How is a colonoscopy performed? Useful video about capsule endoscopy in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal diseases. What is a bowel colonoscopy
The intestinal canal is responsible for the digestion of food and the condition immune system. In order to timely detect malfunctions in the work of the body, it is necessary to undergo an annual examination. One such technique is colonoscopy.
What is a colonoscopy of the intestine? This concept means a diagnostic procedure, during which the intestinal walls and mucous membrane are examined from the inside. Thanks to such manipulations, various pathological processes can be detected.
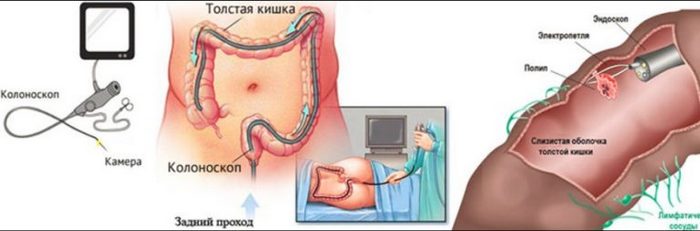
The technique is carried out using a special device called a colonoscope. This is a tube, the length of which is one and a half meters. At the end of the device is an eyepiece, LEDs and a camera. When the internal examination starts, an image is displayed on the computer screen. Also, with the help of a colonoscope, you can take the material for histological examination.
Features of colonoscopy of the intestine
Colonoscopy of the intestine is a modern examination technique. Thanks to her, you can:
- assess the condition of the mucous membrane, the motility of the digestive organ and identify the presence of inflammatory processes;
- clarify the diameter of the intestinal canal and, if necessary, expand it due to scar tissue;
- recognize even the slightest changes in the intestinal walls of various pathological formations in the form of cracks, polyps, hemorrhoids, sores, diverticulum, tumors and foreign bodies;
- remove the seen foreign bodies and take a small piece of the mucosa for examination;
- remove small benign formations. This process will avoid surgical intervention;
- to recognize the causes of intestinal bleeding and eliminate using the method of thermocoagulation.
You can perform the procedure in any public or private clinic. It is recommended for people over 40-45 years of age, as well as for those who complain of abdominal pain, nausea, constipation or diarrhea.
Indications for the study of the intestine
Who is eligible for colonoscopy? Examination of the digestive tract using this technique is prescribed:
- with complaints of pain in the abdomen;
- in the presence of discharge from the rectum in the form of mucus or pus;
- with bleeding from the intestinal tract;
- in violation of intestinal motility;
- weight loss, anemia, subfebrile temperature, the presence of oncological diseases;
- when a foreign body enters the intestinal canal;
- in the detection of benign lesions.
Also, a colonoscopy of the large intestine is prescribed for suspected intestinal obstruction, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, and malignant tumors. This diagnostic method helps to detect various diseases of the mucous membrane and take material for histology.
Restrictions on bowel examination
Colonoscopy of the rectum is a great way to identify various problems that occur in the digestive tract. But there are a number of restrictions in the form:
- infectious processes of an acute nature, which are characterized by an increase in temperature, poisoning of the body and weakness;
- pathological processes in the cardiovascular system. These include heart failure, myocardial infarction, the presence of artificial valves;
- a sharp drop in pressure;
- lung failure;
- peritonitis, perforation of the intestinal walls;
- diverticulitis;
- acute inflammatory processes in the presence of ulcerative colitis;
- severe intestinal bleeding;
- hernia of the umbilical and inguinal type;
- pregnancy;
- pathological processes that lead to impaired blood clotting.
The above conditions increase the risk of developing side effects. Therefore, this technique is replaced by other types of research. It is worth noting that colonoscopy of the rectum has nothing to do with colposcopy. The second type of study involves taking material from the cervix in women.

Preparing for a Colonoscopy
How is the procedure for colonoscopy of the intestine and what is needed in order to prepare for the study? In fact, it occupies one of the important places. The better the patient prepares for manipulation, the better and more truthful the result will be.
Preparatory measures are based on the observance of a special diet and high-quality cleansing of the large intestine.
Compliance with a specialized diet
A proper diet will free the intestinal walls from toxins and remove fecal stones. Preparatory measures should begin two to three days before the procedure.
From the menu, products should be completely excluded in the form of:
- fruit and vegetable crops;
- greens;
- berries, legumes and nuts;
- fatty meat, fish and sausages;
- porridge You can not eat oatmeal, barley and millet porridge;
- pasta;
- carbonated drinks;
- black bread;
- whole milk and coffee.
