How does the 12th duodenum work. Structure, disease and treatment of the duodenum
Duodenum(lat. duodenum) - the initial section of the small intestine, following immediately after the pylorus. continuation duodenum is the jejunum.
Anatomy of the duodenum
The duodenum got its name from the fact that its length is about twelve finger widths. The duodenum does not have a mesentery and is located retroperitoneally.
The figure shows: duodenum (in Fig. English Duodenum), pancreas, as well as bile and pancreatic ducts, through which bile and pancreatic secretion enter the duodenum: the main pancreatic duct (Pancreatic dust), additional (Santorini) pancreatic duct (Accessory pancreatic duct), common bile duct (Common bile-duct), large duodenal (vater) nipple (Orifice of common bile-duct and pancreatic duct).
Functions of the duodenum
The duodenum performs secretory, motor and evacuation functions. Duodenal juice is produced by goblet cells and duodenal glands. Pancreatic juice and bile enter the duodenum, providing further digestion of nutrients that has begun in the stomach.Sphincters of the duodenum and the papilla of Vater
On the inner surface of the descending part of the duodenum, about 7 cm from the pylorus, there is a Vater nipple, in which the common bile duct and, in most cases, the pancreatic duct combined with it, open into the intestine through the sphincter of Oddi. In about 20% of cases, the pancreatic duct opens separately. Above the nipple of Vater, 8–40 mm may be santorini nipple, through which the additional pancreatic duct opens.Endocrine cells of the duodenum
The Lieberkühn glands of the duodenum contain the largest set of endocrine cells among other organs of the gastrointestinal tract: I-cells that produce the hormones cholecystokinin, S-cells - secretin, K-cells - glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, M-cells - motilin, D-cell and - somatostatin, G-cells - gastrin and others.Short chain fatty acids in the duodenum
In human duodenal contents, the main share of short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) is acetic, propionic and butyric. Their number in 1 g of duodenal contents is normal (Loginov V.A.):- acetic acid - 0.739±0.006 mg
- propionic acid - 0.149±0.003 mg
- butyric acid - 0.112±0.002 mg
duodenum in children
The duodenum of a newborn is located at the level of the 1st lumbar vertebra and has a rounded shape. By the age of 12, it descends to the III-IV lumbar vertebra. The length of the duodenum up to 4 years is 7–13 cm (in adults up to 24–30 cm). In young children, it is very mobile, but by the age of 7, adipose tissue appears around it, which fixes the intestine and reduces its mobility (Bokonbaeva S.D. and others).Some diseases and conditions of the duodenum
Some diseases of the duodenum (DUD) and syndromes:Our intestines consist of several main sections, which can be periodically subject to various inflammatory processes. For example, if the upper intestine becomes inflamed, in the region of the 12th duodenum, then this indicates the development of a disease called duodenitis. In this article, we will consider the causes of the inflammatory process, the main symptoms, as well as treatment methods.
Anatomy of the 12th duodenum
The duodenum is a kind of intermediate section located between the human intestine and the stomach itself. Because of this, the intestine can be affected by infection and inflammation. That is, this can happen when food leaves the stomach and passes through the duodenum, or at the moment when the contents of the intestine, due to certain negative factors, rise up to the intestine.
Or the inflammatory process of the duodenum 12 occurs in 99% of clinical cases against the background of other pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, in particular, it can be: exacerbation of gastritis, stomach damage with pancreatitis, disease - cholecystitis or colitis.
The risk group for duodenitis includes mainly the elderly.
Why does the duodenum become inflamed?
The duodenum becomes inflamed only after damage to the mucous membrane of this organ. The most common cause of mucosal damage is increased secretion of hydrochloric acid in the stomach.
Hydrochloric acid in excess is able to melt the mucous membrane of all organs of the gastrointestinal tract, such as the intestines, stomach, and duodenum.
When gastric juice penetrates the intestines, it begins to irritate its walls, therefore, an inflammatory process begins to appear.
