Colitis who treats. Symptoms of rectal colitis
Colitis is an inflammation of the intestinal mucosa. The intestine is a complex system. It consists of thin and thick sections. The large intestine is represented by the colon, sigmoid and rectum. Thus, the terminal part of the intestine is the rectum. It consists of an ampulla and anus. The ampulla is a place of accumulation of feces. The anus is the exit gate of the body. Around it is a system of muscles and nerves responsible for the process of defecation.
Inflammation of the terminal part of the colon is called proctitis. Proctitis occurs quite often. Let's talk more about the causes of this unpleasant disease.
The causative agents of syphilis - pale treponema - can also cause nonspecific inflammation in the rectum.
Dysbacteriosis. Violation of the ratio of beneficial and harmful bacteria can provoke colitis. - this is not the cause of colitis, but a predisposing factor.
- The second reason is the violation of the diet. Improper nutrition (excess protein, alcohol, spices, fast food) provokes a change in the act of digestion and defecation. Undigested food enters the rectum, decay processes are actively going on, excess mucus is released. This can weaken the defenses of the intestines and cause inflammation.
Most often, a violation of the diet causes the so-called spastic colitis (irritable bowel syndrome). It is considered a functional disease and is cured after the normalization of nutrition.

The cause of intestinal ischemia can be autoimmune diseases. They affect capillaries and arterioles.
Venous stasis also plays a serious role in the violation of the nutritional function of the intestine. Blood does not leave the veins due to heart failure, their hemorrhoidal transformation and thrombophlebitis. The ischemic process in the intestine has a severe course.
Symptoms and forms of proctitis
Let's talk about clinical picture, which causes colitis The symptoms of this disease can be varied. 
Most often there is pain. Pain is a signal from the body that something is wrong. With proctitis, the pain is dull, bursting in nature, aggravated by defecation. It radiates to the perineum, scrotum and penis in men, to the labia in women. Sometimes with proctitis, there is not pain, but burning and itching.
A patient with colitis often has scratching around the anus.
Allocations. They are different types. With ordinary catarrhal colitis, a mucous secretion is secreted. It is not colored, mixed with feces. In ulcerative colitis, blood clots appear in the stool. She is scarlet. With a purulent form of colitis, a large amount of pus comes out with feces.

The prevalence of inflammation of the colon in ulcerative colitis
General symptoms
With purulent proctitis, there is intoxication of the body, sometimes the body temperature rises. There is diarrhea or constipation. There are tenesmus - false urge to defecate. This is the spastic component of the disease. With a long course of the disease, anemia develops in patients with an ulcerative form (pallor, weakness, hypodynamia).
The forms of this bowel disease depend on:
- from the causes of the disease (ischemic, spastic, infectious colitis);
- from the duration of the course of the disease (acute and chronic colitis);
- from changes in the intestinal mucosa (catarrhal, mucous, hemorrhagic, ulcerative, necrotic).
How to detect proctitis?
Engaging in self-diagnosis in this case is very risky. The diagnosis must be made by a specialist doctor.
With proctitis, after collecting anamnesis, the doctor performs the most accessible examination of the rectum - digital. This procedure, unpleasant for the patient, can be very informative. The doctor can feel ulcerative defects, polyps and tumors of the rectum. In men, the prostate gland is examined for the presence of concomitant pathology. In women, you can feel the internal genital organs and assess their condition.
But finger research will not be enough. The next step is rectoscopy. The study is carried out using fiber optic optics. An LED with a camera is inserted into the intestine. At the same time, its mucosa is evaluated, pieces of tissue are taken for a biopsy. Rectoscopy allows you to examine the rectum throughout and get a reliable clinical diagnosis.
Before conducting a rectoscopy, the patient is carefully prepared for the study. In order for the examination of the intestine to be informative, it must be cleared of feces.
Additional research for proctitis is a coprogram and analysis of feces for worm eggs. Coprogram characterizes the process of digestion. It reveals the insufficiency of digestive enzymes. Analysis of feces for eggs of worms will determine uninvited guests. Sometimes a scraping from the anal area is performed.
Treatment
A proctologist deals with the treatment of rectal colitis. Treatment of proctitis is purely individual. After all, a patient with spastic colitis should only normalize the diet, and a patient with ischemic colitis may go through several operations to normalize the condition.
