Acute colitis symptoms. General description and causes of the disease. Symptoms of colitis and diagnostic methods
The stereotype that colitis and colic are one and the same is not true. Colitis is a disease that is not accompanied by colic.
It has several types, as well as peculiar symptoms and treatments.
What is colitis?
Colitis- a disease accompanied by an inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the large intestine. It is provoked by bacteria and intoxication.
Coli is considered one of the most common diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.. Every second person with dysfunctions of the digestive system faces manifestations of chronic colitis.
Colitis affects men in their 40s and 60s and women in their 20s and 60s.
The disease can be hereditary, so there is a high risk of its occurrence if someone in the family suffered from it.
Causes
I have a lot of colitis possible causes occurrence. These include:

Symptoms of colitis and diagnostic methods
Symptoms of colitis can be very different, as they depend on its type. Here are the main types identified taking into account its course:
- spicy;
- chronic.
By etiology, colitis can be classified as follows:
- spastic;
- pseudomembranous;
- enterocolitis;
- ischemic.
Acute colitis is characterized by the appearance of severe edema during the enlargement of the intestinal mucosa. A large amount of mucus or pus appears in the distal section, the walls turn red. Small hemorrhages are not excluded.
Within a few weeks, those suffering from acute colitis may experience the following symptoms:
- gagging and vomit;
- general deterioration of well-being;
- low productivity;
After the form of the disease becomes chronic, inflammation in the area of the ligamentous-muscular apparatus is added to the inflammation of the mucous membrane. The intestines in the affected area are reduced in size.
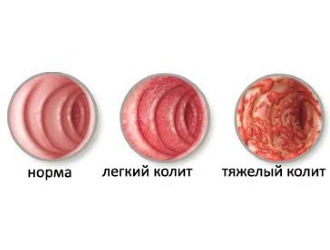 Chronic colitis has several characteristic symptoms:
Chronic colitis has several characteristic symptoms:
- extremely unpleasant smell of feces;
- bowel problems (diarrhea or constipation);
Ulcerative colitis is most often hereditary. It can be identified by several accompanying phenomena:
- a slight increase in body temperature;
- rectal bleeding;
- rectal purulent discharge;
- weight loss;
- anemia.
In advanced cases, symptoms can be much more severe. For example, intestinal obstruction and peritonitis are not excluded. If ulcerative colitis is left untreated for several years, the risk of bowel cancer increases.
Spastic colitis can hardly be called a serious illness. It occurs after overwork, stress and other physical activity. Spastic colitis has four characteristic symptoms:
- gases;
Pseudomembranous colitis occurs with dysbacteriosis. Its symptoms depend on the form. In a mild form of pseudomembranous colitis, only one symptom is diarrhea while taking antibiotics. But, moderate and severe have several symptoms:
- abdominal pain, aggravated during bowel movements;
- persistent diarrhea;
- elevated temperature;
- malaise;
- gagging and vomit;
- hypotension;
- tachycardia.
Enterocolitis accompanies acute gastritis. Listed below are its symptoms:
- headaches;
- decrease in productivity;
- abdominal painaccompanied by rumbling;
Ischemic colitis in necrotic form is characterized by pain in the left abdomen. In the episodic form, in addition to pain, there is diarrhea, bloating, vomiting, and weight loss.
If signs of the disease are found, it is worth paying a visit to a gastroenterologist or a caloproctologist. After the examination, you need to pass the feces for analysis so that the specialist can evaluate the functioning of the intestines. You can also detect colitis using these studies:
- colonoscopy;
- ultrasound procedure;
- irrigoscopy;
- sigmoidoscopy.
How to treat colitis?
Any type of colitis requires a special diet. It increases the effectiveness of treatment, as it reduces the burden on the digestive system.
The essence of the diet- consumption of the most soft stewed, steamed and boiled food. It is advisable to eat small portions about five times a day. Pay attention to foods that are highly undesirable to consume:
There are many treatments for colitis. They should be chosen by a specialist, taking into account the type of disease and the characteristics of the organism. The list contains all the ways to treat colitis:
Special therapy for ulcerative colitis. In this case, corticosteroid (Prednisolone), biological (Humir) and special (Pentas) preparations should be used.
There are some folk remedies helping with colitis:
- Honey-apple mixture. Dissolve two large spoons of honey in a glass of apple juice. Use the mixture three times a day.
- Hypericum infusion. Pour two tablespoons of dried chopped St. John's wort half a liter of boiling water. Insist received for fifteen minutes. Drink in an infusion in one day in small portions.
- Microclyster. Using microclysters, inject sea buckthorn oil into the body. Fifty grams - a dose for adults, thirty grams - for children.
Prevention of colitis
Prevention measures for colitis are simple and straightforward:
- Eat right. Vitaminize the diet and give up low-quality harmful products.
- Rest when your body requires it. The word "rest" here means both mental and physical unloading.
- Take care of your overall health. Do not be lazy to undergo an annual medical examination and consult a doctor if you suspect a disease.
Video on the topic: Colitis. Symptoms, treatment
Forecast
Colitis causes a lot of inconvenience, but is easily cured. If you follow a diet and take all the necessary drugs, the disease will go away without negative consequences. Particular attention should be paid to the treatment of ulcerative colitis, because with erroneous actions and untimely treatment, it will entail oncology.
What should be remembered about colitis?
Taking into account all the features of colitis, we can conclude:
- Colitis is not contagious. Being close to a person suffering from this disease is dangerous only if it has arisen due to an infection.
