Lethal dose of arsenic. What is characteristic of arsenic poisoning and what should be done
This chemical element- the killer's favorite weapon. He appeared in many works of art and often became the cause of the death of major political figures. They strengthened their health and removed intractable husbands. Some of its compounds can harm a person even in small quantities, but on the other hand, mineral waters and some medicines containing it help restore health. It's time to remove the aura of mystery and get to know this intractable and dangerous substance better.
Arsenic is a chemical element known as arsene. Atomic number - 33, refers to semimetals. A change in valence over a wide range makes it possible to obtain compounds of different properties, some of which can kill a person, while others, on the contrary, cure diseases such as cancer and leukemia.
Element properties
The content of arsenic in the earth's crust is negligible. It is not formed during magmatic processes due to its volatility after heating, but during volcanic eruptions, arsenic compounds enter the atmosphere in large quantities. There are about one hundred and eighty minerals based on arsenic, since this element can take on different valencies. But in nature, arsenic combined with sulfur is more common (formula As 2 S 3). 
But not in nature?
In everyday life, the most common and stable is gray arsenic (formula - α-As). This is a rather fragile steel-gray crystal, which tarnishes in air and becomes covered with a film due to prolonged contact with open air. There are also yellow, black and brown modifications of the element, which turn into gray after heating.
It is obtained by heating the rock that contains arsenic, or by restoring pure arsenic from its oxides.
History
First of all, arsenic is a poison. But in the ancient world, people used this mineral to make dyes and medicines. For the first time, pure arsenic was obtained by Albert the Great in the thirteenth century AD. Paracelsus also mentioned this element in his works, but under a different name. In eastern countries, in parallel with Europeans, they also investigated the properties of this amazing substance and could even diagnose death from poisoning. But their knowledge has not reached our days.
As a separate chemical element, arsenic was introduced into the periodic table by Antoine Lavoisier.
Causes of poisoning
Arsenic poisoning is not uncommon these days. But this is more the fault of an accident than a targeted murder. You can encounter it almost anywhere:
- in nature: groundwater that feeds the springs can pass through rocks containing this mineral;
- it is contained in smoke: burning industrial waste is extremely toxic;
- in seafood: since arsenic is well deposited in cold water, then during the eruption of volcanoes located at the bottom of the oceans, it may well enter the body of fish and shellfish;
- in industry: used as an auxiliary element in the production of glass, semiconductors or other electronic devices.
In addition, intentional arsenic poisoning as an attempt at suicide or murder cannot be ruled out.
The pathogenesis of poisoning
Getting into the human body through the skin, lungs or intestines, arsenic is carried through the bloodstream through the body, penetrating into all organs and tissues. It cannot overcome but it penetrates well through the placenta, poisoning the fetus. A long elimination period makes it possible to detect poison even a week after poisoning. 
The lethal dose is 0.05 to 0.2 grams. And it can be obtained both simultaneously and gradually, if chronic poisoning occurs. Typically, this condition is observed in workers in agriculture, the fur and leather industries, as well as chemical enterprises.
Clinic
When a lethal dose is ingested, the consequences are not long in coming. Within half an hour, a person begins to feel symptoms of general intoxication, such as headache weakness, lethargy, nausea and vomiting. They are not specific to any poison. It is simply the body's reaction to the action of a toxic substance. How to make sure that it was arsenic poisoning? The symptoms are as follows:
- cramping pain in the abdomen;
- diarrhea in the form of rice water;
- persistent garlic odor from the mouth;
- severe dehydration and thirst.
Depending on which system was affected by the poison in the first place, several forms of poisoning are distinguished: gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, urinary, nervous. In addition, as mentioned above, there is also chronic arsenic poisoning. Symptoms in this case do not develop so rapidly and are more pronounced on the skin:
- Hyperkeratosis: Excessive production of the surface layer of the skin.
- Redness or pigmentation of places with thin skin - eyelids, armpits, temples, neck, nipples and genitals.
- Peeling and roughness of the skin.
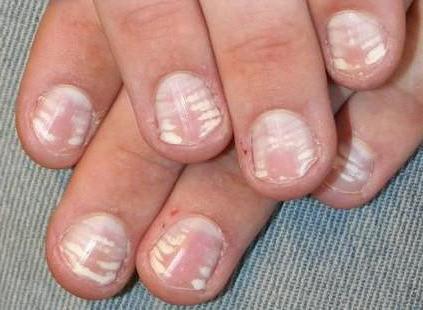
- The appearance of white lines on the nail plates.