Secondary duodenitis
Another reason for the formation of an inflammatory process in the duodenum is secondary duodenitis, which occurs due to the fact that food processed in the stomach does not immediately enter the intestine, but lingers in the duodenum. Why it happens?
Secondary duodenitis occurs due to the fact that the tone of the walls of the intestinal tube decreases, which means that food cannot pass into the intestine on its own, it must be additionally pushed (and this function, due to certain negative factors, does not work).
When food processed in the stomach stays in the duodenum for a long time, it, in turn, begins to become inflamed. Processed masses of food, saturated with gastric juice, have a negative effect on the intestinal mucosa. Food may also not pass due to the fact that there are adhesions in the duodenum, intestines or stomach, as well as deep scars that prevent food from passing further through the intestines. This condition of the intestine is possible after inaccurate surgical intervention on the intestine or other organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
What causes the duodenum to become inflamed?
The duodenum can become inflamed due to poisoning with low-quality expired products; after heavy drinking; due to the abuse of fatty, spicy, sour and salty foods. Also, the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract could be damaged by any mechanical object.
If we talk about the chronic inflammatory process of the duodenum, then factors such as:
- Untreated, that is, this means that in addition to the inflammatory process in the intestine, the liver is affected in a person. Treatment will need to be carried out in two directions;
- Inflammatory process of the gallbladder;
- Damage to the gastric mucosa;
- Bowel disease or it is also defined as Crohn's disease;
- Pathological non-absorption of fats in small intestine;
- Malignant and benign neoplasms in the organs of the gastrointestinal tract;
- in a chronic form;
- The defeat of the stomach and other organs of the gastrointestinal tract by the bacterium Helicobacter Pulori.
Inflammatory process in a chronic form
Inflammation of the duodenum, which occurs in the body in a chronic form, develops due to the fact that a person:
- Does not monitor his diet, eats dry food, on the go and consumes fast food instead of a healthy balanced meal;
- Constant nervous tension, stress, depression, shock;
- Smoking;
- Alcoholism;
- Long-term treatment with antibiotics and, as a result, a negative effect on the work of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Infections in the stomach and others internal organs person.
Symptoms of duodenitis
How to understand that you have started an inflammatory process in the 12th duodenum? As a rule, on initial stages the disease proceeds absolutely imperceptibly for a person, that is, he does not experience any negative impact on himself.
Then, when the disease progresses, a person has a digestive disorder, diarrhea, flatulence may occur, or vice versa -. Naturally, every night the stomach hurts and hunger appears. In the acute stage, a person coughs up blood, diarrhea also contains blood clots. General state- very weak, exhausted.
If duodenitis is not treated for a long period of time, then a person may develop atrophy of the mucous membrane, that is, the tissues completely die off and no longer perform their natural biological functions.
Treatment of inflammation of the 12th duodenum
To cure the inflammatory process of the duodenum, the patient is prescribed a special strict diet, which is combined with drug treatment:
- The pain is stopped by No-Shpa, Papaverine;
- To lower the acidity of the stomach - Almagel and Omeprazole;
- To effectively protect the mucous membranes from negative effects, De-NOl is prescribed;
- When the duodenum is damaged by Helicobacter bacteria - Flemoxin Solutab.
The duodenum performs the necessary functions to maintain the vital activity of the body, in particular, it ensures the absorption of organic elements.
Symptoms of intestinal inflammation always include acute pain, so treatment is primarily aimed at stopping the attack.
In the initial stages, as a rule, the symptoms are not very pronounced, so diagnosis requires laboratory tests.
The structure of the duodenum
The human intestine can be conditionally divided into thick and thin sections. The small intestine includes the duodenum, the main functions of which are to absorb important trace elements and transport food to the large intestine.
The duodenum in humans is the initial part of the intestinal tube, extending directly from the stomach, with which it is separated by a sphincter.
The structure of the duodenum is the smallest part thin department: the length of the intestine is about 0.3 m, while the total length of the small intestine is about 6 m in an adult.