All of the above dishes are poorly absorbed by the body, which leads to increased gas formation.
The patient is allowed to eat before the procedure:
- wheat bread;
- boiled lean meat in the form of beef, chicken;
- fish in the form of pink salmon;
- vegetable-based broths;
- dry cookies in the form of biscuits;
- fermented milk products in the form of kefir, curdled milk, yogurt.
The last meal should be the day before at twelve o'clock in the afternoon. During the next day, you can drink only water or tea.
Bowel cleansing
Colonoscopy of the rectum and large intestine implies mediocre cleaning. It is done with laxatives or enemas.
If cleansing is done with an enema, then two enemas should be given the night before. To do this, you need a mug of Esmarch and two liters of water.
If preference is given to laxatives, then they are taken a little during the day. Most often, Fortrans is prescribed, since it does not lead to a violation of the water-salt balance. About three to four liters of solution should be consumed per day, depending on the weight of the patient.
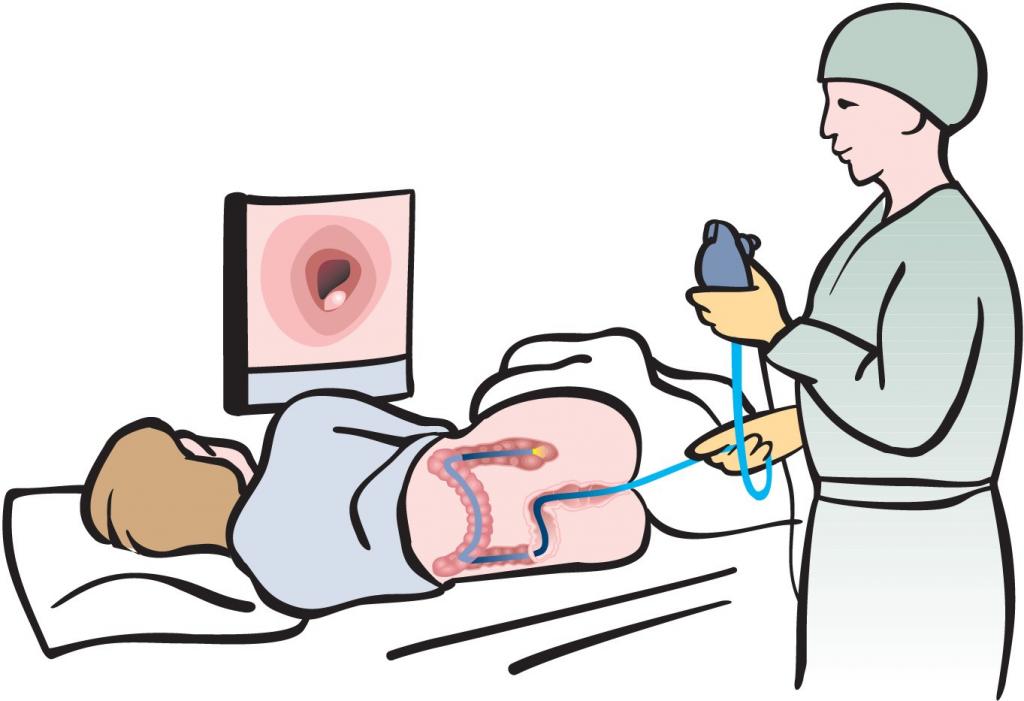
How is a colonoscopy performed? This type of manipulation scares patients, because during the procedure a special tube is inserted into the intestinal canal.
The execution scheme is as follows.
- The patient lies on the couch, on the left side. The legs are bent at the knees and pressed to the stomach.
- The doctor treats the anus with antiseptic and gently inserts the tube.
- If the patient has hypersensitivity, then anesthetic preparations in the form of gels are used before the manipulations.
- After that, the doctor slowly and carefully advances the device further. Meanwhile, the intestinal walls are examined, and the image is displayed on the monitor.
- To straighten the folds in the intestines, air is supplied from the tube.
The duration of the procedure is about 15-20 minutes. If a colonoscopy is performed as a therapeutic or diagnostic manipulation, then the duration can increase to 30-40 minutes.
Possible Complications of Colonoscopy
During the study, air is pumped into the rectum. At the end of the procedure, it is sucked back. But at this time, the patient may feel an unpleasant bursting feeling. To avoid this phenomenon, doctors advise taking activated charcoal. To do this, it must first be dissolved in water.