Urgent measures
Arsenic is reduced to washing the stomach with plenty of water and washing it off the skin. If a person is unconscious, then after you turn him over on his side, you need to urgently call ambulance. In no case do not give the victim a laxative or sorbents. If the poison has already managed to get into the red blood cells, these activities will be of little help.
In especially severe cases, it is necessary to start cardiopulmonary resuscitation before the arrival of doctors. Signs of arsenic poisoning can be mistaken for a common intestinal infection, so be sure to tell the doctors all the details of the poisoning.
Treatment in a hospital
Arsenic poisoning requires hospitalization and observation by specialists. The victim needs oxygen inhalation, abundant invasive therapy to remove the remnants of the poison from the body. If, after the tests, it is found that the patient has reduced hemoglobin and red blood cells, then he is additionally injected with a glucose-novocaine mixture. When exhaling arsenic vapors, mucosal edema may develop, as a result, we have difficulty breathing. In this case, the patient should be injected with aminophylline, and in severe cases, also incubated to connect the artificial respiration apparatus.
Unithiol is considered a specific antidote (the main active substance- dimercaprol), which binds to arsenic and forms insoluble compounds that are excreted in the urine. The drug is administered at the rate of 2-3 milligrams per kilogram of body weight. Repeat the procedure every six hours during the first day, and then twice a day for another couple of weeks. 
The doctor needs to find out how severe the patient's arsenic poisoning is. Treatment will depend on the dose of poison. Modern techniques allow you to set it quite accurately.
Forensic examination
As you know, arsenic poisoning could get away with murderers for a long time, since it was not possible to detect the toxin in the blood or hair of a person. Historians agree that Napoleon Bonaparte died from this poison, but the official version claims that untreated stomach cancer was the cause.
In order to prevent such incidents from recurring, and the criminal could be found, chemists and physicists from all over the world, without saying a word, began looking for a way to detect arsenic in the victim's body. Olaf Bergman, Carl Scheele and James Marsh participated in this study. It was the last of them who was able to obtain pure arsenic during his experiments, which could be used as evidence. The sensitivity of the reaction could show 0.001 g of the poison content in the blood of the deceased.
A hundred years later, poisoning with arsenic compounds was no longer a secret for the investigation, as chemists were able to achieve greater accuracy and subtlety of the procedure.
Military targets
After the First World War, when the use of poison gases entered the circle of means for defeating the enemy, scientists enthusiastically began to experiment with new weapons. The chemical impact on the enemy of arsenic compounds or its vapors caused abscesses, necrosis of the skin, swelling of the mucous membranes and death from suffocation before the poison entered the bloodstream.  Even a slight concentration was enough to demoralize a man and kill him. One such remedy was lewisite. He had a wonderful smell of flowering geraniums, but even a drop of it could greatly damage the body. For this property, the soldiers called it "the dew of death."
Even a slight concentration was enough to demoralize a man and kill him. One such remedy was lewisite. He had a wonderful smell of flowering geraniums, but even a drop of it could greatly damage the body. For this property, the soldiers called it "the dew of death."
Mineral water
The permissible concentration of arsenic in a liter of drinking water is 50 micrograms. But in 2002, this norm was revised, as a result of which a more stringent one was adopted - up to 10 micrograms. The alarm on this issue was sounded in Taiwan. Their artesian water contained so much arsenic that it was amazing they hadn't died out yet. The concentration was more than 180 times higher than the norm allowed by modern standards.
The question arose of purifying water and delivering it to the regions of Southeast Asia at the lowest economic cost. by the most in a simple way was the oxidation of trivalent arsenic to pentavalent and its precipitation. 
medical application
In small quantities, almost all elements of the periodic system of D. I. Mendeleev are necessary for the normal functioning of a person, because it is not in vain that they are present in the body. And who has not heard the phrase that in small doses and poison is a medicine? It is known that arsenic helps to improve hematopoiesis, speed up the metabolism and growth rate of tissues, including bones. Microdoses even improve immune system. In ancient times, arsenic compound paste was used to treat ulcers and open wounds, tonsillitis, and relapsing fever.
In the thirteenth century, Thomas Fowler invented an arsenic-based solution, which he named after himself and used to treat mental and skin diseases. The fascination with this medicine and its derivatives reached its peak at the turn of the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries. But with the introduction of new knowledge about physics, chemistry and the human body, the toxic nature of this compound was nevertheless revealed, and its use began to decline.
Natural mineral waters enriched with arsenic are still used to treat anemia, leukemia and some diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, it is part of the mummy used in cosmetology. Natural sources of this element are seafood, wild rice, cereals, lentils, carrots, grapes (and raisins), strawberries.