It got its name because of the length, which approximately corresponds to 12 fingers (fingers).
The duodenum is located retroperitoneally, that is, it is located in the retroperitoneal space.
Despite the relatively modest size, from an anatomical point of view, the structure of the intestine has four parts:
- upper (on the border of the last thoracic and first lumbar vertebrae);
- descending (to the right of the first three lumbar vertebrae);
- horizontal (at the level of the third lumbar vertebra);
- ascending (rises to the second lumbar vertebra).
The wall of the duodenum has a typical structure for any part of the small intestine, its inner layer is a mucous membrane with circular folds, villi, crypts.
On the descending part there is a large papilla of the duodenum 12, at the top of which the common bile duct opens, as well as the excretory duct of the pancreas.
It should be noted that the last duct can open with an accessory papilla, which is located just below the large one.
The second layer of the wall of the duodenum is the submucosa, which is a loose connective tissue. It contains large vascular and nerve plexuses.
The third layer is muscle tissue, which regulates muscle tone and promotes contraction of the human intestine.
The fourth layer is the serous membrane, which performs protective functions against external stimuli.
Above the duodenum is the liver with adjacent gallbladder, on the right there is contact with the right kidney in the region of its gate, as well as with the right ureter, pancreas, ascending colon and common bile duct.
The horizontal part is in contact with the transverse colon, as well as with the sections of the small intestine and mesenteric vessels.
On the left are loops of the jejunum, which also belongs to the small intestine.
In spite of small size, it is safe to call the duodenum 12 the most important and most useful part of the small intestine, because without it the digestion process is impossible.
In the walls of the duodenum, the necessary processing of secretion products takes place due to the successful buffer location at the junction of such irreplaceable organs of the digestive system as the stomach, pancreas, gallbladder with bile ducts, liver and right kidney.
In addition, the duodenum produces its own enzymatic formations, due to which there is a better assimilation of all the elements necessary for life.
Such enzymatic formations of the intestine include histamine, serotonin, cholecystokinin, and some others. Without them, all secretion products, for example, of the pancreas, are practically useless.
It is impossible not to note the important function of absorption of organic elements due to excellent vascularization, that is, the work of blood vessels in the pancreatic wall, as well as the function of moving food masses to other parts of the intestine to continue the digestion process, which is possible due to the developed muscle layer.
Inflammation of the duodenum
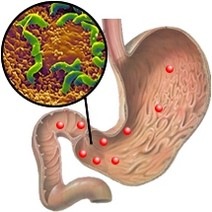
The sensitive walls of the duodenum, as well as a practically neutral acid-base environment, create the most favorable conditions for the development of pathogens, this often leads to the fact that the duodenum becomes inflamed, and the work of its most important functions is disrupted.
Inflammation of the duodenum is also called duodenitis, which can occur in both acute and chronic forms.
According to statistics, males of young and mature age, up to 40 years, are most susceptible to duodenitis.
The causes of duodenitis are infectious agents (Helicobacter pylori is the main one), improper diet and daily routine, in which night sleep hygiene is not observed, exhaustion of the nervous system caused by various stress reactions, bad habits, in particular alcohol abuse and regular smoking, as well as ill-chosen diets.
Such diets include those in which there is a long break between meals of a person.
We should not forget about the genetic predisposition to duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum 12).
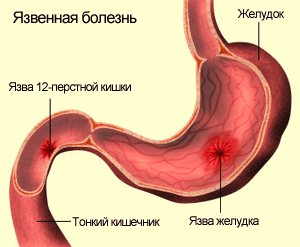
The symptoms of duodenitis are identical with the symptoms peptic ulcer. For this reason, an accurate diagnosis in a person is possible only after endoscopic and radiological examinations.
Symptoms of duodenitis are always acute. The patient feels a sharp pain in the pyloroduodenal region, which is also called the epigastric region.
Pain, which is typical for duodenitis and ulcers, increases in the case of a long break between meals (the so-called hungry pain).
