What is long head tendon tenosynovitis. Tenosynovitis: causes, manifestations and approaches to therapy
Pain in the joints is not always directly related to their pathology - often unpleasant sensations are caused by soft tissue damage. The most common of these is tenosynovitis (tenosynovitis), associated with inflammatory changes in the synovial membrane of the tendons. Normally, it provides additional support during movements, facilitating their implementation due to the lubricant contained within it.
Due to a variety of reasons, damage to this inner shell can occur, after which an inflammatory process starts in it. Unlike degenerative diseases of the joints and soft tissues, tenosynovitis is an acute process. Therefore, with the timely application of therapeutic measures, it is possible to quickly eliminate the symptoms of inflammation, relieving the patient from discomfort during movement.
Although the tendons pass near almost any joint, not every one of them is susceptible to the development of pathology. There are special points of the musculoskeletal system, where the development of tendovaginitis is most often observed. These include ligaments of the wrist, knee and ankle joints. All of them have characteristic features of development and course, although the treatment in each case is carried out according to the same principles.
concept
Many patients are immediately frightened when they see a diagnosis of tenosynovitis in a card or statement - what is it? The incomprehensible name immediately creates associations with a terrible and incurable disease that will lead to a sharp deterioration in health. But, in fact, almost every person suffers this pathology under the guise of a slight injury during his life.
Tendovaginitis in more than 90% of cases is acute, and after completion does not leave any pathological changes. It is extremely rare (usually while maintaining the action of the provoking factor) it becomes chronic. To better understand this process, you should consider it from the point of view of anatomy and physiology:
- To reduce friction in the joint area, some ligaments are enclosed in separate or common synovial sheaths. These structures have a structure similar to the shells of the joint.
- The tendons are in their cavity quite freely due to the liquid lubricant inside - the synovial fluid. This position allows them to slide freely relative to the surrounding soft tissues during movements in the joint.
- Any damage - external or internal - provokes the development of an immune response. An acute inflammatory process begins in the defect area.
- Edema of the synovial sheath leads to its narrowing, as well as a decrease in lubrication. Therefore, the friction of the tendons during repetitive movements gradually increases, which leads to an increase in mutual damage.
- Constant mechanical irritation leads to the activation of surrounding nerve endings, which contributes to the onset of symptoms of the disease.
The course of the disease depends entirely on the cause that caused its development - if the inflammation is non-specific, then it is unlikely to leave pronounced consequences.
Development mechanisms
Although the general basis for the disease is the inflammatory process, its appearance can be caused by a variety of factors. For convenience, they can be divided into two large groups - traumatic and specific:
- Direct injury is much more common - it is associated with a direct blow to the area of the synovial sheath, or caused by functional overload of the tendon. But in each case, the pathological mechanism is the same - mechanical damage to the sheaths of the ligament. An inflammatory process develops in the area of the defect, which is aggravated by constant friction during movements.
- Specific direct damage is associated with a penetrating wound of the synovial membrane, through which microbes enter it. They already cause a real immune response, often accompanied by the development of purulent inflammation.
- A specific indirect lesion is considered reactive - this is a reflected reaction of the immune system to any general infection. Often, tenosynovitis becomes the outcome of a viral illness, manifesting itself a few days or weeks after recovery.
Despite the variety of mechanisms, the disease in each case has similar symptoms, the origin of which can only be determined by questioning the patient.
Localization
Since the disease is general principles flow, then its manifestations in some cases will also be very similar. Therefore, it is necessary to highlight some signs that are characteristic of the development of tenosynovitis:
- The main symptom is always pain. His distinguishing feature- this is the appearance only with specific movements associated with the work of the affected tendon. At rest, the pain usually disappears completely.
- An important diagnostic feature is the change in pain during active or passive movements. If a person himself performs flexion or extension, then the discomfort is more pronounced. This is due to the contraction of the muscles that actively act on the affected ligament.
- With a superficial location of the focus, a change in the skin over the inflamed synovial vagina is noted. A small area of redness appears, which has rounded outlines and is hot to the touch.
- With pressure in the region of this focus, a clearly defined nodule or cord-like seal can be felt.
- If at this moment you try to make a movement that provokes discomfort, then you can determine a slight crunch - crepitus. It is associated with friction of the tendon against the inflamed and edematous walls of the synovial sheath.