Arsenic - one of the most famous poisons, is actively used in dental practice. Accidentally poisoning with arsenic is difficult, but in history there are many cases of the deliberate use of this poison in order to remove enemies.
Arsenic is a rock, possibly getting into groundwater, and through them into wells. It is also formed as a result of the combustion of coal, some chemical. substances.
Oddly enough, arsenic can be found in seafood. It has to do with pollution. sea waters waste from various industries.

It is also used in some industries, for example, the manufacture of semiconductors. It is contained in some paints, antifungal drugs. Arsenic is used to make rat poison.
In addition to an attempt at intentional poisoning or suicide, the substance can get in as a result of safety violations, accidents. There are cases of eating by young children, left unattended, rat poison.
The action of arsenic
Poison can enter the body not only through the esophagus. It can be inhaled or even through the skin.
It quickly dissolves in the blood, spreading through circulatory system. This poison acts at the cellular level, disrupting the most important processes, has a negative effect on the digestive system and nervous system. For the onset of death, a dose of 0.05 grams is sufficient.
If a large dose of this substance has been ingested, we are talking about acute poisoning. If the poison enters the body repeatedly in small quantities, chronic poisoning may occur. This type of poisoning is typical for agricultural workers working with some other industries where it is used as a raw material.
Arsenic is excreted from the body very hard. Even after 14 days, traces of it still remain. It is excreted mainly through the kidneys.
Symptoms
The poison begins to act half an hour after it enters the body. The speed of exposure depends on how full the stomach is with the remnants of food. As a result of inhalation of vapors, the effect occurs at lightning speed.
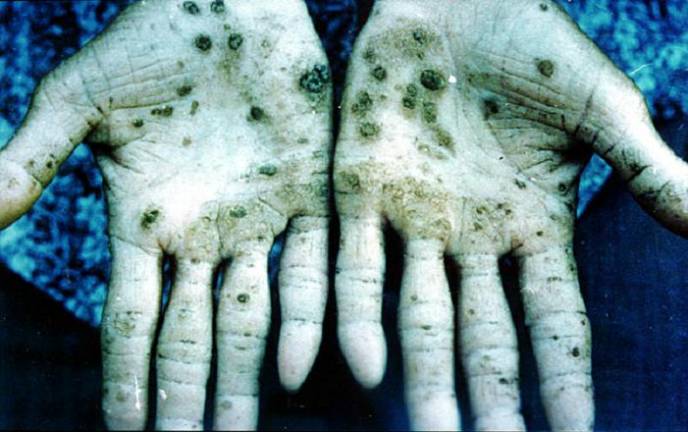 Obvious symptoms of arsenic poisoning on the hands
Obvious symptoms of arsenic poisoning on the hands Symptoms of arsenic poisoning are in many ways similar to other types of poisoning. This:
- vomit;
- weakness;
- headaches;
- stomach ache;
- dehydration.
Symptoms that will help you understand that it is arsenic:
- garlic breath;
- stool like rice water.
The cardiovascular system also suffers, pressure drops. Appear mental disorders, convulsions. Everything ends in coma and death. There are signs of jaundice - yellowness of the skin, urine darkens. Due to the fact that kidney failure develops, blood appears in the urine.
Spasm of the larynx
In case of poisoning, the larynx swells, breathing becomes difficult. The esophagus suffers, arsenic burns it. Erosion of the esophagus, ulcers appear.

The above symptoms may not be all. Depending on the prevalence of symptoms, there are two types of poisoning, gastric and neurological. The latter proceeds in a more severe form, with it the patient quickly falls into a coma.
Chronic poisoning manifests itself only a few days after the penetration of the poison. It affects the functioning of the brain, suffers from the central nervous system. The legs are the first to suffer. The heart, liver, blood vessels also suffer. Hepatitis appears. The level of hemoglobin falls, the patient feels weak. Hair loss is possible.
The skin is also affected. Hyperpigmentation, redness, peeling of the skin, growth of its surface layer may appear. White lines appear on the nails.
Are visits to the dentist dangerous?
Often the question arises about the possibility of poisoning in the dentist's office. To lull the nerves, an arsenic-based paste is sometimes used. It kills the nerves, and the tooth stops hurting.
 Arsenic in dentistry
Arsenic in dentistry The paste is applied to the affected area for two days. If kept longer, symptoms of poisoning appear. The poison eats away the dental tissue, which leads to tooth loss, the gums and surrounding tissues become inflamed. There may even be bone necrosis.