Colonoscopy should be done in a specialized institution where only experienced doctors work. It is best if it is a state clinic. If all the recommendations are followed, then everything will pass without complications, and the technique will be harmless.
In rare cases, a number of complications occur during colonoscopy in the form of:
- perforation of the intestinal walls. The mucous membrane is damaged, as a result of which a purulent process may begin. Then the patient urgently undergoes surgery to restore damaged tissue;
- bleeding from the rectum. It can also manifest itself due to damage to the mucous membrane or blood vessels. Eliminated by cauterization or injection of adrenaline;
- pain in the abdomen. Most often manifested against the background of the removal of benign formations. You can eliminate the unpleasant feeling with the help of antispasmodics or analgesics.
With the development of adverse complications, the patient should urgently consult a doctor. This is especially important if the symptoms are accompanied by nausea, vomiting, dizziness and weakness. Other unpleasant consequences may also occur in the form of loss of consciousness, diarrhea with blood, vomiting of feces. Then an urgent call for an ambulance is required.
Alternative methods of examination of the intestine
If for some reason the patient has contraindications, then another method of examination can be chosen. These include:
- sigmoidoscopy. A small device called a sigmoidoscope is used, which is inserted into the rectum to a depth of 30 centimeters;
- irrigoscopy. This method of research involves the use of x-rays with a contrast agent;
- channel. This is a modern method that does not require the introduction of tubes into the digestive tract. A scanner is used for research, so manipulations are considered gentle and harmless.
Which method is better to choose, the doctor will tell based on the indications and the presence of restrictions.
Intestinal colonoscopy is widely used in gastroenterology. This diagnostic method allows the doctor to see the mucous membrane with his own eyes. Such a bowel test is informative in relation to ulcerative, inflammatory diseases, in the detection of neoplasms of the large intestine. When using colonoscopy, the doctor can biopsy the desired fragment without surgery. What is a colonoscopy? For some patients, this is not only an examination of the intestines, but also the only way to save their life.
Who needs a colonoscopy
Like any medical examination, colonoscopy is used in recommended cases. Even patients with the same diagnosis may need it to varying degrees. Indications for colonoscopy can be divided into 2 groups: absolute (mandatory) and relative. Mandatory indications include:
- Bleeding of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Recurrent intestinal obstruction.
- Confirmation of non-specific ulcerative colitis.
- Crohn's disease.
- Recurrent episodes of abdominal pain of unknown origin.
- Polyps of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Exclusion of neoplasms of the large intestine (cancer search).
The study is carried out with persistent constipation. This case refers to relative readings. In addition to the indications described above, the World Health Organization recommends such a diagnostic procedure every 5 years after reaching the age of 40, and in the risk group for the development of familial polyposis - from 12-14 years.
Who should not have a colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is a highly informative method. Visualization of the intestine allows to clarify the diagnosis and therapeutic manipulations. The method emotionally and physically puts a strain on the patient's body. Therefore, contraindications are quite extensive and relate not only to restrictions on the part of the gastrointestinal tract:
- Acute infectious diseases (intestinal, respiratory, etc.).
- Suspicion of peritonitis.
- Significantly expressed organ failure (pulmonary, cardiac).
- Ischemic colitis of significant severity.
- General serious condition of the patient.
- Severe ischemic colitis in the acute stage.
- The presence of significant disorders in the blood coagulation system.
- Extensive ulcerative colitis in the acute stage.
Colonoscopy is a fairly safe method with well-known nuances and complications. There are a number of private questions regarding contraindications. One of them is whether it is possible to do a colonoscopy during menstruation. The standard response of the endoscopist will be negative. It is better to postpone the study to another time. Exceptions are life-threatening situations. Emergency diagnostics according to vital indications must be carried out during menstrual bleeding.
Preparing for a colonoscopy
The effectiveness of instrumental research will directly depend on previous preparation. If it is performed in full, then the mucosa can be comprehensively examined, revealing even minimal pathological formations. The presence of intestinal contents reduces the possibility of advancement and examination, and therefore casts doubt on the reliability of the results obtained. 
The patient should be fully aware of how to prepare for a colonoscopy. Of the huge variety of methods, it is worth preferring those recommended by the Russian Endoscopic Society. Generally recognized 2 options for training.
