Bloody discharge in the stool in an adult. Blood with feces in men: causes and diagnosis.
Don't wait for your condition to improve! Timely testing for occult blood in the feces will help dispel all dark doubts. Based on the results and assumptions, the doctor will help in making an accurate diagnosis and prescribing the appropriate treatment.
Reveal diseases internal organs The gastrointestinal tract is sometimes quite difficult. Bleeding associated with certain diseases may be intermittent or insignificant in volume. This complicates self-diagnosis of the presence of blood or mucus in the stool. An analysis for occult blood in the feces will help detect pathological processes in the body and heal the patient in time.
The need for research
 The fecal occult blood test is a special diagnostic method using chemical reagents. For its implementation, a sample of feces is required, which, when exposed to special substances, changes its color. The study is necessary, first of all, for those who suffer from diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or have a suspicion of precancerous conditions. The analysis helps to reveal the presence of latent red blood cells, as well as hemoglobin.
The fecal occult blood test is a special diagnostic method using chemical reagents. For its implementation, a sample of feces is required, which, when exposed to special substances, changes its color. The study is necessary, first of all, for those who suffer from diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or have a suspicion of precancerous conditions. The analysis helps to reveal the presence of latent red blood cells, as well as hemoglobin.
The study is indicated for the following changes in the state of a person:
- discomfort during the act of defecation, pain;
- mucus, bloody streaks, foam in the feces;
- a sharp change in the structure of feces;
- decreased appetite, weight loss;
- fever for no apparent reason;
- stomach ache.
If you experience these symptoms, you should consult a doctor. He will advise you to take a stool test for occult blood and will be able to determine the reasons for its presence with a positive result.
Causes of feces in the blood in adults
If the interpretation of the stool analysis showed the presence of blood, then this may indicate the development various diseases. Often a positive result can indicate a dangerous human condition, up to oncology. Therefore, only a specialist can establish an accurate diagnosis. The main reasons leading to the detection of occult blood in the stool:
- anal lesions, additionally manifested with symptoms in the form of itching, pain, pain during defecation, irritation of the anus;
- diverticulosis associated with severe pain in the abdomen, elevated body temperature, stool disorder, blood discharge;
- oncological diseases, in which streaks of blood, mucus are found in the feces; a person's appetite decreases and body weakness is observed.
Most often, bloody mucus in the stool is found by women after the birth of a child. Experts attribute this to the possible appearance of hemorrhoids. Due to the huge loads during pregnancy and childbirth, the vessels are damaged, causing varicose veins. Usually, the blood in the feces of women who have given birth does not have dangerous pathologies under it and ceases to disturb after a few days.
In addition, there are other reasons for the detection of occult blood. So, some intestinal diseases can provoke the appearance of blood secretions, mucus in the feces is possible. Sometimes the culprits of all troubles note the presence of sexually transmitted infections in humans. Whatever the reasons, a timely visit to the doctor will allow competent treatment according to the diagnosis, and save the person from unpleasant symptoms.
Feces in the blood of a child
 Many parents, horrified to find that the child pooped with blood, begin to panic. In most cases, this is not related to the dangerous condition of the baby. Blood streaks in children's feces indicate the following:
Many parents, horrified to find that the child pooped with blood, begin to panic. In most cases, this is not related to the dangerous condition of the baby. Blood streaks in children's feces indicate the following:
- anal fissures due to prolonged constipation or difficulty defecation;
- allergy to cow's milk in young children;
- the use of products that can stain feces red.
The famous doctor Komarovsky claims that frightened parents sometimes confuse blood with dyes. It should be remembered that the child ate the day before. Maybe it's sweets or some medicines. Komarovsky will highlight some more reasons for the appearance of such abnormalities as blood streaks and mucus in the feces. They are less common, but also found:
- inflammatory processes in the intestines;
- enteric viral infection;
- polyps on the intestinal mucosa.
Komarovsky notes that only a doctor determines how much treatment a child needs and what it will be like. Self-diagnosis will not help determine the real causes of bloody stools.
Blood in the feces of the baby
Usually, young children often have food allergic reactions. According to Komarovsky, blood streaks in the feces may indicate inflammation of the intestine due to allergies. To this symptom is added intermittent and restless sleep of the child, disorder of the stool.
Often, when constipation appears in the baby, small cracks form in the anus. In order to avoid the appearance of blood in the stool due to difficult bowel movements, Dr. Komarovsky believes that the mother should adjust her diet. Quite rarely, a newborn who is on artificial nutrition has a volvulus of the intestine. In addition to detecting blood in the feces, the child has vomiting. In such cases, you should immediately seek medical help.