At proper treatment poisoning is not possible. In addition, modern drugs are produced on a different basis, without this dangerous substance.
First aid
Call an ambulance immediately. The patient is laid on his side. If there are no signs of life, you should try to resuscitate.
If the poison gets on the skin, wash it off with detergents.
As a rule, treatment is carried out in a hospital. The decision must be made by the physician.
Treatment of poisoning
In a hospital setting, the treatment of poisoning includes the following procedures:
conclusions
Arsenic is a dangerous poison, poisoning is often fatal. To avoid mortal danger, follow a number of simple measures.
Observe preventive measures when working with hazardous substances, drink water from safe sources, store substances containing poisons separately from food, out of the reach of children.
Drugs poisoning people no need to look for a long time, many of them are in the nearest pharmacy or at home. The modern pharmaceutical market offers consumers a large number of drugs, with the slightest overdose of which serious changes occur in the body.
Also, attackers know available poisons, for example, arsenic has long been used as a toxin, and the ability to recognize harmful substances and use them for their own purposes leads to irreversible consequences.
Arsenic is called an element of the periodic table, and it is found in the environment, industrial production, semi-metal and dentists use it.
Intoxication occurs due to neglect of safety rules or intentionally, the outcome of poisoning depends on this. The hazardous component can get into food, on the skin, and its vapors are also poisonous.
How to poison a person with arsenic? In the old days, poison was added to food or drinks, today criminals use a similar method to eliminate an opponent. Entering the body in any way, the semi-metal quickly affects red blood cells, combines with protein and ends up in the internal organs - the liver, kidneys, spleen, heart. Cellular respiration is disturbed, the digestive organs work worse.
When ingested up to 0.2 g. arsenic develops acute poisoning, the symptoms of which are increasing nausea and vomiting, soreness, diarrhea, dehydration. The risk of death in this case is increased.
Gradual intoxication when a small dose of poison is added to food affects the heart muscle, resulting in myocarditis, and there is also an expansion of capillaries in the body. General sweetness, hair loss and ailments respiratory system become constant companions of the victim.
How easy it is to poison a person And what do attackers use in this case? Connoisseurs identify several options suitable for obtaining a quick result. The list includes the following poisons:
· poison for rats and mice;
· diphenhydramine;
· phenol.
Poison against rodents belongs to pesticides and is often used in agriculture, and the lethal dose for humans will depend on the active substance and the state of health of the victim.
How to poison a person with mouse poison? The toxin is easily mixed with food, and this component is also dangerous when in contact with the skin. Symptoms do not form immediately, only after a few days signs such as weakness, loss of appetite, bleeding gums and local hemorrhages on the oral mucosa are noted.
Poisons against rodents are aimed at worsening blood clotting, so the manifestations of poisoning resemble those of hemophilia. Death occurs as a result of heavy bleeding and internal hemorrhages.
Dimedrol is an anti-allergic drug, often used as a sedative. But uncontrolled intake of this medicine is dangerous, which is what attackers use. How can you quietly poison a person with "Dimedrol"? The lethal dosage of tablets is about 5 pieces, and intoxication develops after a few hours.
An overdose of the drug leads to damage to the central nervous system, so an inadequate state develops with signs of fear and confused speech. The medicine does not affect the level blood pressure, however, it can be reduced against the background of general soreness and drowsiness.
It is important to know that Dimedrol is incompatible with alcohol, which is what criminals use before how to poison a person at home. In this case, the drug provokes an increase in heart rate, extraordinary contractions of the heart muscle, as well as the appearance of hallucinations and the development of tachycardia. The risk of death when taking pills orally with alcohol is extremely high.
About, how to safely poison a person with the help of Dimedrol, many criminals know. However, there are poisons much more toxic and almost certainly fatal.
For example, particles of a substance - liquid and vapor - cause an extensive burn of the skin, eyes and respiratory tract, and after a few minutes, symptoms of intoxication develop. The lethal dose of poison is on average 4 years.
Serious phenol intoxication is characterized by the development of fever, failure of the respiratory and circulatory rhythms. And also there are signs such as white spots on the mucous membrane as a result of poisoning, severe abdominal pain, sweating, diarrhea and vomiting. If a sufficient dose of poison is ingested, death occurs within 24 hours due to a decrease in the respiratory rate and acute cardiovascular failure.
Inhalation of saturated vapors of phenol provokes the appearance of cough, headache, severe agitation and leads to an increase in the number of red blood cells in the urine. As a result, the described substance is used by those persons who know how to poison a person to death.
