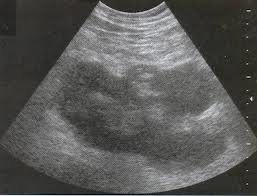 Also, changes in echo density are found in pancreatic tumors. It is often very difficult to determine exactly what is causing the change, pancreatitis or cancer, without additional examination, especially if these two diseases are combined with each other.
Also, changes in echo density are found in pancreatic tumors. It is often very difficult to determine exactly what is causing the change, pancreatitis or cancer, without additional examination, especially if these two diseases are combined with each other.
It is more difficult to determine chronic pancreatitis by density in children, since in 86% of cases this disease will act as a secondary one against the background of another, and therefore, echo density may be increased, decreased, or remain unchanged in the first time after the onset of the disease.
In any case, a change in pancreatic density in itself cannot serve as a valid basis for prescribing treatment if there are no other symptoms that would indicate a specific disease.
Today, you can often see the conclusion of an ultrasound scan, which indicates that there is an increased echogenicity of the pancreas. Some people, having learned about this, quickly try to find a treatment, the rest, on the contrary, consider this phenomenon to be completely unimportant. Nevertheless, such an ultrasound syndrome indicates a rather dangerous pathological process in the gland. It is not considered a diagnosis and requires prior consultation with a specialist.
What does echogenicity imply?
Echogenicity of the pancreas is a term used only in relation to the interpretation of ultrasound. Talks about the ability of the tissue targeted by ultrasound to reflect it. The reflected high-frequency sound is recorded by the same device that starts the waves. The difference between these two indicators creates an overall dynamics of different shades of gray, which can be observed on the screen of the device.
All organs have their own indicators of echogenicity, moreover, they can be homogeneous or not. The following relationship is noted: the denser the organ, the higher the echogenicity (displayed in a lighter shade). Liquid high-frequency sounds pass. This is called "echo-negativity", and structures of a liquid nature are called anechoic. For the urinary and gall bladders, heart cavities, gastrointestinal tract, blood vessels, ventricles of the brain, this "behavior" is the norm.
Increased echogenicity of the pancreas is observed when there are not enough normal glandular cells inside the tissue of the organ (the fluid helps to reduce echogenicity, and these cells are saturated with it).
Such changes are noted locally and diffusely. In addition, certain factors can affect this indicator for a short time.
Causes of increased echogenicity
A diffuse change in the permeability of an organ tissue for ultrasound is a sign of a pathological process, but it also happens within acceptable limits. This is not typical for areas with increased echogenicity - this is often a pathology.
The echogenicity of the pancreatic parenchyma increases due to the following factors:

Formation within the gland connective tissue occurs mainly due to previous inflammation or metabolic failures. In this situation, the patient is able to recall cases of unstable stools, pain in the abdomen. Ultrasound can show not only an increase in echogenicity, but also a decrease in the size of the organ, the tuberosity of its outline.
Hyperechogenicity in the pancreas is a short-term phenomenon that manifests itself:
During these short-term conditions, the echogenicity of the organ is increased to a moderate degree, as opposed to pathological processes, when significant hyperechogenicity is noted.
Hyperechoic inclusions
These phenomena in the pancreas are:

Elimination of pathological hyperechogenicity
Therapy is prescribed when the diagnosis of factors that contributed to the transformation of tissues inside the gland is carried out. In a situation with acute and chronic pancreatitis, treatment is carried out in a clinical setting. Therapy of conditions, if the echogenicity of the organ is increased, can only be prescribed by a specialist who establishes the cause of such ultrasound symptoms:

There is currently no self-treatment of this pathology in the pancreas. The specialist diagnoses the cause of the change in the tissue, directs the treatment for its further elimination and restoration of the functioning of this organ. When the cause of these changes is diabetes mellitus, then the therapy will be aimed at maintaining the sugar content in the bloodstream, the patient is prescribed strict adherence to dietary nutrition.
In order to prevent problems in the future, you need to balance your diet, you should remove fatty and fried foods from the menu, give up addictions (alcohol abuse and smoking). In order not to miss the beginning of changes in the tissues of the pancreas, it is necessary from time to time to be examined by a specialist and take preventive measures.