Preparation for analysis
 Before undergoing the study, it is better to check with your doctor how the fecal occult blood test will be carried out. Patient preparation is necessary in the case of using a chemical method due to the fact that false readings of invisible hemoglobin of animal origin or contained in medicines. The immunochemical method gives more accurate results and does not require preparatory actions on the part of the patient. Such a study will reveal only human hemoglobin. In any case, to obtain reliable results, there is a plan of basic recommendations:
Before undergoing the study, it is better to check with your doctor how the fecal occult blood test will be carried out. Patient preparation is necessary in the case of using a chemical method due to the fact that false readings of invisible hemoglobin of animal origin or contained in medicines. The immunochemical method gives more accurate results and does not require preparatory actions on the part of the patient. Such a study will reveal only human hemoglobin. In any case, to obtain reliable results, there is a plan of basic recommendations:
- within 3 days before the delivery of feces, do not eat meat, green vegetables and tomatoes;
- avoid taking certain drugs: iron-containing, laxatives, vitamin C and aspirin;
- additional methods for diagnosing the intestine should be postponed for another period and not carried out a few days before the analysis;
- women should wait with research during critical days;
- it is strictly forbidden to put enemas.
Once the 3-day preparation has been completed, it is necessary to collect feces. A stool collection container should be purchased at a pharmacy to exclude false positive results. After a bowel movement, take a small amount of feces from 3 different places. The approximate amount of material should be half a tablespoon. The sample must be delivered to the laboratory within a few hours.
Proper preparation contributes to an accurate analysis result and, accordingly, correct treatment. Do not disregard the doctor's recommendations.
A very disturbing sign of many diseases is blood in the stool. Regardless of age, it can appear in every person and requires immediate consultation with a specialist.
The sooner the nature of bleeding from anus the faster and more successfully the treatment will be.
To eliminate such an alarming symptom as blood in the stool, it is very important to differential diagnosis and identify its cause.
You can understand it if you study the nature of the discharge, and comparing it with the accompanying symptoms. The table below shows the nature of bleeding and other symptoms characteristic of various diseases:
| Disease | The nature of bleeding | Other symptoms |
| Haemorrhoids | Scarlet blood on the surface of the stool after a bowel movement. Scanty or moderate amount. |
On examination, the doctor discovers hemorrhoids inside or outside the rectum. |
| anal fissure | Scanty amount of scarlet blood after stool. |
When examining the intestine, mucosal defects are visible. |
| peptic ulcer | A small amount of blood from the anus. |
On examination, a predominantly through defect in the wall of the stomach, blood in the stomach is found. |
| Varicose veins of the esophagus | Profuse bleeding with black stools and bloody vomiting. |
The examination reveals dilated veins in the esophagus, damage to the mucous membrane, the presence of blood. |
| UC, Crohn's disease | Chronic bleeding, blood in the stool. |
Examination of the intestine reveals local or extensive ulcers. |
| Infectious diseases | minor bleeding |
Blood tests show inflammatory changes. The causative agent is found in the analysis of feces. |
The presented table is introductory, and is not at all a reason to make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment on your own.
Blood from the rectum, even a little, always has a cause. Therefore, the first thing a person who sees drops of blood on toilet paper should do is to turn to specialists.
In particular, you should not postpone a visit to the doctor if the bleeding:
- plentiful and does not stop for a long time;
- accompanied by vomiting;
- accompanied by bleeding from the nose, there are bruises and hematomas on the body;
- accompanied by a general deterioration in the condition;
- accompanied by fever and severe abdominal pain.
Which doctor should you visit if you notice bleeding from the anus in yourself or a child? This is primarily a proctologist and therapist.

The doctor will refer the patient to a series of examinations, with the help of which the source of the discharge will be determined. The most common types of instrumental diagnostics are:
- Rectoscopy - examination of the lower segments of the rectum. It is necessary to detect hemorrhoids, anal fissure, tumor formations in the studied areas.
- Colonoscopy is an endoscopic examination of the colon. With its help, the doctor will be able to detect any changes.
- Irrigoscopy is an x-ray examination using contrast. Allows you to get a clear image of the study area.
- Gastroduodenoscopy is an endoscopic examination, during which pathological tissues are taken (biopsy), and ulcerative defects, if any, are cauterized.
- Laparoscopy or abdominal operation– can be used for diagnosis or treatment. These methods allow you to examine the abdominal cavity, conduct a biopsy, take fluid for research. For diagnostic purposes, it is carried out in cases where other types of research have not helped to make an accurate diagnosis.