The element arsenic is a metal, a representative of the XV (according to the old classification V) group in the periodic system of Mendeleev, belongs to the nitrogen subgroup. Arsenic steel grey. In nature, it is the only stable nuclide.
The photo of the arsenic deposit.
general information
It was called the ubiquitous element, because it can be found everywhere. This is its uniqueness.
It occurs naturally in both organic and inorganic forms, with the latter being highly toxic.

Also, this substance is found in industrial products, products of human life. In the body of an adult, its content corresponds to 15 milligrams.
The photo shows native arsenic in the form of dense masses.
Poison or drug
This chemical element is, in fact, one of the most controversial. The fact that a meager pinch of its oxide or one breath of arsenic hydrogen is enough to kill means that arsenic is a poison. But, on the other hand, there are compounds of this element that are no more dangerous than, for example, table salt.
Benefit
The secret of the usefulness that this metal represents to the body lies in its quantity. In small doses, it performs useful functions:

The daily requirement of the body for this element corresponds to 50-100 mcg.
If arsenic does not reach the body, then the following symptoms are possible:
- decrease in the amount of triglycerides in the blood;
- delayed growth and development of the body;
- increased fertility.
The use of this element and its compounds in modern medicine. Preparations based on it are indicated for anemia, leukemia, and exhaustion. It is used in dentistry.
The use of arsenic in dental practice
The photo shows the process of filling a tooth.
Its inorganic forms are used as a means local action(cauterizing, necrotizing, etc.). As drugs of general action, they are used as metabolic regulators.
Its organic compounds are used in chemotherapy, as drugs for the treatment of spirochetosis and diseases caused by protozoa.
Harm
Organic compounds are less dangerous. Their poisoning can cause nervous disorders or pain in the abdomen.
Inorganic compounds are poisonous. The consequences of poisoning with them can be from irritation of the stomach to a decrease in the production of red and white blood cells and the development of cancer.
Its elevated concentrations in the body can lead to infertility and provoke miscarriages.
Contact with arsenic may cause dermatitis. Inhalation of fumes or consumption of food and drink containing an increased concentration of this substance leads to a decrease in immunity, heart disease and brain damage, DNA damage.
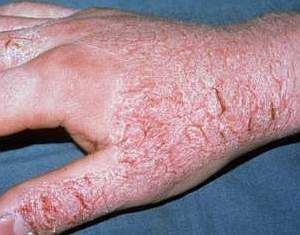
Contact with arsenic can cause dermatitis
The body's resistance to this element is sometimes amazing. History knows the facts of its use by peasants XIX century from the village of Styria in Australia to improve complexion, increase appetite, improve breathing and improve immunity.
We started this procedure with a daily intake of 1 grain (32 mg), gradually increasing the dosage. It was reported that the doses reached 0.26g-0.39g 4 times a week. In other words, these doses are proportional to three, reliably determined as lethal.
These facts were confirmed by the researcher McLagan K., thanks to the analyzes of the urine of the peasants.
Possibility of poisoning
The need for arsenic for the normal functioning of all body systems is undeniable. Its presence in small amounts is beneficial in the processes of hematopoiesis, metabolism, growth of bones and tissues.
However, higher doses or long-term use can provoke not only arsenic poisoning, but also the development of cancer, genetic disorders.
Causes of intoxication
The inorganic form of this element occurs naturally in small quantities. Its negligible doses in drinking water are a disaster for many millions of people in more than one country.
The concentration of arsenic in food is quite low. However, in seafood and fish, it can be quite high, because marine life absorbs it from the aquatic environment.
Arsenic poisoning is at risk for people working with this element. It can be contained in the smoke from the process of burning industrial waste, burning coal, smelting ores. It is used in the manufacture of glass, electronic devices and semiconductors.
It is used in leather and fur production.
Arsenic poisoning can occur in people living in buildings constructed from wood treated with arsenic, or on agricultural land where pesticides were previously used.

Vegetables treated with pesticides are dangerous
Routes of entry into the body
The probability of poisoning with this substance can occur in three ways: through the gastrointestinal tract, the surface of the skin and inhalation of toxic fumes.
How does arsenic work, penetrating into the human body? It quickly enters the plasma, and then into the erythrocytes. Connecting with globin, it is picked up by the bloodstream and enters the liver, brain, heart, affects the kidneys, stomach, and lungs.
Damage to the nervous and digestive systems. The action of arsenic occurs at the cellular level. At the same time, important biochemical functions and the process of respiratory activity of cells are violated.
The lethal dose of arsenic corresponds to 0.05 - 0.2 g.