Most often, tenosynovitis develops in the area of the joints bearing a constant functional load, which disrupts the healing process when the sheath of the ligaments is damaged.
Knee-joint

This articulation is surrounded by a large number of ligaments that have different functionalities. The lateral and posterior group of tendons do not have separate synovial sheaths, since they mainly perform a supporting function. Therefore, the development of the disease is more susceptible to those formations that carry a constant dynamic load:
- Most often, there is a lesion of the "goose foot" - the area of \u200b\u200battachment of the semitendinosus, tailor and thin thigh muscles. This place is located on the inner surface of the joint, and, due to small sizes ligaments, often involved in the pathological process. In this case, there are sharp pains in the indicated area when walking or running, the appearance of a painful induration, an area of redness on the skin.
- The tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscle at the border with the upper pole of the patella is less commonly affected. The disease always has a traumatic origin, and is caused by excessive sports or household stress. In this case, there is edema above the patella, local pain when the leg is extended, and relative weakness of the quadriceps muscle.
tenosynovitis knee joint rarely takes a chronic course, but it is capable of frequent relapses under the influence of these risk factors - injuries.
Ankle joint
The lesion in this localization has a mixed character - traumatic variants of the disease are more common, less often reactive. The occurrence of symptoms in the ankle joint almost always ends favorably, due to the good ability of the ligaments to recover. The most common injuries to the following tendons are:
- In the first place in terms of occurrence is tenosynovitis in the region of the inner edge of the foot, where they pass to the sole of the flexor tendon of the fingers. Their damage often occurs when a person awkwardly stumbled or jumped. After that, pain appears in this area, aggravated by walking or active flexion of the fingers - other symptoms are usually absent.
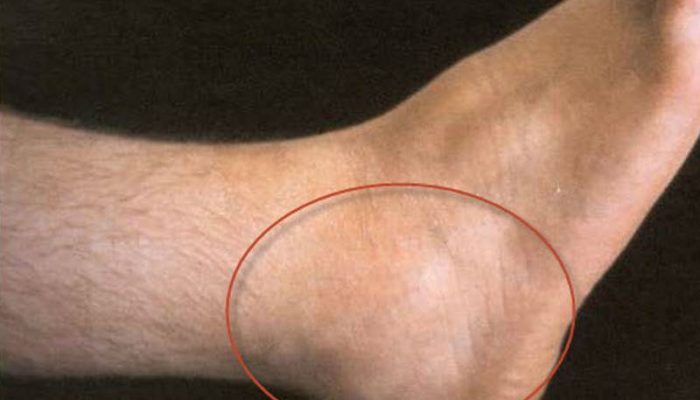
- Less commonly, there is a lesion of the extensor tendons passing in the synovial membranes at the border of the rear of the foot and ankle joint. They are located quite superficially, therefore, in addition to pain in their projection, when walking or standing up “on toes”, edema or local induration appears above them.
- Rarely, tenosynovitis of the Achilles tendon is usually reactive or due to direct trauma. Since the ligament is accessible for inspection, inflammatory changes along its length immediately become noticeable. Pain occurs when walking, localized in the heel region.
If the pathological factor that led to the development of the disease is not eliminated, then the symptoms may become permanent, limiting the patient's activity.
nodular
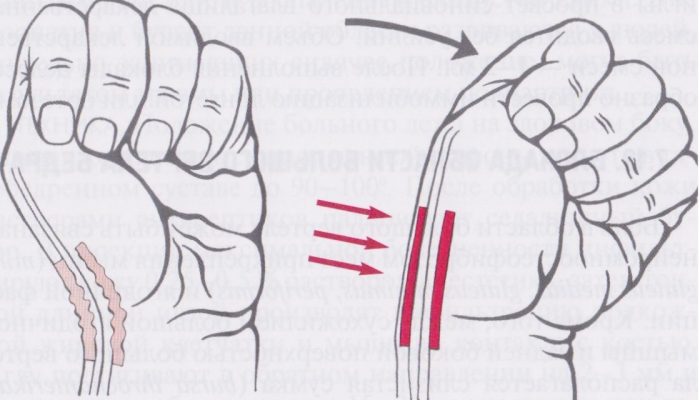
A feature of inflammation that occurs on the tendons in the area of the hand is its frequent chronic course. Under the influence of the load, permanent damage to the synovial vagina occurs, leading to the development of irreversible degenerative changes in it. Therefore, it began to be called nodular tenosynovitis - an inflammatory process in combination with deformation of the ligaments and their membranes.