With any of them, patients with a normal stool for 2, and with a delay in bowel movement for 3 days, you must follow a diet. It implies the complete exclusion of plant fiber. Permissible products are broths, boiled fish, eggs, dairy products, tea, sugar, clarified juices, honey. You can drink water. On the eve of the manipulation, the patient does not eat at lunch and in the evening. On the day of the study, he excludes breakfast. Acceptance of sweet tea or clear broth is allowed. The exception is diabetic patients who are allowed a fiber-free breakfast (egg, kefir).
Bowel cleansing before a colonoscopy may differ in the way it is done:
- With a laxative. On the day before the study, from 15:00 3 (with constipation 4) liters of Fortrans are dissolved in 1 liter of water. The resulting solution must be taken within 180 - 240 minutes.
- With enemas. At 14:00 of the day preceding the study, the patient takes a laxative, and at 18:00 and 20:00 performs cleansing enemas with water at a temperature of about 22 - 24 degrees Celsius, 1.5 liters each. In the morning before colonoscopy, a cleansing enema is performed three times: at 6:30, 7:30 and at 8:30. The composition and volume are similar to the previous ones. If the last time the water does not contain feces, then the procedure is completed. If fragments of feces are found, continue until clear water appears.
Before performing a colonoscopy, you need to understand how it is done. The most common question of patients is whether it hurts to do the study. There can be no unequivocal answer to this question, since the level of pain sensitivity in different people varies significantly. Anesthesia can be done in several ways. Most often, 3 options are used:
- Local anesthesia. A method in which an anesthetic is administered by the colonoscopy equipment itself. During the advancement of the colonoscope and the expansion of the intestine with the help of air, the patient feels what is happening. It is from his comments that the doctor receives additional information about the possibility of further action. The anesthetic solution is injected locally.
- General anesthesia. With this method, the patient does not feel anything during the manipulation. He is under anesthesia.
- Sedation. Medical support that allows you to conduct a study without anesthesia. With this method, the patient takes medication in advance. He is conscious, can follow the recommendations of the endoscopist. Pain sensitivity is dulled.
The choice of the optimal method of anesthesia is the task of the doctor. To do this, he takes into account the place of the alleged localization of the process, and the patient's condition, and the presence of concomitant pathology. After analyzing the data, the safest and most comfortable option is preferred.
What to choose: CT of the intestine or colonoscopy?
The large intestine can be examined in several ways: barium enema, sigmoidoscopy, computed tomography (CT) of the intestine, or colonoscopy.
Each method is preferred for certain clinical situations. It is actively used for the diagnosis of neoplasms of the intestine. CT scan(CT). When it is carried out, many of the obtained images are combined in a computer into a detailed 3D model. Bowel CT or colonoscopy - which is better? Each diagnostic method has its own advantages and disadvantages.
CT scan
CT is characterized by:
- high precision;
- atraumatic;
- the possibility of use in cases where colonoscopy is contraindicated (with an eroded intestinal surface, etc.);
- less time spent;
- the possibility of reviewing the results at any time in full;
- allows you to see the condition of the tissues surrounding the intestines;
- less dependence on a specialist;
- easier tolerated by elderly debilitated patients;
- does not require additional load in the form of anesthesia.

The disadvantages of the method is the inability to use in obese patients, in pregnant women and in children under 14 years of age. The procedure is expensive and not always accessible to the population (it can be located far away and in 1 instance for a large number of patients).
The advantages of colonoscopy are the ability to assess the condition of the mucous membrane (color), take material for research, carry out therapeutic measures (polypectomy), and the possibility of a detailed examination of small elements. The disadvantages of the method are invasiveness, trauma, soreness, dependence on anatomical features (strictures, sharpness of the intestinal rotation angles).
Based on the characteristics of these methods, they will be recommended by the doctor in suitable situations. For example, to diagnose the outcome of the treatment of Crohn's disease in an elderly patient, the doctor will prefer CT, and to diagnose polyposis - colonoscopy. Each research method has its niche of application.
Colonoscopy - what is it?
Colonoscopy is a modern instrumental study that is used to diagnose diseases of the colon and rectum. This diagnostic method allows you to directly see the state of the intestinal mucosa and morphological changes in its walls.
If necessary, a biopsy can be performed - a piece of tissue is cut off under local anesthesia for its subsequent histological examination. In addition to the study, it is possible to simultaneously perform medical procedures. The cost of this examination is relatively low, so it is widely used in private and public clinics. 