Signs of intoxication
Arsenic poisoning can be acute or chronic. Manifestations of acute intoxication occur quickly after a significant dose of this substance has entered the body.
Chronic poisoning increases gradually, when the metal systematically and for a sufficiently long period of time penetrates into the internal organs and accumulates in them. After two weeks, it is found in the teeth and hair, bones and nails.
90% of this substance is excreted by the kidneys, and the remaining 10% is excreted through the intestines.
Signs of an acute form
Acute intoxication manifests itself after half an hour after the penetration of the poison. In the process of inhalation of fumes or swallowing on an empty stomach, the toxic substance very soon penetrates into the bloodstream, the clinic develops at lightning speed. In such a case, the risk of death is likely.

Spasms of the larynx, pulmonary edema - signs of arsenic poisoning
If the poison has entered the body with food, then the signs will appear after a few hours. Acute intoxication is characterized by the following symptoms:
- sharp pain in the temporal region, dizziness;
- lethargy;
- nausea and possible vomiting;
- spasmodic pain in the abdomen;
- the stool has a semblance of rice water;
- the smell of garlic from the mouth;
- dry mouth, thirst;
- dehydration.
This form of intoxication is characterized by damage to many organs, which corresponds to the following symptoms:
- heart palpitations, pressure drop, failures of contractions of the heart muscles;
- mental excitability, convulsions, fever, coma;
- spasms of the larynx, pulmonary edema, difficulty breathing;
- burns, erosions and ulcerative formations of the mucous membrane of the larynx and food tract, bloody discharge in expectorations;
- death of erythrocytes, darkening of urine, development of jaundice;
- with the development of hemolysis, the death of the renal tubules begins, the ability of the kidneys to excrete and form urine is lost, blood discharges are found in it.
According to dominance clinical signs distinguish the gastrointestinal type of intoxication, when the primary symptoms are lesions of the digestive system. A very severe symptom is paralytic, with a pronounced neurological clinic and an increase in a coma.
Chronic form of poisoning
Signs of this form of intoxication make themselves felt after 2-8 weeks. The metal, having a toxic effect, damages the cerebral cortex, which leads to the development of encephalopathy. Causes damage to peripheral nerves that control function lower extremities. As a result of the development of neuropathy, pain appears, sensitivity is disturbed, muscle weakness appears in the lower and upper extremities.
With chronic intoxication, the development of hepatitis is possible.
Changes in the heart muscle are found. Myocarditis progresses, as well as pericarditis. A stable expansion of capillaries is found. It is likely that the liver is damaged by toxins - hepatitis develops. It is not excluded the development of laryngitis, tracheitis, bronchial lesions. Hemoglobin drops. Hair loss is possible.
With regular exposure to poison, changes in the skin and nails are observed:
- hyperpigmentation of the upper eyelids, neck, scrotum;
- redness of the armpits, temporal zone, nipples;
- hyperperatosis - excessive growth of the upper layer of the epidermis;
- thickening and dryness of the skin;
- the appearance of white stripes on the nail bed.
The consequences of arsenic poisoning are very serious up to the development of skin and lung cancer, because it is a carcinogen.

It is necessary to wash the stomach
Help for the victim
Symptoms of intoxication with this substance develop very quickly, therefore, before the arrival of an ambulance, it is necessary to provide first aid to the victim.
First aid
If you find at least two of the above symptoms, you should act immediately. Immediately call an ambulance. However, before her arrival, it is categorically impossible to be inactive. A number of standard procedures should be carried out:
- make a gastric lavage with boiled water or water with salt;
- wash the skin in contact with the poison with water and detergent;
- provide plenty of drink in small doses (water with vinegar or citric acid);
- take 4-5 activated charcoal tablets (the result will not be immediate due to the weak binding of arsenic by charcoal);
- do not use laxatives;
- support vomiting with warm milk;
- if the victim is unconscious, lay him on his side;
- if necessary, perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Hospital treatment
Perhaps with a mild form of poisoning, it will be possible to avoid hospitalization. However, with severe and moderate intoxication, the victim must be taken to a hospital.
Arsenic poisoning can be accidental, intentional (suicide or attempted murder), occupational, iatrogenic, or environmental exposure to arsenic. In the latter case, its source is usually soil, water or food products, while pentavalent arsenic compounds predominate among inorganic substances.
In the last 20 years, arsenic impurities in drinking water have become the leading cause of mass chronic poisoning with this substance. The EPA recently lowered the maximum allowable concentration of arsenic in drinking water to 0.01 mg/L. The reason for this was the data of statistical modeling, according to which at an arsenic concentration of 0.05 mg/l, previously considered acceptable, the risk of lung and bladder cancer increases.