If we talk about treatment in general terms, we can distinguish etiotropic and symptomatic therapy. Etiotropic treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause of colitis. Symptomatic treatment relieves symptoms caused by inflammation in the intestine.
If microorganisms are the main cause of colitis, then antibacterial or antiprotozoal drugs are required. If the cause of colitis is malnutrition, then you need to follow a special diet. In the acute stage, everything is excluded, except for viscous cereals and broths. Then you can expand the menu. But it is better to refuse fried, salty, smoked, spicy, sour and fatty foods forever.
If the cause of colitis was an injury, then you need to help the body heal the wound. In this, enemas with healing substances and suppositories are used. Enemas can be done with sea buckthorn oil or calendula. And suppositories "Methyluracil" enhance tissue regeneration.
If in or a neoplasm, then the operation cannot be avoided. With polyps, it is carried out with endoscopic equipment. And with tumors, especially malignant ones, a complex open intervention will be required. The same threatens the patient with advanced ischemic colitis.
To relieve symptoms, antispasmodics are used (they reduce the spastic component) - no-shpa, papaverine. Hemostatic drugs are used to reduce bleeding.
Proctitis is an unpleasant disease. Many people needlessly delay their visit to the doctor. This bowel disease can not only cause mild discomfort (such as the spastic variant of the disease), but also be fatal (ischemic colitis). Be attentive to yourself!
We treat hemorrhoids at home
 Have you ever tried to get rid of hemorrhoids at home on your own? Judging by the fact that you are reading this article, the victory was not on your side. And of course you know firsthand what it is:
Have you ever tried to get rid of hemorrhoids at home on your own? Judging by the fact that you are reading this article, the victory was not on your side. And of course you know firsthand what it is:- Seeing blood on paper again.
- Suffer every trip to the toilet from discomfort, itching or an unpleasant burning sensation.
- Wake up in the morning with the thought of how to reduce swollen painful bumps.
- Again and again hope for success, expect results impatiently and be upset by a new ineffective drug.
We have studied a huge number of ways to deal with hemorrhoids at home. The most effective was Marta Volkova's method, who talked about an effective and inexpensive way to get rid of HEMORRHOIDS forever in just 5 days ... Learn more >>
Colitis is an inflammation of the lining of the large intestine. Among the inhabitants, it is generally accepted that colitis is the same as colic. However, it is not. Colic is a symptom of a disease, and intestinal colitis is a disease in itself. The fact is that many microorganisms live in the large intestine. Some of them are useful and make up the natural intestinal microflora. Others release toxic substances that contribute to the development of colitis and other diseases. Under the influence of certain factors, the concentration of harmful substances released by bacteria increases, and this leads to inflammation of the mucous membrane.
Symptoms and causes of development
The symptoms of intestinal colitis are often similar to those of other intestinal diseases. The following signs of the disease are observed:
- pain in the intestinal area;
- gagging;
- bloating;
- diarrhea;
- increased fatigue;
- frequent urge to defecate.
However, we should not forget that colitis is acute and chronic, and their symptoms are somewhat different.
There are 2 forms of intestinal colitis:
- acute;
- chronic.
They have different symptoms and process.
acute form can be called food poisoning, allergies, or taking certain medications. It develops quickly and begins, as a rule, with hyperthermia. The acute form is characterized by the following features:
- pain in the abdomen;
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- fatigue;
- urge to defecate (often false).
In the absence of proper treatment or its incorrect scheme, the disease becomes chronic.
The chronic form is sluggish, not always noticeable to the patient. Colitis complicated by dysbacteriosis, poisoning, problems with the pancreas and other factors can go into a chronic form. Signs of chronic colitis:
- thirst;
- slight swelling;
- lack of appetite;
- nausea from time to time;
- constipation.
As a rule, when chronic form pain not visible.
Chronic intestinal colitis in adult women and men can develop as a result of a constant improper diet. At risk are women who are fond of dubious diets for weight loss.
Types of intestinal colitis
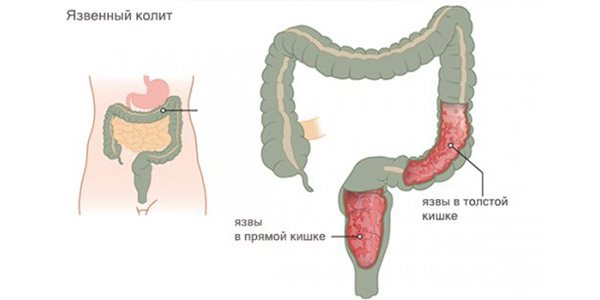
Ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis of the intestine is accompanied by ulcers on the mucous membrane of the colon. Its reasons may be:
- genetic predisposition;
- infectious poisoning.