Blood in the stool in an adult
 Bloody discharge in the stool in adults can have many causes. Much depends on the lifestyle of a person, his age. For example, most middle-aged people are familiar with the problem of hemorrhoids, which also cause bleeding.
Bloody discharge in the stool in adults can have many causes. Much depends on the lifestyle of a person, his age. For example, most middle-aged people are familiar with the problem of hemorrhoids, which also cause bleeding.
Adults are prone to bad habits, they can abuse tobacco, alcohol, which negatively affects the condition of the stomach and liver. Diseases of these organs are also the causes of blood in the stool.
Let's look at the most common causes in which adults have feces mixed with blood.
anal fissure
With this disease, bright scarlet blood appears on the surface of the feces. A crack occurs due to chronic constipation, excessive straining during bowel movements.
When bleeding is short and not heavy, it may not occur after each bowel movement, but once every few days.
Haemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids develop due to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, provoked by various factors. The result is overstretching and damage to internal hemorrhoids.
With hemorrhoids, blood in the stool appears up to several times a month and has a darker shade than with an anal fissure. Added to this symptom are:
- itching and burning in the anus;
- prolapse of hemorrhoids.
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis
This inflammatory disease characterized by an expression of the mucous membrane of the rectum and colon. Against the background of inflammation, the patient not only observes blood in the stool, but is also characterized by impurities of pus and mucus.
Associated symptoms:
- stomach ache;
- diarrhea;
- fever;
- body intoxication.
With untimely treatment, UC is complicated by inflammation of the peritoneum, intestinal perforation and intestinal obstruction.
Crohn's disease
A hereditary disease that can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract. Predisposing factors: smoking, infectious diseases, food allergies, stress.
In addition to blood in the stool, the disease is accompanied by:
- repeated loose stools with impurities of pus and mucus;
- severe pain syndrome;
- skin rash;
- feverish state;
- soreness of the joints.
Intestinal infections
Infections can affect different parts of the intestine. They are divided into:
All of them cause fever, frequent liquid stools containing impurities of mucus and pus, the presence of blood in the stool. With viral hemorrhagic fever characterized by hemorrhagic rash and bleeding, including intestinal. Another viral lesion, cytomegalovirus, causes bloody diarrhea and sharp pains in the abdomen.
Tumors
Blood in the feces can cause benign (polyps, warts, warts) and oncological processes.
In severe cases, it is possible to develop intestinal obstruction, perforation of the rectum, inflammation of the peritoneum.
venereal infections
Anorectal syphilis, herpes, granuloma venereum, rectal gonorrhea, and other sexually transmitted diseases can also damage the rectal mucosa.
The result is blood in the stool.
Fecal occult blood test
The presence of black stools (melena) gives doctors reason to prescribe. The essence of the diagnosis is to detect hemoglobin in the excrement or its absence. Its presence indicates a problem in the gastrointestinal tract.
The main causes of black feces are:
- Varicose veins of the esophagus, complicated by bleeding. Characteristic of portal hypertension syndrome, which is often observed in cirrhosis of the liver. These pathologies are also accompanied by vomiting with blood, chest pain, sweating, tachycardia, low blood pressure.
- Mallory-Weiss syndrome is a superficial rupture of the cardia of the stomach or esophagus. This problem is common among drinkers and those suffering from perforated ulcers.
- A peptic ulcer can cause tarry stools. With severe bleeding, chills, nausea, fainting, black liquid stools up to several times a day, brown vomiting are characteristic.
Also, the causes of melena can be stomach cancer, tumors of the esophagus, nosebleeds, tuberculosis, stomatitis, periodontal disease.
Blood streaks in stool
Many diseases do not cause profuse bleeding from the anus, appearing only as small streaks in the feces. Their presence in the feces is also a reason for the diagnosis.
in normal or loose stool bloody streaks may indicate a prolonged inflammatory process, an infectious bowel disease, intestinal flu. In this case, they are scarlet in color and appear after prolonged diarrhea.
This symptom can be caused by viruses and bacteria that have affected the intestines. The result is a violation of the microflora and damage to the walls of blood vessels, causing blood clotting.
Bloody streaks in the stool are frequent companions of polyps, hemorrhoids, malignant lesions of the intestine.
If streaks of blood in the feces are observed for several days in a row, combined with weight loss, lack of appetite, pulling pains in the lower abdomen, you need to urgently go to the hospital.
In a child, the presence of veins may indicate an advanced phase of dysbacteriosis. When affected by worms, blood clots may appear.