Pathophysiology
The main target of trivalent arsenic is the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. As a result of its inhibition, the formation of acetyl-CoA decreases, which leads to a slowdown in the reactions of the Krebs cycle and ATP synthesis. The poison also blocks the recycling of lipoic acid in the Krebs cycle. In addition, it inhibits acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase, which catalyzes the last step in fatty acid oxidation, further reducing ATP production. Trivalent arsenic also inhibits the activity of glutathione synthase, G-6-PD (required for the synthesis of NADPH) and glutathione reductase.
Arsenic blocks potassium channels of delayed rectification, which provide repolarization of cardiomyocytes. This results in ventricular tachycardia, including torsades de pointes. Reduced glucose transport and suppression of gluconeogenesis can lead to glycogen depletion and hypoglycemia.
The toxicity of pentavalent arsenic may be partly due to its reduction to the trivalent state. In addition, it can disrupt oxidative phosphorylation by replacing inorganic phosphate during glycolysis. Prolonged exposure to arsenic increases the risk cardiovascular disease, portal fibrosis of the liver and malignant neoplasms.
Symptoms of arsenic poisoning
The symptoms of poisoning depend on the specific compound ingested, the amount, and whether the poisoning is acute or chronic. At high doses of highly toxic compounds (for example, arsenic anhydride), symptoms of acute poisoning quickly develop, and with prolonged intake of small doses of arsenic with drinking water, a different clinical picture slowly develops. Symptoms of subacute arsenic poisoning can develop both in survivors of acute poisoning and with prolonged intake of poison from the environment.
Acute poisoning
Most early symptoms acute arsenic poisoning when taken orally - signs of gastrointestinal damage (nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea). They appear in the first minutes, at most - a few hours later. The diarrhea of arsenic poisoning is severe, almost like that of cholera, and the stools may look like rice water. Both hypovolemia and the direct action of arsenic can lead to damage to various organs. Cardiovascular disorders range from sinus tachycardia and orthostatic hypotension to shock. Acute encephalopathy is possible, progressing over several days and manifesting as confusion, coma and epileptic seizures. Its cause is considered to be the brain and pinpoint hemorrhages in the brain. Possible acute lung injury syndrome, ARDS, respiratory failure, hepatitis, hemolytic, acute renal failure, rhabdomyolysis and death. AKI may result from hypotension-induced renal ischemia, precipitation of myoglobin or hemoglobin in the renal tubules, cortical necrosis, or direct action of arsenic on the renal tubules.
Subacute poisoning
After acute arsenic poisoning, new symptoms of damage to the central nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, lungs, cardiovascular system, hematological and dermatological disorders may persist or appear for days or weeks. Perhaps the development of persistent encephalopathy (headache, stupor, confusion, memory impairment, personality changes, irritability, hallucinations, epileptic seizures). Abducens nerve lesions and bilateral sensorineural hearing loss have been reported. Neuropathies usually develop 1-3 weeks after acute poisoning, but sometimes earlier. Among the possible dermatological manifestations are alopecia areata, herpetiform rashes on the oral mucosa, diffuse spotty itchy rash and pityriasis peeling, not accompanied by itching. Occasionally, mesovian stripes are observed - transverse white stripes on the nails 1-2 mm wide. In case of subacute poisoning with inorganic arsenic compounds, nephropathy, fatigue, loss of appetite and weight loss, torsades de pointes and persistent symptoms of gastrointestinal damage are also possible.
Chronic arsenic poisoning
Chronic poisoning with small amounts of inorganic arsenic compounds is usually caused by occupational contact or exposure from the environment. Symptoms of gastrointestinal damage (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea) are less common than in acute poisoning. Long-term consumption of poison with drinking water is associated with an increased risk of skin lesions (including malignant neoplasms), arterial hypertension, diabetes, lesions of small arteries and various malignant neoplasms internal organs. The skin is very sensitive to the toxic effects of arsenic. Hyperpigmentation, hyperkeratosis, squamous and basal cell carcinoma, Bowen's disease are described. Chronic exposure to arsenic has been shown to increase the incidence of diabetes mellitus, restrictive respiratory disease, and vascular disease in population studies. In particular, a connection was found between prolonged exposure to poison and damage to the leg arteries found in Taiwan, accompanied by increasing tissue ischemia up to gangrene of the feet. Among the most common neurological symptoms- encephalopathy and neuropathy.