Indications for the procedure
In order to confirm the diagnosis, determine the degree and localization of morphological changes in the intestinal wall, this examination is performed for such diseases:
- bleeding from the walls of the colon or rectum - in this case, colonoscopy is also a therapeutic measure that allows for thermocoagulation - stopping bleeding with the help of local exposure to high temperatures;
- benign tumors - colonoscopy for intestinal polyps also allows their removal;
- malignant tumors of the walls of the colon - to clarify the diagnosis, a biopsy of the tissues of the colon is performed;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease - autoimmune diseases accompanied by the formation of ulcers and granulomatous inflammation of the intestinal mucosa;
- intestinal obstruction;
- chronic constipation;
- weight loss, anemia, prolonged low-grade fever of unknown etiology.
Contraindications for the study
There are body conditions in which colonoscopy is undesirable, as it can lead to the development of complications. These include:
- shock is a condition in which systemic systolic arterial pressure below 70 mm Hg. Art.;
- myocardial infarction - necrosis (necrosis) of a section of the heart muscle;
- acute inflammation of the peritoneum (peritonitis);
- intestinal perforation - a breakthrough of a section of the intestinal wall with the formation of a through hole and the release of contents into the peritoneal cavity;
- acute diseases accompanied by fever and intoxication;
- acute colitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the colon) - colonoscopy in this case is carried out only after the acute inflammation subsides;
- massive bleeding into the intestinal cavity - can lead to the impossibility of a normal examination of the intestinal walls;
- the patient has artificial heart valves - due to the risk of infection during colonoscopy, a course of antibiotic therapy is preliminarily applied;
- inguinal or umbilical hernia - a sac-like protrusion in the abdominal wall, where a loop of the intestine can fall out;
- diverticulitis - a disease in which inflamed protrusions - diverticula form in the intestinal wall;
- refusal of the patient to undergo a colonoscopy;
- improper preparation, which reduces the information content and quality of the examination.
How to examine the intestines without a colonoscopy?
If there are contraindications or the patient refuses to perform the procedure, it is possible to check the intestines without colonoscopy using other instrumental methods, the information content of which may be lower:
- virtual colonoscopy;
- sigmoidoscopy - is carried out only with the exact establishment of the localization of the process in the rectum;
- radiography with a barium mixture - an examination with the introduction of a contrast agent into the cavity of the colon, followed by an X-ray of the intestine, allows you to visualize defects in the intestinal wall and the presence of formations that protrude into the cavity;
- ultrasound examination of the large intestine - requires special and modern ultrasound equipment, which most clinics do not have.
The essence of the method
The principle of intestinal colonoscopy is the introduction of a fiber optic tube with a camera and lighting into the clean large intestine. On the monitor screen, the endoscopist has the opportunity to see the walls of the intestine and assess the presence of them. pathological changes. Therefore, this study is also called fibrocolonoscopy. Also, for medical procedures and performing a biopsy, instruments and manipulators are introduced, which carry out micro-operations on the walls of the colon. The entire procedure can be recorded for documentation in video format (video colonoscopy).
Sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy, which is better?
There are also other similar methods for examining the intestines:
- Virtual colonoscopy - a special inert gas is injected into the intestine to stretch its walls, then an x-ray examination is performed - computed tomography;
- Sigmoidoscopy - the principle is the same, but not all colon, but only the rectum, this must be remembered.
Definitely, sigmoidoscopy is a less painful research method, but it does not allow you to see changes in the colon, namely in its sections such as the ascending, transverse and descending colon, and the sigmoid colon
Colonoscopy technique
Checking the intestines by colonoscopy includes 2 stages:
- preparation for colonoscopy;
- direct examination.
Preparing for a colonoscopy
Preparation must begin 3 days before the study. A diet before a colonoscopy is necessary to prevent the accumulation of toxins on the walls of the intestine. It excludes the intake of fried, fatty foods, legumes, coarse vegetable fiber. In the evening and in the morning, the intestines are cleansed with the help of special laxatives - Fortran, Lavacol. These drugs are available in powder form, 1 sachet is diluted in 1 liter of water, for an adult, 3-4 sachets are needed. The price of drugs is low, therefore, in comparison with the usual cleansing enema, it is preferable to use them.
Does a colonoscopy hurt?
In general, the procedure may be accompanied by unpleasant sensations of stretching, pressure, cramping and bloating in the abdomen. Sedation during colonoscopy helps to avoid these sensations to some extent. It consists in the introduction before the start of the examination of sedative (sedative) drugs - diphenhydramine, gidazepam, barbiturates.