There are two separate groups of tendons on the hand - on the dorsal and palmar surfaces of the wrist joint. Their defeat is accompanied by the appearance of similar symptoms:
- The development of pathological manifestations from the tendons on the inner surface is more often observed. Tenosynovitis is manifested by aching pain in the wrist area when the fingers are clenched into a fist, the occurrence of edema or painful compaction, redness there. With a long course of the disease, the nodules become dense to the touch - they can often be seen even with an external examination.
- The defeat of the synovial sheaths on the back of the hand is also accompanied by pain when clenching the fist, and its intensification when extending the fingers. There is a painful to the touch and movable seal over the wrist joint, increasing in size with extension in it.
The nodules that occur during the chronic course of the disease are not eliminated over time - they are growths connective tissue in the area of shell defects.
Treatment
Help with tenosynovitis is mostly non-specific in nature - the patient can carry out most of the therapeutic measures at home. Almost all of them are based on creating an optimal motor mode for the affected ligament in order to ensure the full healing of its membranes. To do this, you need to perform the following activities:
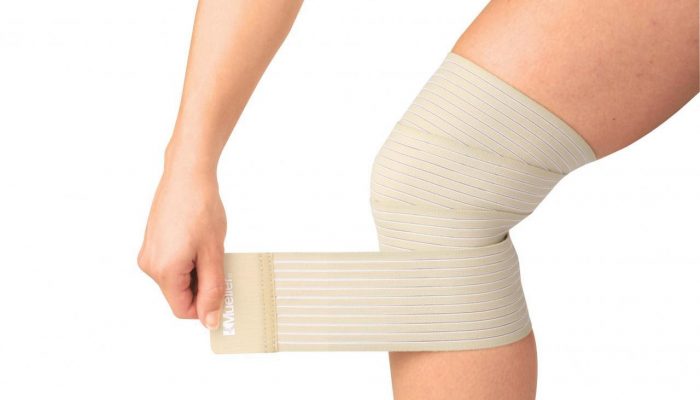
- During the first days after the onset of symptoms, it is required to create functional rest for the tendon. For this, absolutely any devices that allow artificially limiting mobility in the joint are suitable.
- The easiest way is to make a bandage with an elastic bandage. Eight-shaped options are suitable for the area of \u200b\u200bthe wrist or ankle joint - they will perfectly limit both flexion and extension in the joint. For the knee, it is better to make a turtle bandage - it has good supporting properties.
- Soft bandages or orthoses with adjustable stiffness are a good alternative to elastic bandages. But if they are not there, then it is not necessary to purchase them only to fix the joint for several days.
- After about three days, you can start the program physiotherapy exercises- it will need to be performed daily for 30 minutes. Classes begin with the development of passive movements, and only after a few days you can gradually introduce active exercises.
In addition to these methods, pain medication and physical therapy are now being added to speed up the recovery of ligament function.
Medical

Artificial elimination of the inflammatory process allows the body to quickly start healing processes in the affected synovial vagina. modern medicine can offer a wide range of drugs and techniques that suppress the pathological mechanisms of the disease:
- The standard of care is the appointment of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) - in various forms of administration. Tenosynovitis is mainly used local funds- ointments or gels (Voltaren, Nise, Ketorol). Only with severe inflammation is it possible to take pills situationally, which allows you to suppress the symptoms.
- If NSAIDs are not enough to control the manifestations, then the issue of local administration of hormones is decided - injections of Diprospan. The injection is placed in the area of the affected synovial vagina, allowing you to reduce pain and swelling.
- Additionally, local irritants are prescribed - Dimexide applications, Kapsikam or Finalgon creams. They have a distracting effect, and also improve blood circulation in the area of the pathological focus.
- There are practically no restrictions on physiotherapy procedures - you can use any available method. To relieve pain, electrophoresis or phonophoresis with novocaine, paraffin or ozocerite applications are suitable. To improve recovery - laser or magnetotherapy, inductothermy, electrophoresis with enzymes.
The optimal combination of organizational and medical methods reduces the duration of the disease, allowing a person to quickly return to their usual activity.