Diagnosis of arsenic poisoning
The method of measuring arsenic concentration in the body, the time of sampling and the interpretation of the results depend on the nature of the poisoning (acute, subacute, chronic, long-term effects) and the clinical picture. Factors such as the accumulation of organic arsenic compounds (eg, dimethyl arsenite and arsenobetaine) in chronic renal failure or their intake with food can influence the results of the analysis. In urgent cases, before starting treatment with complexing agents, determine the concentration of arsenic in a single portion of urine. A high concentration with a typical history and clinical picture confirms the diagnosis, but a low concentration does not rule out poisoning. Since the rate of excretion of arsenic in the urine is variable, the diagnosis is considered definitive when its concentration in daily urine is > 50 µg/L or > 100 µg/g creatinine.
If the concentration of arsenic in the urine is only slightly elevated, it is necessary to take into account the data of the anamnesis and clinical picture, since it is known that eating seafood can briefly increase the concentration of arsenic in the urine up to 1700 mcg / l. If the source of the poison could be seafood, they find out which compound is contained in the urine. If this is not possible, the measurement is repeated after the victim refrains from eating fish, shellfish and algae for a week.
Some laboratory parameters are important in the diagnosis of both chronic and subacute poisoning, in the latter case they may change days or weeks after acute arsenic poisoning. These include clinical analysis blood, activity of liver enzymes, indicators of kidney function, urinalysis, concentration of arsenic in daily urine. Normocytic, normochromic or megaloblastic anemia, leukocytosis followed by leukopenia (the number of neutrophils decreases to a greater extent than the number of lymphocytes), relative eosinophilia, thrombocytopenia, a rapid drop in hemoglobin levels (a sign of hemolysis or gastrointestinal bleeding), basophilic erythrocyte granularity are possible. Serum concentrations of creatinine and bilirubin and aminotransferase activity may increase, and the concentration of haptoglobin may decrease. Proteinuria, hematuria and pyuria are possible. After cessation of contact with arsenic, its excretion in the urine gradually decreases over time, but small amounts of arsenic can be excreted even several months later.
Abdominal X-ray taken shortly after ingestion of the poison may reveal radiopaque material in the gastrointestinal tract. The sensitivity and specificity of this method are unknown, so a negative result does not rule out poisoning. The ECG shows flattening of the T wave, ventricular extrasystoles, nonsustained monomorphic ventricular tachycardia, and torsades de pointes. For the diagnosis of axonopathy, including asymptomatic, examine the speed of propagation of excitation along the nerves.
Treatment for arsenic poisoning
Acute arsenic poisoning is life-threatening and requires active treatment, if necessary in the ICU. It is important to keep in mind some features. First, it is necessary to closely monitor the water balance, since swelling of the brain and lungs is possible. Secondly, drugs that prolong the QT interval, such as antiarrhythmic drugs of classes 1a, 1c, should be avoided. For the same reason, it is important to maintain normal serum levels of potassium, magnesium, and calcium. Thirdly, it is necessary to ensure normal plasma glucose levels and glycogen stores.
In vitro, arsenic is poorly bound by activated charcoal, but in vivo, activated charcoal is quite effective. If radiopaque material is found in the gastrointestinal tract, bowel lavage is indicated. From the skin, the poison is easily removed with soap, water and a washcloth.
Indications for therapy with complexing agents and the timing of its onset depend on the condition of the victim and the concentration of the poison in the body. If the condition is severe, and the diagnosis of acute arsenic poisoning is definitely established or sufficiently probable, treatment is started without waiting for the results of the analysis. With subacute and chronic arsenic poisoning, you can wait for the express analysis data and only then start treatment, but only if the victim's condition does not worsen. In the US, dimercaprol and succimer are used. Their doses, method of administration and side effects considered in Chap. A23 and A24. In acute arsenic poisoning, dimercaprol is first prescribed. It is administered parenterally, so gastrointestinal motility does not affect it. However, dimercaprol has a narrow therapeutic range, and therefore, after removal of arsenic from the gastrointestinal tract and stabilization of hemodynamics, they usually switch to succimer. Penicillamine is not used because it binds arsenic poorly and does not counteract its toxic effect.
Hemodialysis
During hemodialysis (regardless of whether dimercaprol is administered), arsenic is removed in small quantities, so patients with normal kidney function are not indicated for hemodialysis. In victims with kidney failure arsenic clearance during hemodialysis is 76-87.5 ml/min. In one study, about 3-5 mg of arsenic was excreted from the body during a 4-hour hemodialysis session, which is insignificant compared to its excretion by normally functioning kidneys.