Baby's bloody stool
In children, the causes of blood in the stool are no different from those in adults. However, the most common events that cause spotting in childhood, are dysbacteriosis, intestinal obstruction, food allergies.
Intestinal dysbacteriosis
In infants, dysbacteriosis occurs against the background of improper feeding, errors immune system, antibiotic treatment. As a result, parents and pediatricians have to deal with liquid stools with blood impurities.
With dysbacteriosis, streaks in the feces of a child can be combined with mucus. This condition is accompanied by flatulence, lack of appetite, diathesis. Dysbacteriosis is diagnosed by laboratory examination of feces.
Fissures of the rectum
With constant constipation, the child develops rectal fissures, which can also cause blood in the stool in the child.
Constipation can occur with malnutrition, rickets.
During the first two years of a baby's life, it is very important to properly organize the therapeutic and prophylactic intake of vitamin D and ensure plenty of fluids.
Intestinal obstruction
A terrible cause of blood in the feces in children under two years of age is intussusception of the rectum, leading to intestinal obstruction. This condition can be congenital (incomplete rotation of the intestinal tube), or acquired (unbalanced complementary foods, changing the mixture, overfeeding the baby).
With intussusception, the child screams loudly after eating, can vomit profusely in a fountain, poops with diarrhea mixed with blood. Within a few hours, the stool becomes red and slimy. This is a very dangerous condition that requires immediate medical attention.
food allergy
In young children, allergic reactions are very common. Allergies can occur to milk protein, gluten, citrus fruits, flavors, and food additives.
Allergy symptoms can vary:
- skin reactions;
- diarrhea, foamy stools;
- streaks, blotches of blood in the stool;
- anxiety;
- poor weight gain.
Dysentery
Blood in the stool may occur in dysentery. In this case, the child has diarrhea, frequent urge to defecate, fever. Almost always, in addition to blood, mucus appears in the stool, sometimes pus.
In addition, the child complains of abdominal pain. There is also dehydration.
If the parents saw that there was blood in the child's feces, they should immediately contact the pediatrician. An ambulance should be called if the child has:
- fever;
- frequent diarrhea;
- vomiting and regurgitation with a fountain;
- agitation or retardation.
What to do if the feces are with blood?
It is important to know that rectal bleeding is one of the signs not only of hemorrhoids, but also of malignant pathologies of the large intestine.
Even if blood in the stool occurred only once, and after that the stool was normal, a doctor's consultation is necessary, since blood indicates damage to the mucous membrane and a problem in the body.

Proctological diagnostics consists of a digital examination of the rectum, rectoscopy. To clarify the diagnosis, X-ray, endoscopic examinations of all parts of the intestine are prescribed.
Treatment methods depend on the diagnosis:
- In conditions such as gastric bleeding and intestinal obstruction, the patient must be urgently hospitalized for surgical treatment.
- With an anal fissure, it is important for the patient to normalize the stool and relieve sphincter spasm. In the chronic course of the disease, excision of the anal fissure is performed.
- There are two treatment options for hemorrhoids. Conservative therapy shown on initial stage pathology with the use of local symptomatic agents and venosclerosing drugs. Surgical treatment is resorted to with advanced hemorrhoids or with the development of complications.
- Nonspecific ulcerative colitis is treated with glucocorticosteroids, cytostatics, sulfasalazines. In case of a complicated course, an emergency operation is performed.
- Crohn's disease is treated with metronidazole, ciprofloxacin, mesalazine.
Blood in the stool can appear when bleeding in any part of the digestive tube. Black stools indicate bleeding from the stomach and esophagus, and streaks of blood in the feces indicate bleeding from the large intestine. Uniform staining of feces with dark blood is observed with lesions small intestine. And the discharge of blood from the anus after a bowel movement is a symptom of external hemorrhoids or anal fissure.
The appearance of blood in the stool is an occasion to immediately consult a doctor. and does indicate a life-threatening condition - bleeding from a gastric ulcer or duodenal ulcer. But blood streaks in the feces can speak not only of acute conditions, but also of chronic pathologies. However, this is not a reason to postpone a visit to the doctor.
Structure and function of the gastrointestinal tract
Common causes of appearance
Let's look at what pathologies can cause blood clots in the stool and how to detect them. After reading this article, you will understand how dangerous it can be. this symptom and that only an experienced specialist will help to eliminate this manifestation. Therefore, do not hesitate, consult a doctor as soon as possible, because the presence of blood streaks in the feces already indicates the neglect of the process.The reason may be:
- Nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
- colon polyps;
- Malignant oncopathology;
- diverticulitis;
- internal hemorrhoids;
- Worm infestations;
- Intestinal infections.
diverticulitis
A diverticulum is a sac-like protrusion of the wall of a hollow organ (esophagus, stomach, intestines, Bladder). Diverticulosis is a disease characterized by the appearance of multiple diverticula. The disease can exist asymptomatically for a long time, but when certain factors affect the intestinal wall, the diverticulum becomes inflamed, capturing the surrounding tissues as well. This is how diverticulitis develops.