Surgical
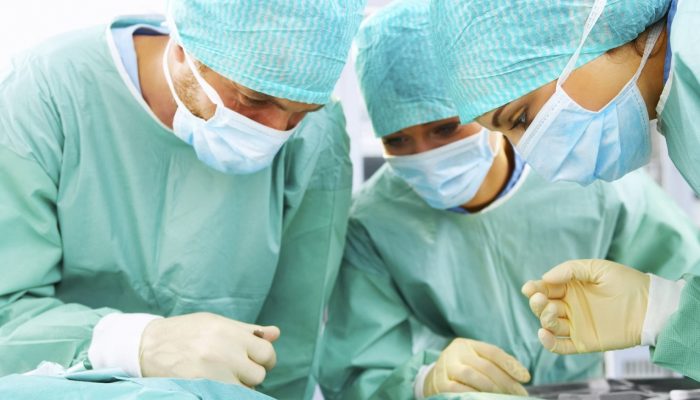
When the inflammation becomes purulent, or the pain syndrome cannot be eliminated by conservative methods, indications for surgery appear. It allows you to radically eliminate the existing pathological focus:
- First, the altered synovial sheath is isolated from the soft tissues surrounding the joint.
- Then it is opened, and all deformed or inflamed parts of the shell are excised.
- The pathological focus is repeatedly washed to remove exudate, as well as areas of the affected membranes.
- A tendon plasty is performed - nodules and growths of connective tissue are removed. Then it is again placed in its usual place, only without the shells surrounding it.
The loss of the synovial sheath still affects the work of the ligament in the future, although only slightly - with a good rehabilitation program, the changes can be corrected. And removing the source chronic inflammation allows you to get rid of unpleasant symptoms that violate the usual activity.
A syndrome in which inflammation of the tendons of the thumb occurs is called de Quervain's disease. The pain associated with this ailment appears from the friction of swollen tendons against the walls of the tunnel designed for their movement.
In any person, the muscles of the hands are bent with the help of contractions of the muscles of the forearms. It is for this that the tendons of the flexor and extensor muscles are involved. The first are drawn to the hand through the side of the palm, and the second through the back. Their correct position is provided by transverse ligaments. The same channel serves to pass the long abductor muscle. Very hard work is done in flexion and extension of the thumb tendon, which is involved in many tasks. Their inflammation is also called tendovaginitis. As a result of this process, they greatly increase in size and become too large for their channels.
The causes of the syndrome can be completely different. For example, tendovaginitis can cause constant repetition of the same brush movements. Such actions can be considered holding a baby, playing golf, positioning hands during computer games and so on. Such manipulations create a great load on the tendons of the hand, especially the thumb. Most patients with this disease are observed in the age group of people 30-50 years old. At the same time, women are more likely to get sick, which can be caused by pregnancy and caring for a baby. This disease is as common as the disease of the knee, ankle and shoulder joints.
De Quervain's syndrome causes the following symptoms:
- pain at the attachment point of the thumb to the hand (joint);
- swelling of the base of the finger;
- difficult movements in the wrist;
- increased pain with pressure;
- pain in the wrist joint with pressure on the head of the joint of the thumb;
At the beginning of the disease, pain appears only with intensive movement of the hand, and after a certain time it becomes constant. This pain radiates to the entire hand, sometimes to the biceps, forearm, and even to the neck. In some cases, the pain goes to the very tip of the finger.
Often pain arise in a dream, with any wrong movement. A person loses the ability to firmly hold objects in his hand. In the absence of adequate treatment of the disease, it can spread further along the arm, affecting the forearm. The ability to perform any work with your hands is sharply reduced. If there has been an injury with subsequent tissue infection, tenosynovitis may develop. Tenosynovitis is an inflammation of the tendon sheath of an infectious nature.
At the very beginning, the doctor conducts a visual examination of both hands of the patient. He compares them appearance and condition, which makes it possible to determine the degree of damage to the tendon. Usually the disease is not manifested by reddening of the skin or an increase in its temperature over the sore spot. This is possible only with improper self-treatment of the disease, which patients often do before going to a specialist. You can see only a certain swelling over the tendons of the thumb.
The doctor begins palpation of the hand, the person has pain in the affected area, which reaches its climax over the styloid process of the radius. There is usually no pain in the area of the tendons, and a dense round thickening can be found behind the styloid process.