As a rule, with ulcerative colitis, the temperature rises.
spastic colitis
A feature of this type is reduced peristalsis. Constipation is a symptom of this type of disease. Bloating, abdominal pain, and gas formation may also occur. The danger of spastic colitis is that the intestinal muscles can atrophy over time.
catarrhal colitis
This type of disease lasts only a couple of days and is a stage in the development of colitis. The symptoms are:
- pain in the left side of the abdomen;
- discomfort due to an increase in the size of the colon;
- Availability spotting in a chair;
- weakness;
- nausea.
Catarrhal colitis is easy to identify, so visual diagnosis is sufficient in this case. It is dangerous because it can quickly go into an acute stage, and then into ulcerative colitis.
atrophic colitis
With atrophic colitis of the intestine, as the name implies, the muscles of the large intestine atrophy, so this type is close to spastic colitis. If spastic colitis is left untreated for a long time, it can turn into an atrophic form.
In some cases, atrophic colitis becomes ulcerative, and then the risk of intestinal perforation increases.
This type is difficult to diagnose, it requires modern equipment and a highly qualified doctor.
erosive colitis
Many experts consider this type one of the stages of ulcerative colitis. In the case of erosive colitis, there is a slight thinning of the walls of the colon, which is not life-threatening. The main symptoms of erosive colitis are as follows:
- lack of appetite;
- nausea;
- stomach ache;
- belching;
These same symptoms are characteristic of many other diseases of the digestive system, so only an experienced doctor will be able to make an accurate diagnosis.
diffuse colitis
This type of colitis is the most severe along with ulcerative colitis. It affects the small and large intestines. It is usually easy to diagnose. The most common symptoms are:
- severe diarrhea with impurities, pain during and after defecation;
- pain in the stomach and intestines;
- loss of appetite up to its complete absence;
- violations of intestinal motility: it may be too active or reduced;
- grayish coating on the tongue.
Methods for diagnosing colitis
First of all, the patient takes a blood test. This is necessary in order to identify the inflammatory process in the body, since with inflammation the level of substances in the blood changes.
Instrumental diagnostics are being carried out. For example, one of the methods is contrast irrigoscopy. It allows you to make an x-ray of the intestine and determine the presence of tumors.
In modern clinics, ultrasound procedure intestines and abdominal organs and an MRI is done. These methods most accurately determine the state of the organ.
In addition, an examination of the rectum by a proctologist is mandatory to exclude the presence of cracks and.
If malignancy is suspected, a biopsy is performed.
Colitis treatment
Treatment of colitis in adults is of different types, depending on the type of disease and its stage.
If the cause of the disease is infectious poisoning, antibiotic treatment is prescribed. Since antibiotics can disrupt the intestinal microflora, therapy is carried out with them to maintain the natural microflora.
Also, in case of poisoning that caused colitis, adsorbing drugs are prescribed. Adsorbents help to get rid of toxic substances. Treatment includes anti-inflammatory medications and antidiarrheal medications.
It should be remembered that in the first place, the cause that caused colitis is eliminated. However, if this cause is hereditary or genetic, then treatment is aimed at getting rid of the symptoms.
Diet for colitis
With colitis, you should be careful about nutrition. As a rule, doctors prescribe diet number 4. The following foods should be excluded:
- seeds;
- nuts;
- raw vegetables;
- smoked food;
- fried food;
- sour food.
Also, with colitis, it is advised to drink plenty of water, as the body loses it faster.
Prevention
Prevention of colitis is, first of all, a healthy lifestyle. You should follow the diet prescribed by the doctor.
But the main thing is the elimination of any factors that can provoke colitis.
According to the WHO, gastrointestinal cancer accounts for 45% of all malignant diseases. To prevent this formidable condition, it is necessary to actively treat its precancerous form - colitis of the rectum.
Colitis of the rectum or proctitis - inflammatory disease affecting the lining of the large intestine. This pathology is not as harmless as it might seem at first glance. There are several forms of it:
- catarrhal;
- polyposis;
- erosive;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis.