Symptoms of inflammation of the duodenum or duodenitis, in particular acute pain, occur due to the fact that gastric juice continues to be secreted, despite the absence of food.
Its small amount overcomes the protective sphincters and enters directly into the duodenum, the mucous membrane of which begins to break down under the influence of an acidic environment.
It should be noted that the use of some medicines has a similar effect as side effects(non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, hormones, etc.).
The most important symptoms of duodenitis include not only acute pain, but also vomiting, after which there is temporary relief, heartburn due to the ingress of gastric juice into the esophagus, and belching, in which a sour taste clearly appears, indicating a violation of the acid-base balance and the prevalence of an acidic environment. in the stomach and intestines.
The patient is characterized by the fact that with the onset of the disease, he often begins to eat food, because with an empty stomach, the pain intensifies.
There is also a sleep disturbance, the patient is forced to wake up, because he feels acute pain caused by the predominance of the parasympathetic autonomic nervous system over the sympathetic nervous system in this period of time nervous system, in connection with which the production of hydrochloric acid in the stomach increases.
Treatment of duodenitis
The intestine is one of the most important organs in the human body. Violation of any of its functions makes it impossible to digest organic substances digested in the stomach, as well as the normal transportation of various toxins and waste products from the body.
Since the symptoms of inflammation of the duodenum (duodenitis) are always pronounced, treatment should be aimed at eliminating the sharp pain during an attack.
When the attack is stopped, the course of treatment will consist of several stages. First of all, it is imperative to eliminate all bad habits.
Even a small dose of alcohol or those substances that are inhaled when smoking increases the production of gastric juice.
It must be remembered that duodenitis is a serious incurable disease, however, symptoms can be stopped for a long time if the patient follows all the doctor's instructions.
Complications of duodenitis are very serious possible consequences, which include a duodenal ulcer, internal bleeding, up to the development of malignant oncological diseases.
It is important not to forget that only a correct, healthy lifestyle can keep the disease within limits. This lifestyle includes stress reduction, normalization of night sleep, moderate physical exercise, the use of drugs only as directed by the attending physician, as well as a healthy balanced diet.
The pain will practically not bother the patient if he refuses fatty, spicy, salty and too sweet foods, and the basis of the diet will be lean meat and fish, various cereals, vegetables and fruits.
If an attack of duodenitis occurs, and the patient feels acute pain, then it is possible to use drugs that relieve muscle spasm (for example, Spasmalgon), as well as those that lower the acidity in gastric juice (Gastala).
Proton pump inhibitors (Omeprazole, Omez, Ultop, etc.) block the increased production of hydrochloric acid in the stomach, which reduces unpleasant symptoms.
Often, patients are prescribed antibiotics, such as Clarithromycin, Metronidazole, macrolides, and others.
Patients are most often characterized by such a violation of the diet, when during periods of exacerbation of inflammation of the duodenum 12 (duodenitis), they eat food for the last time just before bedtime, which is a serious burden for the body and is contrary to the rules of a healthy diet.
To eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum), you can use folk remedies.
The methods of dealing with heartburn, a constant companion of duodenitis, include the use of a solution of ordinary baking soda, which, having an alkaline environment, helps to reduce acidity.
Duodenitis is an inflammation of the duodenum, the first part of the small intestine, which is very common, especially in children. This disease occurs either in a chronic or in an acute form.
Its causative factors range from an incorrect diet to hormonal imbalance in the body of women and men.
The above organ performs a number of special functions in the human body. The duodenum is one of the most important organs of the digestive system.
It refers to the part of the small intestine responsible for metabolism in the body, regulation of the gastrointestinal tract, production of certain hormones, and pancreatic dietary juices.
When there is inflammation of the duodenum, symptoms and treatment this disease will be interconnected, because the course of therapy can be prescribed by a doctor, starting, first of all, from the existing signs and manifestations of duodenitis.
Treatment of the duodenum should not be carried out independently. After the appearance of the first signs of a disease such as duodenitis of the duodenum, it is urgent to consult a professional doctor.