In case of low pain threshold the patient, the lack of effect from sedative drugs colonoscopy is performed under anesthesia (drug sleep), as well as conventional surgery. To perform micro-operations on the walls of the intestine and take a biopsy for pain relief, the mucous membrane through the endoscope is treated with local anesthetics - novocaine, lidocaine. Important absence allergic reactions on these drugs to avoid complications.
How is the procedure carried out?
Intestinal examination is performed in the supine position on the left side. The endoscopist doctor gently inserts the tube into the rectum and advances it through the entire large intestine to the caecum. At the same time, an image of the intestinal walls appears on the monitor screen. Then the probe is slowly withdrawn back. The procedure itself takes about an hour on average.
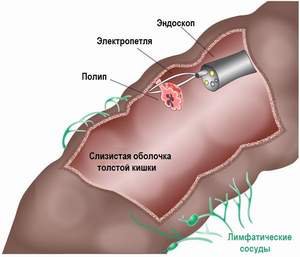
To take a biopsy, small forceps are inserted through a special channel of the endoscope, with which a piece of tissue is cut off and removed. Preliminary through this channel are introduced local anesthetics. Removal of polyps is carried out using a loop, which captures and cuts off the formation at its base. Since the procedure takes place in a medical institution, it is recommended that the patient stay for about an hour after the colonoscopy under the supervision of health workers in order to avoid the development of unforeseen complications.
It is worth remembering that this is one of the most informative methods for examining the intestines, without which it is impossible to establish the causes of a number of diseases.
People are often embarrassed to admit bowel problems and put off going to the doctor. However, if a person has pain in the lower abdomen, constipation, bleeding from the anus and other unpleasant symptoms, he should contact a specialist as soon as possible, who will write out a referral for procedures. A common manipulation is a colonoscopy, what it is, you will learn in detail below. The research method is informative and gives a complete clinical picture.
What is a bowel colonoscopy
Fibrocolonoscopy involves examination of the intestines using a colonoscope - a flexible long apparatus in the form of a tube with a light guide. The device is equipped with an eyepiece, air tubes and forceps, which painlessly take cellular material. Virtual colonoscopy is often prescribed by specialists. The method is based on the action of X-rays. The study has limitations - does not allow sampling histological material and its biopsy, to detect polyps up to 5 mm.
Indications
Sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy are two different examinations of the large intestine that specialists perform with such symptoms:
- heat for a long time, the cause of which is unclear;
- persistent diarrhea or constipation;
- intestinal obstruction;
- suspicion of benign and malignant formations;
- discharge of blood or pus from anus;
- rapid weight loss for no apparent reason;
- anemia;
- ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease;
- sensation of a foreign object in the rectum;
- the presence of blood and mucus in the stool.
Contraindications
Videocolonoscopy should not be performed on patients with the following pathologies:
- stroke, acute heart attack;
- hypertension;
- arrhythmia;
- anemia of unknown etymology;
- atherosclerosis;
- shock state;
- intestinal perforation;
- aortic aneurysm;
- pulmonary heart failure of a pronounced nature;
- the presence of adhesions in the abdominal cavity;
- fulminant form of colitis;
- peritonitis;
- acute stage of ulcerative colitis.
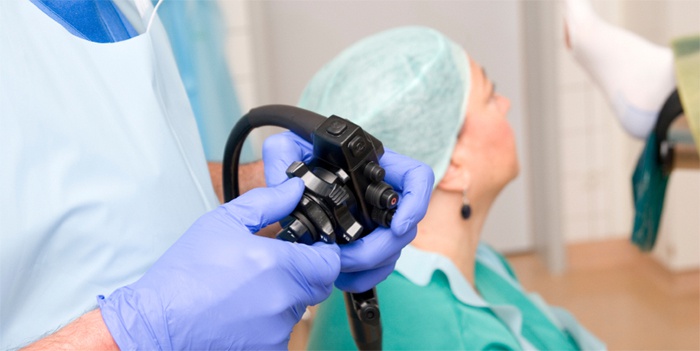
The contraindications of the procedure include poor preparation of the intestines, repeated surgical interventions in the pelvic region, large hernias. Can a colonoscopy be done for hemorrhoids? Doctors do not prohibit this procedure, on the contrary, the intervention will allow timely identification of the nodes and start their emergency treatment.