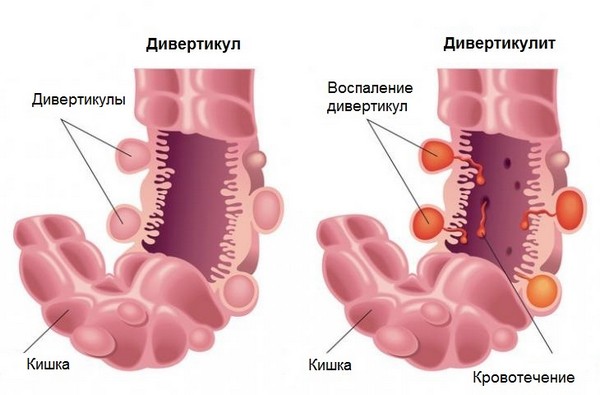
What do diverticula and diverticulitis look like?
Diverticulitis is a more dangerous pathology due to the likelihood of developing many complications. The appearance of feces with streaks of blood is just a symptom of a complication - bleeding from the diverticulum. Along with this, patients complain of the following manifestations of diverticulitis:
- Violation of the digestive processes: nausea, vomiting, change in the nature of the stool;
- Constant pain in the abdomen, which is not stopped by taking antispasmodics;
- With inflammation of the diverticulum, along with blood in the stool, mucus can be detected, as well as an increase in temperature and manifestations of intoxication.
Both single and multiple diverticula can exist asymptomatically and be detected during examination for other pathologies. The most accurate diagnosis of diverticulosis is established after X-ray examination of the gastrointestinal tract with contrast.
Interesting: On x-rays, diverticula are very clearly defined in the form of sac-like protrusions, but this one modern way as endoscopy does not always confirm the diagnosis of diverticulosis.
internal hemorrhoids
With internal hemorrhoids, enlarged hemorrhoids are located inside the rectum and are not visible when viewed from the anus. During bowel movements, the nodes can be injured and light blood streaks remain on the surface of the feces. Hemorrhoids are also characterized by other local symptoms: itching in the anus, pain during defecation, constipation, swelling in the anal area outside the act of defecation.
Recall: external hemorrhoids can also be accompanied by the release of blood, but usually the blood is released at the end of the act of defecation, and its traces can remain on linen and toilet paper.
The causes of hemorrhoids vary, but the most common are regular constipation and a sedentary lifestyle. Often, inflammation of the hemorrhoids occurs in pregnant women, which is associated with an increased load on the vessels, including the hemorrhoidal veins.
Diagnosis of internal hemorrhoids is carried out by examining the anal area and performing rectoscopy (endoscopic examination of the rectum).
Proctitis is an inflammation of the rectum. Also emit inflammation of the rectum and sigmoid colon- proctosigmoiditis. Both of these diseases can be combined with the appearance of blood clots in the feces, but only with the formation of erosive and ulcerative defects. Then the patient is diagnosed with erosive, ulcerative or ulcerative-necrotic forms of proctitis.
The causes of inflammation of the rectal mucosa are diverse. Proctitis can cause hemorrhoids, anal fissures, rectal injuries, intestinal infections, specific infections (tuberculosis, syphilis), malnutrition, intestinal dysbacteriosis and many other adverse factors.
The appearance of blood streaks in the stool in an adult is not a specific symptom for this pathology, but occurs in advanced cases. At the same time, patients complain of pain in the perineum and lower back, stool disorders, fever and impaired general condition organism. Along with blood, mucus and pus may appear in the stool.
For the diagnosis of proctitis, a digital examination of the rectum and stool analysis (coprogram) are usually used. Sometimes rectoscopy is performed, and in severe cases, a biopsy of the rectal mucosa.
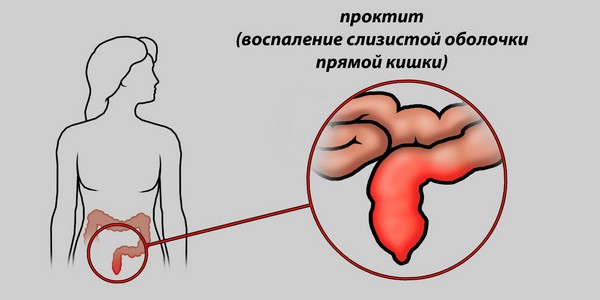
Where is proctitis localized?