At the next stage of the examination, the patient puts his palms on the table and tries to turn them in one direction and the other. As a rule, there are no difficulties with tilting towards the first finger, but movements are constrained from the side of the little finger. The patient cannot withdraw much thumb to the side in the position of the brushes, placed on the edge with the palms inward. The difference in this ability between a healthy and diseased hand is significant, which is what the doctor is trying to determine.
The Finkelstein test, which is used during examination, involves pressing the first finger to the palm and clenching the remaining fingers into a fist. In this case, the person must reject the brush to the little finger, which causes severe pain in patients. The doctor may ask the patient to take certain objects with both hands and pull them. A sick hand will not be able to hold its burden, as it is weakened, and the doctor can easily select the object. No additional research is usually required. The diagnosis can be accurately made on the basis of such an examination.
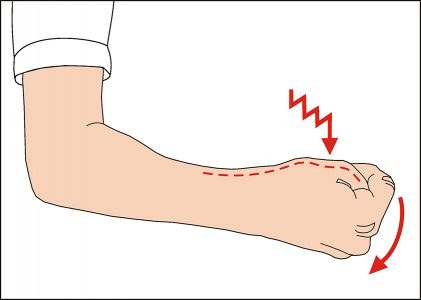
The syndrome can be treated conservatively and with the help of surgery. With conservative treatment, it is necessary to stop creating loads on the affected hand, immobilize diseased ligaments, bringing the thumb to a bent state against the index and middle fingers. At the same time, the palm itself unbends to the back. To ensure this position, the patient is put in plaster from the fingertips to the very middle of the forearm. This is necessary in order to avoid further injury to the diseased joint and provide conditions for treatment.
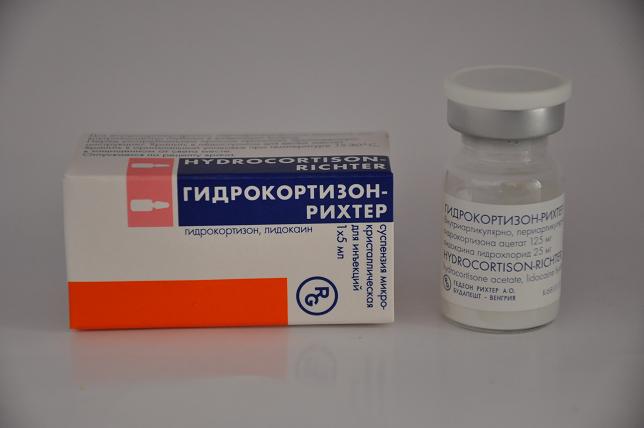
The disease is associated with an inflammatory process, therefore, for several weeks, while the hand is plastered, they resort to physiotherapy, taking anti-inflammatory drugs, blockade of painkillers, and local administration of drugs. An excellent anti-inflammatory effect is the introduction of Hydrocortisone into the affected area. Such injections must be performed 2-6 times with two or three-day breaks. After such treatment, the rehabilitation period begins, which lasts from two weeks to one month.
A conservative method of treatment may not give the desired effect in a disease that lasts a long time. So you can eliminate the symptoms for some time, remove the pain, but soon the disease may return with renewed vigor. In such situations, surgical intervention is necessary.
If conservative treatment fails, a special operation is performed. It is also indicated for lesions of the tendons on both sides. It is possible to carry it out both in a hospital and on an outpatient basis, with a local anesthetic.
Surgical treatment is often carried out planned, in a hospital setting. After the introduction of novocaine (or other anesthesia) in the most painful place, the doctor makes an oblique incision with a scalpel in the projection of the styloid process. After that, it is necessary to take the skin, subcutaneous tissue, blood vessels and nerves to the side using a special tool. When the dorsal ligament is exposed, the surgeon makes incisions and partial excisions.
If, after a protracted illness, sections of the tendons have grown together with their channels, the doctor cuts off all adhesions that have arisen. When the movements of the tendons become absolutely free, the closure of the wound begins. You need to do this layer by layer, and then put a scarf bandage on your hand. The sutures are removed after 8-10 days, and the efficiency of the brush returns after about 2 weeks.
During the recovery period, the areas of the thumb, index finger, and half of the middle finger may become numb. The reason for this is anesthesia or some compression of the fibers of the radial nerve. These processes should not cause much concern, they are absolutely normal and will cease to cause inconvenience in a few weeks after the operation.