The duodenum is an important component of the digestive system as it connects the stomach and small intestine. If this organ becomes irritated and enlarged, the whole process of digestion may be disturbed.
Treatment in the event of an inflammatory process must begin immediately.
Irritation caused by certain agents, such as acid, drugs, and injuries, provokes the occurrence of a large number of cases of inflammation of the duodenum.
Infections also pose a risk to this organ of the digestive tract. Progressive cases with other symptoms may be indicative of a more serious and chronic condition, such as Crohn's disease.
Acid is one of the strongest substances in nature. When this substance is in the stomach, it acts especially intensively, because it participates in the process of digestion and helps to digest the incoming food.
If acid from the stomach seeps into adjacent organs with a more sensitive wall, the acid can have an adverse effect.
It often occurs in the esophagus, as well as in the duodenum, which leads to the development of an inflammatory process.
A person's own actions can also lead to inflammation of the duodenum. In particular, some medicines can damage the duodenum.
Oddly enough, this effect is often caused by drugs designed specifically to combat inflammation.
Some evidence suggests that stress can also worsen organ wall conditions in the presence of inflammation.
Traumatic injury can have a similar devastating effect.
Infection, especially bacterial infection, is a causative factor in many cases of inflammatory processes, inflammation of the duodenal bulb is also no exception.
The bulb is localized at the exit from the department that controls the flow of food from the stomach into the intestinal cavity at the beginning of the duodenum.
In particular, a bacterium called Helicobacter pylori has a very negative effect on the digestive system and causes duodenitis.
The duodenum is a favorite site for these bacteria because the environment allows the bacteria to secrete a protective enzyme.
Structural abnormalities can sometimes cause duodenitis. The valve that separates the intestines from the stomach is generally sensitive to various defects and abnormalities.
When any disturbances occur, spasms can occur, causing acid rejection and leakage.
In some cases, duodenitis may be part of a more general digestive disorder.
For example, one of the common ailments characterized by inflammation of the intestines called Crohn's disease affects the wall and tissues of various parts of the digestive tract, from the colon to the duodenum.
Other symptoms and signs accompanying gastritis or duodenitis, may include:
- pain syndrome in the stomach;
- lack of appetite;
- diarrhea
- weight loss;
- fever
- bloody stool.
There is an assumption that a combination of genetic predisposition and erroneous reactions immune system also plays a role in the development of this condition.
Infectious agents can even cause immune cells to mistakenly attack normal cells in the digestive tract.
Chronic inflammatory process in the duodenum can cause symptoms in the form of ulcers, which are affected areas in the digestive tract.
Although the acute type of inflammation may not have any symptoms, ulcers can cause internal bleeding and pain in the stomach.
In rare cases, inflammation of the duodenal bulb and subsequent ulcers may indicate a tumor.
When gastritis or duodenitis of the duodenum develops, the symptoms and signs of these diseases may appear gradually, causing discomfort. They include:
- Nausea. It always seems to the patient that he will soon begin to vomit, even in situations where food has not yet entered the stomach. Against the background of persistent nausea, the patient loses his appetite. For some products, the patient may have a particular aversion. In certain situations, the very thought of food can cause a person to gag.
- Vomit. Often gastritis and duodenitis cause problems in the pancreas. Because of this, the body cannot produce the necessary enzymes to digest food.
- Vomiting leading to dehydration. Given the possible appearance of such a symptom, it is necessary to restore the disturbed water balance.
- Convulsions of the stomach. Most often, acute pain can occur in the abdomen after sleep, on an empty stomach and after exercise. exercise. The pain is usually localized in the ribs. Due to cramps in the stomach, breathing may be disturbed, there may be a lack of oxygen.
- Diarrhea and constipation. These conditions may be accompanied poor digestion, a drop in the level of immunity, fatigue, pallor of the face, a decrease in the level of hemoglobin and blood sugar. The skin may acquire a yellowish tint, which indicates problems with the gallbladder and liver.