Worm infestations
Helminths enter the body by the fecal-oral route when eating unwashed vegetables, poorly processed meat affected by worms, and contact with infected animals. This pathology disrupts the functioning of the whole organism, causing general intoxication and exhaustion.
In addition to the appearance of red streaks in the feces, helminthiasis of the colon is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Nausea, weakness;
- Constant feeling of hunger;
- Depressed mood, depression;
- Skin rashes, allergic reactions;
- Itching in the anus (with damage to the rectum).
If you suspect helminthiasis, be sure to contact a specialist. Worm infestations are quite difficult to treat, so the sooner a specific therapy is prescribed to the patient, the sooner his condition will return to normal.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of helminthiasis of the colon is simple and based on the study of feces. Identification of helminths and their eggs in the feces allows you to make a diagnosis. Sometimes a set of examinations is supplemented by a blood test for common helminthiases in order to exclude damage by other worms and protozoa.
Important: Almost always, when blood clots appear in the stool, the patient is prescribed an endoscopic examination - a colonoscopy. So the doctor will definitely make sure that there is no danger to the life of the patient. In addition, during a colonoscopy, a bleeding vessel can be cauterized, which immediately stops the bleeding.
All the situations described in which blood clots appear in the feces are chronic, but this does not mean that their treatment should be postponed. Among acute conditions, blood may appear in intestinal infections, but this patient will be more worried about indomitable vomiting, diarrhea and severe exhaustion.
Blood streaks in the stool accompany a lot of pathologies, so self-medication here is pointless and dangerous. Contact the clinic to find out the cause of such a symptom, because timely diagnosis can save a life.
(votes: 1
, average rating: 5,00
out of 5)
All materials on the site are presented
for acquaintance, contraindications are possible, consultation with the doctor is MANDATORY! Do not engage in self-diagnosis and self-treatment!
The causes of blood clots during stool may be due to a large number of factors. More often this happens during the development of hemorrhoids. The patient has pain in the anus, and blood is observed immediately after bowel movement on feces or toilet paper. In this case, there may be scarlet blood or dark. The loss of such an important fluid can turn into chronic form. The result of this is the appearance of iron deficiency anemia.
During the appearance of anal fissures, bleeding also appears. In this case, the liquid comes in small portions, this is often observed when visiting the toilet. Pain is also present and causes a lot of inconvenience to a sick person. In addition, there is no mixing of blood with feces, so it may be absent in the fecal masses. As in the previous case, the patient notices blood in the stool during a visit to the toilet or finds a few drops on the toilet paper.
Inflammatory processes need to be taken carefully. Often pain and bleeding in the anus are the result of proctitis. Represented and its shell. This leads to sores and wounds on the surface. In this case, the patient may notice stool and blood after the toilet. Blood streaks may be present in the feces.
Bleeding may be the result of polyp activity. The amount of blood released will depend on the location of the polyps and their size. In most cases, blood in the stool is present and mixed with them. It strikes colon colitis, which leads to the development of ulcers. In this case, the blood during defecation will be mixed with mucus.
The reasons for the appearance of blood fluid after a stool can be associated with peptic ulcer or gastritis. In the first case, blood is released strongly during the act of defecation, and the stools themselves have a consistency that looks like tar.
It should be noted that blood during defecation does not always indicate the presence of a pathological process. In some cases, its appearance during a bowel movement may be false. This often happens after eating beets, pomegranate juice, currants, tomatoes, red fruits and vegetables. However, if there is pain, and the causes of the condition are not clear, then it is dangerous to delay visits to the doctor.
2 Symptoms of the condition
The presence of blood in the stool during constipation or during the process of emptying is the main symptom pathological condition. However, there are several signs that can give a description of a particular situation. It is important to pay attention to the color of the discharge. The shade of blood depends on the place where the bleeding has developed in the gastrointestinal tract.
There is a certain pattern - the closer the source of inflammation to the anal, the brighter the shade of the blood.
Therefore, if the mucous membrane of the sigmoid or rectum has been damaged, then the blood after defecation will be bright. If the inflammatory process or damage has affected the transverse intestine, then the shade of the discharge will be dark.