Given the etiology of the disease, which is caused by chronic overload of the thumb joint, if its causes are not stopped, a second exacerbation may soon occur. To avoid this, the patient is recommended to change the type of activity if he is a provocateur of the disease. If the cause of the pathology is activities related to household chores, it is recommended to minimize the load on the hand.
Advanced Kerwen's disease can cause serious health complications. The person may become incapacitated. At the first manifestation of symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor for help. It is important to start treatment even when the effect is possible from conservative methods. Although the operation helps to restore the functions of the hand, scars may remain after it, which cause pain symptoms and can make it difficult to move the thumb.
The only effective way to prevent the disease is to reduce physical activity on the thumb during twisting and grasping movements of the hand.
Tenosynovitis is called inflammatory disease, affecting mainly the synovial sheath of the muscle. This pathology can cause disability in case of late diagnosis or improper treatment.
Reasons for development
Currently, there are many theories of the development of synovitis. Most often, it develops as a result of:
- any disease accompanied by an inflammatory process (mainly systemic);
- it can also occur as a result of injuries or injuries of the muscle, which led to the rupture of the synovial vagina;
- exposure to certain strains of viruses and bacteria.
There is also an idiopathic form of tenosynovitis, in which the exact cause of inflammation is unknown.
The tendons of the muscles of the wrist, forearm and legs are most susceptible to the disease. This is due to the fact that the muscles with the longest tendons are located on the limbs. Most often, tenosynovitis of the knee joint develops, since in this area there are points of attachment of the quadriceps femoris, triceps femoris and sartorius muscle. In some cases, tenosynovitis can occur when the surgical wound is not sufficiently treated during interventions on the muscles of the extremities.
Tenosynovitis symptoms
The following clinical signs indicate the development of inflammation of the synovial membrane:
- swelling in the affected area of the tendons, palpable during the examination;
- violation of joint movements;
- soreness mainly in the area of the affected tendons;
- pain during the work of the affected muscle group;
- redness along the entire tendon.
A general examination can reveal swelling at the site of the affected tendon. On palpation - soreness at the site of inflammation. Active movements are limited due to muscle pain during movement. The tendon is palpated as a dense and painful cord.
How to treat tendon tenosynovitis?
First of all, the most physiological position should be given to the affected limb. In addition, an important role is played by the creation of rest and temporary restriction of active movements in order to prevent further progression of the process. For temporary immobilization, it is possible to use splints or light bandages to hold the limb. The use of cold compresses can reduce pain and partially stop the symptoms of inflammation.
Drug treatment of the disease should include relief of pain and reduction of signs of inflammation. From medicines NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) such as ibuprofen, diclofenac ointment (rumacar) are well suited for the treatment of tenosynovitis. If they are ineffective, they resort to the use of parenteral administration of glucocorticosteroids. In some cases, surgery may be required.
Tenosynovitis caused by infection requires an immediate course of antibiotic therapy (delay can lead to the development of an abscess or contractures). If antibiotics are ineffective, they resort to surgical treatment of tenosynovitis with excision of the affected vagina and subsequent restoration of the normal position of the tendon.
After drug therapy, it is necessary to conduct a course of exercise therapy to restore atrophied muscles during the illness. For the fastest recovery, electrophoresis with ionic solutions is shown, as well as mud therapy and bioptron. In addition, hyaluronic acid can be used to prevent the development of scars on the synovial sheath.
If the treatment was started in a timely manner, then the prognosis is favorable and a complete recovery is possible without any consequences. With late delivery medical care possible transition of the process to chronic form with limited mobility of the affected limb or joint. Delay in treating infectious tenosynovitis can lead to sepsis.
Tendinitis of the long head of the biceps
General information about the disease
Tendonitis is an inflammation of a tendon that initially occurs in the tendon sheath or tendon sac. In this case, it is an inflammatory process in that part of the tendon that connects the upper part of the biceps muscle to the shoulder. Most often, the disease appears later too heavy load, when performing a certain type of work or when playing sports.
There are also cases when tendinitis develops not due to excessive loads, but as a result of muscle wear and injury. With tendonitis in the localization of the long head of the biceps, pain is noted in the upper anterior part of the shoulder girdle.
The main causes contributing to the onset of the disease
In order for the tissue layer of the biceps tendon to regenerate, it takes a lot of time. For example, if a person’s professional duties are associated with performing intense and the same exercises with his hands raised above head level, or if he is an athlete (tennis player, basketball player), the tendon part is subjected to regular excessive stress, and normal regeneration is simply not carried out in time. .