Colonoscopy during pregnancy - what is the opinion of experts? In this case, the doctor must evaluate the benefit-to-harm ratio of the procedure. It is carried out only if the patient has profuse and prolonged gastrointestinal bleeding, there are strong suspicions of formation in the large intestine, severe diarrhea with an implicit pathogen (rectoscopy is prescribed), dysphagia, odynophagia, etc.
Find out also what it is, how to treat this disease.
How is a colonoscopy performed?
Conducting rectosigmocolonoscopy is carried out after a three-day preparation of the intestine. The procedure technique is simple. The person lies on his left side and bends his knees. A colonoscope is inserted into the rectum, the tube of which, during manipulation, moves about 1.5 meters deep to the point of transition to small intestine. First, the intestine is inflated with air, which facilitates the movement of the apparatus. The camera at the end of the colonoscope transmits the image to the screen, the doctor analyzes it and takes a photo of the areas with pathology.
Does a colonoscopy hurt? The sensations are painful, but tolerable. Ointment is applied to the end of the colonoscope local anesthesia, and colonoscopy is performed without anesthesia. A child under 12 years old, a patient with adhesions, a destructive process in the intestines and a low threshold of pain sensitivity, will undergo a colonoscopy under anesthesia. The duration of the procedure is about 15-30 minutes.

- The bowel cleansing diet lasts three days. The food should be slag-free - have a high fiber content and have a slight laxative effect.
- The day before the examination, the dietary rules are tightened - for breakfast and lunch you need to eat light foods, in the evening you can only drink. Drinking is allowed on the day of the procedure.
- It is necessary to cleanse the intestines. Many resort to enemas. It is done several times - the first cleansing on the eve of the procedure, the second - immediately before the intervention. The process does not require anesthesia.
Bowel cleansing preparations
Modern medicines more gentle than an enema, and do not lead to complications. How to clean the intestines before a colonoscopy? Fortrans colonoscopy preparation is especially popular. One packet dissolves in 1 liter of water, on average an adult needs to drink 3-4 liters with an intensity of about 1 glass / hour. Dufalac before colonoscopy is also effective. A bottle of 200 ml is diluted in two liters of water and drunk in 2-3 hours.

Diet menu before colonoscopy
The success of the procedure depends on how you eat right. What to eat before a colonoscopy:
- dairy products;
- broths on lean meat;
- boiled poultry, beef, lean fish;
- light biscuits, wholemeal white bread.
In order for the procedure to go without consequences, it is necessary to exclude foods that cause bloating: fresh vegetables, herbs, fruits, berries, black bread, legumes, millet, oatmeal, barley porridge, milk, carbonated drinks, kvass, nuts. The last meal on the eve of the procedure is before 12.00. If you approach the diet responsibly, the device will show reliable data.
Alternative to bowel colonoscopy
There are options for this procedure, which one to choose, depending on the indications. Which is more relevant: barium enema or colonoscopy? The first procedure is an X-ray examination, in which water and barium sulfate are poured into the colon, and then pictures are taken. Manipulation gives highly accurate results in the diagnosis of bowel cancer. Ultrasonic colonoscopy also belongs to the exact methods and is prescribed for diagnosed oncology.
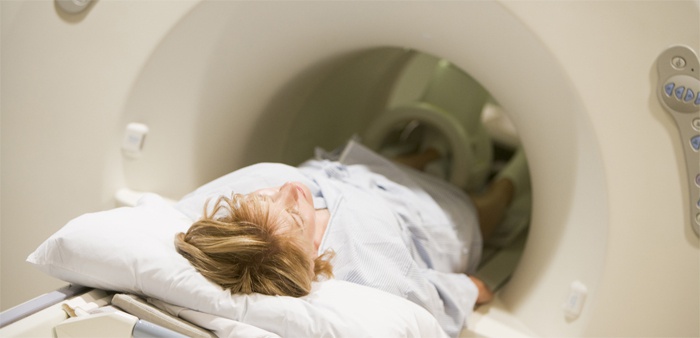
Another exciting question: which is better - an MRI of the intestine or a colonoscopy? The first procedure is more comfortable and does not require special preparation. However, it does not give a full opportunity to examine the intestinal loops superimposed on each other and take material for a biopsy. The cost of the procedures is approximately the same, which one to choose, the attending physician will say.
Video: how a colonoscopy is done
To undergo the procedure for prevention is advised to everyone who is over 40 years old. Colonoscopy, what is it and why is it so important? Yuri Shelygin, Director Science Center colonoproctology, explains the need for manipulation. Elena Malysheva talks about the essence of colonoscopy, in parallel you will see how specialists carry out this procedure.