Bloody discharge may be dark in color and have an unpleasant odor. Such feces are called - melena. This can also occur in the case of stagnation of blood in the cavity of the large intestine for a long period of time. During this time, the blood decomposes due to the multiplication of bacteria and their vigorous activity. Blood is broken down into several components. Hematin has a black color, which is responsible for the color of fecal masses and blood if the patient has started bleeding.

3 The appearance of discharge in children
Bloody stools in adolescents have the same causes as in adults. However, children under 3 years of age are affected by other factors. They are much more likely to have blood from the anus as a result of cracks. In childhood, the process of formation of such lesions occurs much faster, a few days are enough.

Detecting a pathological condition is quite simple. The baby often grunts while going to the toilet. Pain may occur, which is manifested in a corresponding grimace on the face of the child. In some cases, the baby may refuse to sit on the potty. There are drops of blood on toilet paper and bowel movements that have a bright tint.
The parents of the child should not panic. It is important to establish a diet for the baby, which will allow you to get rid of the problem in a few days. As for children under 1 year old, the appearance of blood in them may indicate an allergy to food. It happens that the vessels begin to bleed, and therefore bleeding occurs. Self-treatment is not recommended. The child must be shown to a specialist.
Pain is not the only symptom. Together with it, bleeding occurs, which may be a manifestation of lactose deficiency. Other manifestations of the disease state may develop. These include rashes on the skin, the development of iron deficiency anemia. With a slow weight gain, you should also be wary.

In those children who are on artificial nutrition, bloody discharge indicates intestinal volvulus. The discharge has a jelly-like form, the child is often in a restless state. The baby refuses to eat, he constantly cries. In such a situation, a visit to the doctor is a necessary measure.
4 Signs of pathology
The presence of pain and blood during bowel movements in men often indicates the development of hemorrhoids. However, we should not forget about cirrhosis of the liver, injuries of the walls of the rectum and cracks. Cancer can also lead to bleeding.
In the case of the development of oncological lesions in men, not only blood appears. There are symptoms that should immediately alert. These include the following manifestations:
- Frequent rumbling in the abdomen.
- Pain and other discomfort in the anus.
- Weakness.
- Constipation.
- False urge to empty the bowels.
- Feeling of fullness in the stomach.
- Aversion to food.
- Diarrhea.

Masses of feces have blood streaks. In the future, intestinal obstruction may form. As for cirrhosis of the liver, the signs of the disease include the following symptoms:
- Skin itching.
- Vomit.
- Spider veins appear on the skin of the abdomen.
- Nausea.
- Asthenia.
- Intolerance to certain foods.
Advanced forms of the disease can lead to rupture of pathologically altered vessels. This applies to the esophagus and intestines. This causes bleeding, which is found during a visit to the toilet. In this case, the feces are black in color.
In men, prostate cancer can lead to bleeding. This is especially true for advanced stages. In this case, there is a risk of cancer growing into the intestinal mucosa, which leads to bleeding during bowel movements.

The presence of blood clots during bowel movements in women also has specific causes of development. Often this is formed during the progression of endometriosis. If there is varicose veins of the perineum, then the blood will appear in the last weeks of pregnancy. If a woman underwent radiation therapy during the treatment of oncological forms of diseases that affected the genitals, then the presence of blood may be a consequence of this event.
During pregnancy, the uterus grows, which presses on the organs in the pelvis. There is a loss of elasticity in the walls of the rectum, which leads to its damage. In addition, increased blood supply to the lower intestines, genitals and a slight decrease in blood clotting can lead to bleeding. This condition is normal during pregnancy, however, with prolonged bleeding, you should seek medical help as soon as possible.
5 Diagnostics
Blood during bowel movements is dangerous sign which is important to pay attention to. It is not recommended to deal with the elimination of the disease on your own, since it will not be possible to identify the cause under such conditions. The patient should consult a general practitioner, proctologist, surgeon, and for women also a gynecologist. Only in this case it is possible to establish the exact cause and factors that caused this process.
During a visit to the doctor, an anamnesis is collected. The specialist tries to identify the factors in the formation of a pathological condition. After that, the patient is sent for a rectal examination, which is performed by the digital method. The presented method was and is the main one, it helps to detect external and internal hemorrhoids and pathologies of the rectum of an oncological type.
If the data from the examination is not enough, then the specialist prescribes a colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy. The presented hardware diagnostic methods allow you to notice even the smallest damage. In addition, the techniques make it possible to take content for analysis.
The diagnostic procedure is not complete without laboratory tests. General analysis blood is prescribed more often than others. The level of hemoglobin in the blood is subject to determination, which helps to determine the appearance of iron deficiency anemia. Exposed to the study of feces and urine. Particular attention is paid to the analysis of feces, since the detection of blood in it directly indicates the presence of bleeding.