Quite often, it occurs together with or due to inflammation of the mucous membrane of the stomach and small intestine.
Factors that can cause colitis include:
- hereditary factor. Most often, people who have a burdened heredity, i.e., having a disease of the rectum in the genus, suffer from proctitis.
- A long course of antibiotic therapy, as well as taking laxatives.
- Dysbacteriosis various etiologies. Due to the decrease in the number of beneficial bacteria, the body's defenses are reduced. This provokes the reproduction of pathogenic flora on the mucous membrane of the large intestine.
- A large amount of sweet, flour, salty and peppery in the food consumed. Improper nutrition, as a rule, leads to the development of dysbacteriosis, which was mentioned above.
- Food poisoning or salts of heavy metals.
- Abuse of alcoholic and low alcohol drinks.
- Intestinal infections (shigellosis, salmonellosis, etc.). They undermine local immunity and provoke various diseases.
- Physical inactivity. As a result, blood flow in the large intestine decreases, which also contributes to the development of the disease.
- Allergic diseases.
- Worm infestations.
- Prolonged constipation.
- Wearing tight clothing, belts.
- Wrong regimen of the day (violation of biorhythms).
- Mental disorders.

Symptoms
As a rule, no one pays attention to the catarrhal form of colitis, most often patients turn to the doctor for help when the condition is close to malignant, that is, ulcerative colitis occurs. The main features include:
- Pain. Many believe that the name colitis comes from the word "stab" because of the peculiar pain that is felt during attempts, the act of defecation;
- feeling of discomfort in the anus;
- itching in the anus;
- frequent false urge to defecate - tenesmus;
- painful diarrhea;
- temperature rise to 38 about C;
- It is ulcerative colitis that is characterized by bloody and purulent discharge from the rectum.

Diagnostics
Examination of a patient with suspected ulcerative colitis is as follows:
- History taking (what he eats, what lifestyle he leads, what diseases of the gastrointestinal tract he suffers from, etc.).
- Objective examination: palpation of the anterior abdominal wall, listening to intestinal motility.
- Laboratory types of research: general and biochemical analysis blood tests, allergological tests, fecal coprogram, fecal occult blood test.
- Instrumental types of research: sigmoidoscopy, manometry of the rectum and large intestine, colonoscopy, irrigoscopy, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, as well as a biopsy followed by a histological examination.
What does the treatment consist of?
With proctitis, it is better to turn not just to a therapist, but to a highly specialized specialist - a gastroenterologist or proctologist.
It should be noted that the treatment of colitis should be carried out strictly in stationary conditions with the exception of self-medication. Ulcerative colitis is a precancerous disease, so attempts to treat yourself can lead to a worsening of the process and its transition to a malignant form.
In the hospital, basic treatment is carried out, recommendations are given on a healthy diet and lifestyle, so that in the future the patient can perform all these actions independently at home. They are treated on an outpatient basis, and in case of an exacerbation of the disease, they are again sent to the hospital for intensive treatment.
The treatment consists of the following items:
- Medical treatment. Depending on the cause of proctitis, treatment is prescribed: infectious nature- antibacterial treatment, with food allergies - antihistamine treatment and elimination of the allergic factor. If the cause of the disease is poisoning, then adsorbent preparations are used - Smecta, Almagel, Phosphalugel, activated carbon, Atoxil or Polysorb. For removal I use No-shpu, Papaverine, Bendazol. To replenish the volume of fluid in the body in case of severe poisoning, physiological saline, Regidron, Ringer's solution are used.
- Physiotherapy. Diadynamic therapy, SMT physiotherapy are used.
- Medical nutrition. It is worth eating fractionally, in small portions 5-6 times a day. Food is best boiled or steamed and consumed warm. Products that cause increased gas formation and irritate the intestinal mucosa should be excluded: peppered, salty, flour, sweet, sour-milk products, etc.
- Psychotherapy helps the patient to inspire faith in the best and eliminate anxiety about the development of cancer.
- Spa treatment. Recovery in a sanatorium has a rather beneficial effect on the human body, as well as on its psychological state.
When such a disease occurs, you should not be upset and give up. The most important thing is not to hide this problem, but immediately consult a doctor and strictly follow all his instructions. Then a successful outcome of the disease is guaranteed.