- Belching and feeling of heartburn. In addition, there may be an unpleasant, bitter taste in the mouth.
All symptoms acute form inflammation of the duodenum due to proper therapy usually stops 7-10 days after the onset.
If there is no treatment for duodenitis, and the diet is grossly violated during the recovery period, it often develops chronic form disease, which is characterized by constant pain in the epigastric region and the region of the stomach, nausea, alternating diarrhea and constipation, bloating, lack of appetite, weight loss.
In case of prolonged inflammation in the wall of the duodenum and impaired absorption processes that ensure delivery to organs and tissues nutrients, other systems in the body of a sick person, in particular, the nervous system, may suffer.
Under these conditions, most likely, the patient will be forced to perform additional treatment of other organs.
Treatment
Doctors clarify the patient's symptoms and perform a physical examination during inflammation of the above organ to check for signs such as stomach tenderness, heartburn, excessive irritation or bloating, abdominal discomfort, excessive belching, loss of appetite, nausea, diarrhea and vomiting.
They are also doing research on a likely family history of duodenitis.
Rapid weight loss and swollen abdominal organs are some of the obvious signs that confirm the presence of duodenitis.
To further establish the diagnosis, doctors may recommend tissue biopsy and esophagogastroduodenoscopy (an endoscopic procedure).
During endoscopy, symptoms of the so-called "semolina" can be observed, which are manifested by a dotted rash on the intestine (lymphangiectasia).
Blood, stool and urine tests may also be ordered to determine the correct and accurate diagnosis of the disease.
After examining the results of the survey, doctors develop an individual regimen for taking medications. The course and duration vary depending on the characteristics of the organism of each patient.
Patients with inflammation of the duodenal bulb should also radically change the existing diet. To this end, with the appearance of duodenitis, patients should follow a diet.
It is advisable to eat fractionally, portion sizes should be small.
If the patient is already undergoing treatment with highly effective modern medicines, then grinding food is necessary only in the presence of a severe form of duodenitis.
Preferred during duodenitis are boiled dishes, the diet must include them.
They should be warm, as cold can aggravate spasm and movement disorders of the stomach (during illness clinical manifestations the patient may recur and the pain may worsen).
It is advisable during the treatment of duodenitis to exclude from the menu all products that can provoke irritation or damage the duodenal wall, stimulate the production of digestive juice and change the motility of this organ.
Such products include any kind of sour berries, citrus juices, spices, ketchups, garlic, radishes, onions, radishes, fatty meats, red fish, smoked products, oily fish or meat broths, pickles, lard, mushrooms, cream, fat milk, marinades.
During inflammation in the duodenum, the patient is recommended rice, buckwheat and semolina, oatmeal, mucous and milk soups, soft-boiled eggs, non-acidic jelly, omelettes, vegetable casseroles and soufflés, fresh and low-fat cottage cheese, vegetarian soups, lean meat in the form of steam cutlets, dumplings, meatballs, puddings, dry biscuits, dried white bread, sweet ripe fruits without coarse fiber.
The diet usually includes all of the foods listed.
The use of buckwheat, semolina, rice porridge in the morning is encouraged. To prepare semolina porridge, you should not use a large amount of fat milk, the porridge should be light.
Cereals must be boiled well, do not add vegetable or butter to them. It is advisable to cook cereals during the diet for breakfast, so they will be better digested.
Increased attention should be paid to vegetable fats, their volume is about one third of all consumed fats. The diet allows the use of various vegetable oils (soy, sunflower, corn).
After achieving remission of duodenitis, most of the dietary restrictions can be removed. At the same time, the diet is completed, nutrition can correspond normal diet healthy person.
The patient will need to treat only the residual effects of the disease.
Proper treatment and diet during duodenitis help to minimize the risk of complications.
However, if you neglect the recommendations of doctors and nutritionists, untimely treatment, gastritis and duodenitis can create serious complications, such as inflammation of the duodenal bulb, internal bleeding and perforation of the peptic ulcer.