When the tendon wears out, its tissue degenerative changes begin, collagen fibers become tangled and very often torn. It becomes apparent that during this process, the tendon loses its strength and becomes inflamed, which can lead to rupture.
Quite often, tendonitis of the long head of the biceps develops after a direct injury. For example, if a person falls on the shoulder, this will lead to the onset of the disease, and the transverse ligament of the shoulder may rupture.
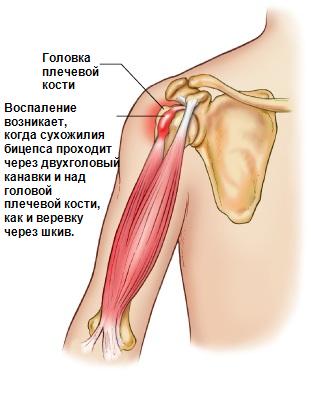
Thanks to this ligament, the formation of connective tissue is located in the bicipital recess, which is located next to the tip of the humerus. When it breaks, the bicep is not held in place and quietly slips out, subsequently it is irritated and inflamed.
The disease can occur if the rotator cuff ruptures, impingement or instability of the shoulder occurs. If the cuff ruptures, this will allow the humerus to move freely and act on the connective formation, which, naturally, will lead to its weakened state.
The appearance of the disease is also facilitated by the instability of the shoulder, which occurs when the head of the humerus is excessively mobile inside the socket.
The main symptoms and clinical picture of the disease
The most important symptom of tendinitis of the long head of the biceps is pain, which is dull in nature. Often, the pain syndrome is localized in the front of the shoulder, but sometimes it goes even lower, to the area where the biceps muscle is located.

Pain increases during movement of the limb, especially if it is raised up. When the limb is at rest, the pain subsides. There is also weakness when turning the forearm and bending the elbow joint.
Disease diagnosis
First, the doctor questions and examines the patient. The patient must give accurate answers about the nature of his work, about possible injuries, if he is an athlete, then about the intensity of training.
During the examination, the doctor pays special attention to how the patient performs certain movements, perhaps they are difficult as a result of muscle weakness and pain. A number of special tests are then performed to determine whether there is damage to the rotator cuff or instability of the shoulder.
If radiographic examination is not enough to select the most suitable treatment, then the doctor can refer the patient to an MRI.
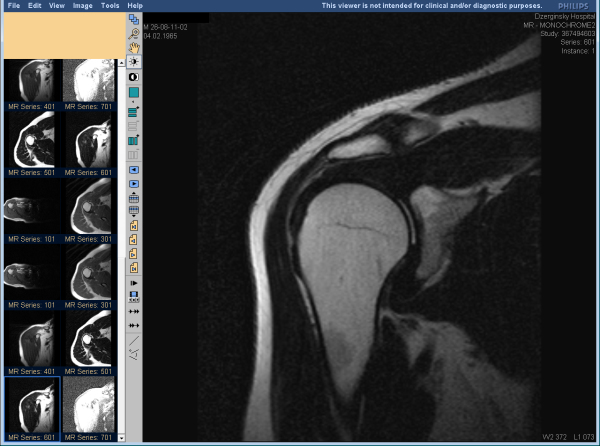
This study can give much more information about the damaged biceps tendon, it makes it possible to see if there is an inflammatory process, if the labrum is damaged, if there are ruptures of the rotator cuff.
In order to determine the presence of other problems with the shoulder joint, the doctor prescribes a diagnostic arthroscopy.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment of this disease can be of two types: conservative and surgical.
The conservative method consists in the complete unloading of the biceps tendons, that is, the patient should exclude the slightest load on this area and provide the tendon with rest. NSAIDs are used to reduce pain and inflammation. Steroid injections are given very carefully because they often further weaken the tendon.
Without fail, the patient should undergo a course of physiotherapy and exercise therapy. Physiotherapy treatment helps to reduce the inflammatory process as soon as possible, and exercise therapy helps to restore muscle mass.

If the patient works in a field where there is a risk of shoulder instability and rotator cuff rupture, then he will be advised to change jobs. This will reduce pain and inflammation, and give a person the opportunity to live a full life.