![]()
6 Treatment activities
Most diseases that lead to the development of bleeding do not carry a mortal danger. However, it is recommended to start treatment in a timely manner, since the transition of the disease to a severe stage can significantly complicate the life of the patient. Therefore, a visit to a gastroenterologist and a proctologist is a prerequisite for a quick recovery.
During the development of some diseases, use rectal suppositories and ointments. This is appropriate in the treatment of hemorrhoids. It is necessary to choose such products that have zinc, titanium or bismuth oxide in their composition. They additionally have a hemostatic effect. Examples of products are Proctosan Neo, Relief Advance and Proctosan. The presence of anal fissures and bleeding requires the use complex therapy. The following laxatives are used:
- Candles with sea buckthorn or glycerin.
- Guttalax.
With the development of pathologies that are associated with the organs of the gastrointestinal system, it is required to deal with the elimination of these diseases. This will get rid of the disease itself and bleeding. Pain and other unpleasant symptoms will also disappear.
Thus, the appearance of blood during the act of defecation can be due to various factors. In each case, to eliminate bleeding, one should deal with the root cause of this phenomenon, and not with the treatment of symptoms. It is forbidden to get rid of the disease on your own, it is recommended to immediately visit a specialist.
The presence of blood in the stool looks quite intimidating, so many people immediately begin to think of various serious diseases. Of course, blood in the stool, mucus or even bloody streaks is a deviation from the norm and it is necessary to identify the causes of this phenomenon. However, don't panic right away.
The fact is that the "red liquid" in the stool of an adult can be just a symptom of irritation of the gastric mucosa. This is not very dangerous, but it happens that the reasons are much more complex.
Causes of blood clots in the stool
To answer the question of why blood appeared in the feces of an adult, you need to look at exactly how it looks. So, it can be fresh (scarlet), burgundy, black and hidden (meaning that blood in the feces cannot be detected with the naked eye). If there are clots in the blood or it is mixed with mucus, this must also be taken into account in the diagnosis.
What does blood in stool look like?
In an adult, streaks of blood in the stool may vary in color. Thanks to this factor, it is possible to determine not only from which section of the gastrointestinal tract the clots come out, but also to find out the causes of the complication.
- A bright red impurity means that she has come a short way. In other words, the causes of bleeding should be sought in the lower intestines (anus, rectum, sigmoid colon).
- Dark maroon clots indicate complications in the middle section - most likely, the transverse or large intestine suffers.
- Veins or clots of black feces indicate that the causes of bleeding are in the stomach or small intestine. During the time that the blood passes through the intestines, it has time to change color and get mucus from the intestinal lining. As a rule, such streaks in the feces of an adult have a very unpleasant odor.
- Hidden blood in the stool. Almost or completely invisible streaks of blood can only be detected by a laboratory assistant. For this, a fecal analysis is given.
What disorders can indicate blood in the stool:
- Anemia. Often the causes of weak bleeding during bowel movements are iron deficiency in the body. It is necessary to donate blood and find out the amount of this microelement. The situation can be easily corrected by taking complex iron-containing preparations.
- Tumor of the gastrointestinal tract. In the presence of oncological diseases blood in the stool will have clearly visible streaks. Why so: the tumor damages the internal blood vessels, they rupture, and blood is coming further through the intestines, leaving in the feces. This situation requires mandatory surgical intervention. Even if the tumor is benign, it can be very dangerous.
- Hemorrhoids, anal fissures. The presence of bright red blood in the stool means that you most likely have hemorrhoids or a traumatic injury to the anus. In this case, mucus or clots rarely appear in the blood, but sometimes they can still be detected. The causes of hemorrhoids in an adult can only be called by a doctor. It is advisable not to self-medicate.
- Rectal cancer. With cancer, the blood will be scarlet, and its admixture will be observed in the feces almost always. Only a qualified doctor who will conduct all the necessary studies will be able to solve the problem and name its causes.
- Ulcer, erosion of the stomach or duodenum. With heavy bleeding in one of the upper sections of the gastrointestinal tract, the blood in the feces can be with mucus, and most importantly, it will be completely black. This is due to the fact that in the process of digestion, the blood breaks down into hematin, which has a black color. Mucus may not be present at all, so you should not focus on it.
- Varicose veins of the esophagus. In this case, the feces will have streaks or an admixture of scarlet blood. Mucus does not appear in such cases.
- Dysentery, salmonellosis. The stool is liquid, blood and mucus are excreted with it. This can occur with infectious diseases.