Colonoscopy of the intestine is modern method examination of most of the area of the large intestine using a colonoscope - a special device in the form of a long and fairly flexible probe, which has an eyepiece, a backlight, a tube through which air is supplied to the intestine, and forceps for sampling. The colonoscope makes it possible to examine the condition of the colon at a distance of more than one meter from the entrance. Some devices also have a camera that allows you to not only capture visible parts of the intestine, but also display them on the screen.
Colonoscopy allows you to:
- analyze the color and reflection of the mucous membrane, as well as the vessels of the mucous layer;
- estimate the size of the lumen and motor function large intestine;
- see all inflammatory processes and formations located on the mucous membrane (hemorrhoids, ulcers, cracks, scars, etc.);
- take a sample of a small piece of the neoplasm and biopsy the result;
- in some cases, remove the pathological tumor;
- remove any foreign body;
- eliminate the source of bleeding.
When should a colonoscopy be done?
Experienced experts believe that a colonoscopy examination should be done by any healthy person over the age of 30 once every five years. If the patient has pain, characteristic burning sensations, or any other symptoms of a violation of the normal functioning of the intestine, a colonoscopy is carried out immediately. You urgently need to see a doctor if you notice that you have:
- pus, blood or mucus began to stand out from the large intestine;
- for several days they do not stop, but, on the contrary, pain in the abdominal cavity becomes more frequent;
- the chair is broken;
- there is an inexplicable bout of anemia;
- irrigoscopy diagnosed a tumor of the abdominal cavity;
- a foreign object got into the intestine, etc.
Some patients have contraindications for colonoscopy. So, this study is not carried out in cases where the following inflammatory processes in the body take place: infectious diseases, poor blood clotting, peritonitis, ulcerative colitis.
Preparing for a colonoscopy
 In order for the process of examining the intestinal mucosa to go without interference and side effects, the patient needs to properly prepare for colonoscopy. This preparation is no different from preparing for other types of bowel examinations. For several days before the colonoscopy, the patient must follow a sparing diet and thoroughly cleanse his body of foreign objects. The slag-free diet includes a list of foods and dishes that contain a large amount of dietary fiber. The patient should not eat flour and confectionery products, bread, any vegetables (especially cucumbers, herbs, radishes) and fruits, berries, legumes, buckwheat and barley cereals, as well as sour-milk products and carbonated drinks. The diet should include lean boiled meat, poultry or fish, vegetable soups and meat broths, clean water, infusions and tea without sugar. On the eve of the procedure, you need to do with dinner in the form of a small amount of tea or water, and in the morning empty the intestines with an enema. During the preparation for the colonoscopy, the patient is allowed to drink laxatives (Fleet, Fortrans, etc.).
In order for the process of examining the intestinal mucosa to go without interference and side effects, the patient needs to properly prepare for colonoscopy. This preparation is no different from preparing for other types of bowel examinations. For several days before the colonoscopy, the patient must follow a sparing diet and thoroughly cleanse his body of foreign objects. The slag-free diet includes a list of foods and dishes that contain a large amount of dietary fiber. The patient should not eat flour and confectionery products, bread, any vegetables (especially cucumbers, herbs, radishes) and fruits, berries, legumes, buckwheat and barley cereals, as well as sour-milk products and carbonated drinks. The diet should include lean boiled meat, poultry or fish, vegetable soups and meat broths, clean water, infusions and tea without sugar. On the eve of the procedure, you need to do with dinner in the form of a small amount of tea or water, and in the morning empty the intestines with an enema. During the preparation for the colonoscopy, the patient is allowed to drink laxatives (Fleet, Fortrans, etc.).
How is a colonoscopy procedure performed?
The technique for conducting this type of examination is quite fast, simple and easy. The patient needs to be naked below the waist and lie down on a hard surface, leaning on the left side. The legs are bent at the knee and pressed to the stomach. After the patient is ready to start the examination, the doctor slowly, carefully and gently inserts the device directly into the colon. For those who are hypersensitive to such procedures, the anus is lubricated in advance with various gels and ointments that have anti-inflammatory and anesthetic effects. The colonoscope slowly moves into the colon, examining its mucous membrane. In order to straighten the intestines, a small amount of air is pumped into them. The whole procedure takes no more than 10-15 minutes. After its completion, the patient may experience slight drowsiness and weakness.