If conservative treatment has not brought any results and the person is still suffering from pain, then surgical treatment is recommended. It is also resorted to in case of detection of other problems in the shoulder area. The most common surgical treatment is acromioplasty. During the operation, which surgeons perform using arthroscopy, the anterior lobe of the acromion is removed.
This makes it possible to expand the distance between the acromion and the adjacent head of the humerus, thus reducing pressure on the tendon itself and nearby tissue.
If the patient has severe degenerative changes in the tendon, then biceps tenodesis is performed. This method consists of reattaching the upper lobe of the biceps tendon to a new location. Such surgery gives a good result, but, unfortunately, it is not durable.
After the operation, rehabilitation lasts about six to eight weeks. A positive outcome will largely depend on the patient himself, that is, on his attitude towards a good end result. Doctors do not recommend stale, shortly after the operation, you need to start physiotherapy exercises.

The exercise therapy doctor will select a set of exercises and control the process of strengthening the muscles of the shoulder and forearm. Usually a positive trend is observed after two to four weeks.
If the patient conscientiously follows all the recommendations of the attending physician, then the complete recovery of the shoulder and forearm will take three to four months.
Prevention
In order to avoid tendonitis of the long head of the biceps, you must adhere to the following recommendations. Firstly, before training, do warm-up and warm-up exercises, try not to do the same movements for a long time. Secondly, do not allow physical overload and avoid injury. Change the load regularly, the intensity of the load should increase gradually, and do not forget to take timely rest.
Video - Tendonitis of the long head of the biceps
Tenosynovitis is an inflammation of the synovial sheath of the tendon that can lead to swelling, creaking, and pain.
signs
The occurrence of pain during palpation of the tendon sheath, the appearance of swelling of the finger. In this condition, the finger remains bent at rest.
When you try to straighten your finger with the other hand, especially by the nail, the pain intensifies.
If there is a lesion of the sheath of the tendon of the eminence of the thumb, then the spread of the infectious process can reach the bag of the radius and then the thumb swells and hurts, and the hand takes on a state bent in a radial deviation.
If the same happens with the tendon of the little finger, and the infection spreads to the bag of the ulna, then the little finger swells, and the fingers of the hand are at rest in a slightly bent position and are felt during passive extension.
The spread of the infectious process in the area between the radial and ulnar leads to the development of a horseshoe abscess.
Development mechanism
Flexor tenosynovitis is a highly devastating hand infection. In the absence of timely treatment, necrotic damage to the tendons is possible, which leads to a loss of function forever.
The most common mechanism for the development of tenosynovitis is damage with the penetration of infection, especially in places with a superficial location of the tendons. Most often, the first, second and third fingers are affected.
However, infection is also possible through blood or other biological fluids.
The reasons
Basically, tenosynovitis develops as a result of various injuries and injuries, followed by an infectious process that can cause staphylococci and streptococci.
In more rare cases, tenosynovitis is caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae, when symptoms of inflammation in the pelvic organs, urethritis, and cervicitis are noticeable. In the case of diabetes, the disease can be provoked by pseudomonas, as well as gram-positive microorganisms and. The risk factor is a weakened immune system.
Treatment
With tenosynovitis, they turn to a therapist or traumatologist, but when determining the signs of the disease, the immediate participation of the surgeon is required. If the victim went to the doctor later than two days after the injury, special treatment should be carried out in the operating room, and up to a day the treatment is carried out in a conservative way.
To start treatment, you should determine whether the patient has tetanus vaccinations.
The affected finger is lifted and provided with a motionless state. Pain reduction is achieved by applying rest or with the help of a splint or splint, immobilization is provided. Applications of heat or cold are also used.
Antibiotics are given intravenously to the patient initial stage Treatment requires broad-spectrum antibiotics. Clindamycin, cefotetam are used. If the patient has immunodeficiency or diabetes, agents active against gram-negative bacteria and Pseudomonas are added to the treatment. Analgesics are used topically, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs systemically, for example, full doses of indomethacin, aspirin, or other similar drugs are prescribed four times a day for a period of one to one and a half weeks.
This disease often causes severe pain therefore, it is necessary to be prepared for the use of narcotic painkillers.
Tendon damage is, use colchicine, or NSAIDs. When the inflammation starts to go away, gentle exercise several times a day, with a gradual increase in activity, is useful. This is very important for the prevention of adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder.