Depending on the causes of inflammation of the duodenum, the symptoms and treatment differ significantly.
The most common cause of the disease is gastrointestinal disorders. Main reasons:
- dyspepsia, which is characterized by discomfort in the stomach after eating;
- cholecystitis;
- ulcer of the stomach or intestines;
- acute hepatitis, which is a viral infection.
- caused by chronic infections;
- gastritis;
- poor blood flow to the intestines, called coronary artery disease
- Crohn's disease;
- Will and Zollinger-Ellison syndromes;
- giardiasis.
- indigestion;
- pain in the center of the abdominal cavity (not everyone knows, therefore they are guided by pain in the center);
- anemia;
- vomiting blood;
- belching
- bloating and flatulence, which may also indicate other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (for example,);
- tarry stool;
- weakness and dizziness;
- feeling full after eating;
- decreased appetite.
The cause of inflammation of the stomach and duodenum can be a bacterial infection of Helicobacter pylori. It can be contained in the stomach for many years before the onset of symptoms of the disease. This microorganism stimulates an increased secretion of acid in the gastric juice, which irritates the duodenum. If left untreated, it can lead to peptic ulcer disease.
Duodenitis can also be caused by severe stress for the body, which is caused by surgery or infection.
Medications designed to reduce inflammation are one of the causes of duodenitis.

The disease can be manifested by a number of unpleasant symptoms:

Depending on the type of disease and its stage, the symptoms may disturb regularly or make themselves felt periodically.

- Endoscopy is considered the most effective. Using a probe with a camera and a light at the end, a study is carried out.
- If problems are identified, a biopsy is taken for testing in the laboratory.
- To exclude the influence of Helicobacter pylori, you need to take an analysis of its content.
The standard duration of treatment for inflammation of the duodenum is about one and a half months. It includes medical and conservative treatment.
The complex of treatment includes drugs of various directions:
- antibiotics;
- drugs that reduce acidity (Almagel, Omeprazole);
- drugs that improve the digestive process (Festal and Mezim);
- preparations for enveloping the mucosa (De-Nol);
- to improve motor skills Domperidone.

Surgical treatment is prescribed only when mechanical obstructions and adhesions that prevent the normal passage of food are identified.
In the treasury folk recipes There are many treatment options for intestinal diseases, including duodenitis:
- Brew flax seeds with boiling water, insist and drink the resulting broth in small sips.
- A mixture of medicinal herbs (melissa, chamomile, lavender, shepherd's purse, licorice roots, cinquefoil and marshmallow) is boiled in a water bath and a glass is drunk before meals (about 40 minutes).
- A mixture of sea buckthorn and vegetable oil taken daily for symptoms of inflammation of the duodenum.
- John's wort infusion is recommended to be taken daily until recovery.
- Good results are obtained from the juice from the stems and leaves of the plantain, combined with honey.
- Soaked rhubarb leaves can be effectively applied to the stomach area when the initial symptoms of the disease appear.
Disease prevention
Sensitive intestinal mucosa may react to irritants even after treatment. Therefore, in order to prevent relapses and not start the disease, you should follow simple rules:
- do not eat too cold or hot food;
- divide the meal into several meals in small quantities;
- exclude alcoholic beverages;
- quit smoking;
- do physical education.
Regardless of the causes of inflammation of the duodenum, doctors do not prescribe a special diet. But it is better to remove everything from the diet, a hundred can irritate the mucous membrane: smoked meats, fatty foods.
The disease can in some cases lead to various complications:
- periduodenitis, which is an inflammation of the serous membrane located around the intestine;
- bleeding from damaged areas;
- peptic ulcer;
- stenosis of the pylorus of the stomach;
- duodenal cancer;
- hormonal deficiency;
- intestinal obstruction;
- peritonitis in rare cases.
Knowing the main signs of the disease, a person will be able to seek help in a timely manner and prevent the development of the disease.