- Colitis is a common disease. Half of those who have experienced digestive diseases know firsthand about colitis.
- Colitis treatment should be accompanied by diet and rest. Otherwise, it will be ineffective.
Colitis- inflammation of the mucous membrane of the colon.
Acute colitis
Often accompanied acute inflammation mucous membrane small intestine(acute enterocolitis), and sometimes the stomach (gastroenterocolitis). Pathogens - shigella, salmonella, opportunistic bacteria, protozoa, etc. The inflammatory process in the colon occurs due to local exposure to its mucous membrane of damaging factors that are in the intestinal contents or enter the hematogenous route and are secreted by the mucous membrane.Clinical manifestations of acute colitis
Pain of a pulling or spastic nature, tenesmus, rumbling in the abdomen, loss of appetite, diarrhea, general weakness. Feces are liquid, with an admixture of mucus, sometimes blood. Stool frequency - up to 15-20 per day. Body temperature is elevated to 38 ° C and above. In cases of severe course, the tongue is dry, covered with a gray or dirty gray coating. The abdomen is somewhat swollen, with severe diarrhea - drawn in. Palpation reveals pain along the colon, rumbling. In the study of blood, moderate leukocytosis with a stab shift, an increase in ESR are determined.Treatment of acute colitis
If infectious colitis is suspected, hospitalization in the infectious department is necessary. Assign appropriate antibacterial or antiparasitic therapy. For toxic colitis, saline laxatives and bowel lavage are used. On the first day, the patient should drink plenty of fluids. Diet No. 4, 4a, 46 is shown. In case of dehydration, 0.9% sodium chloride solution, 5% glucose solution, gemodez are administered intravenously. They also give enveloping, astringent agents (bismuth nitrate, tanalbin, blueberries, etc.), Digestive enzyme preparations (pancreatin, festal, Pankurmen), anticholinergics, painkillers. Enteroseptol, intestopan, colibacterin, bifikol are used to normalize the intestinal microflora. In case of violation of vascular tone, cordiamine, mezaton, sulmikhjamphocaine are indicated.chronic colitis
Chronic colitis is a long-term inflammation of the colon with a relapsing course. Often accompanied by inflammation of the small intestine (enterocolitis) and stomach (gastroenterocolitis). The disease can be caused by pathogens of intestinal infections, opportunistic flora, amoeba, balantidia, helminths. An important role is played by alimentary and toxic factors, concomitant pathology. internal organs ( , chronic enteritis), application medicines(drug-induced colitis), mechanical irritation of the colon wall, abuse of laxatives and enemas.Clinical manifestations of chronic colitis
Patients complain of constipation or diarrhea ("sheep feces", the presence of mucus in the feces in the form of flakes, cylinders, narrow ribbons), pain in various parts of the abdomen, sometimes painful tenesmus, flatulence. Constipation and diarrhea may alternate. After defecation, the patient has a feeling of incomplete emptying. False urge to defecate, accompanied by discharge of gas and the release of clods of feces, covered with strands of mucus streaked with blood, or discharge of mucus in the form of films. The pain is usually dull, aching, localized mainly in the lateral and lower abdomen, aggravated after eating and before defecation. With spastic colitis, the pain is spastic in nature (subsides under the influence of heat), may be accompanied by gas discharge or the urge to defecate. On the clinical picture chronic colitis leaves an imprint of concomitant diseases. Dyspeptic phenomena occur, appetite is disturbed, belching, nausea, sometimes vomiting, heartburn, and a bitter taste in the mouth appear. The patient is disturbed headache, fatigue, poor sleep, subfebrile condition. With superficial palpation, areas of pain in the abdominal wall are revealed, mainly behind the colon. With deep palpation, significant soreness of the affected segments of the colon is determined. They are spasmodic, alternating with extended segments filled with dense or liquid contents, in which rumbling intensifies. The feces are solid or liquid, fetid, contain a large amount of mucus and leukocytes, undigested fiber and intracellular starch, as well as erythrocytes (with erosive and ulcerative forms). At microscopic examination detect dysbacteriosis. The following stages of dysbacteriosis are distinguished: 1) a decrease in the number of bifidus and lactobacilli, 2) an increase in the number of Escherichia coli, enterococci, the appearance of hemolytic and lactose-negative enterobacteria, 3) a large number of hemolytic colibacilli, staphylococci, streptococci, 4) in addition to changes characteristic of the previous stages, find a large number of conditionally pathogenic microorganisms with a high content of proteus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, etc.Diagnosis of chronic colitis
According to sigmoidoscopy, four forms of proctosigmoiditis are distinguished: a) c.mralny (the mucous membrane is hyperemic, the vascular pattern is enhanced), b) erosive (a small amount of hemorrhages and erosions against the background of hyperemic mucous membrane c) atrophic (the mucous membrane is thinned, smooth, pale pink color), d) inflammation of the mucous membrane with a predominance of edema (the vascular pattern is absent, the mucous membrane is dull, edematous, sometimes granular). Colonoscopy reveals the form of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the colon throughout its entire length: catarrhal, purulent, fibrinous, necrotic-ulcerative. When examining blood, leukocytosis with a shift to the left, an increase in ESR are determined. In allergic colitis, Charcot-Leiden crystals are found in the stool. Bacteriological studies feces and serological tests are used to detect chronic dysentery.Treatment of chronic colitis
It is indicated to get N9 2, 4, 4a, 46 (frequent meals, in small portions, during an exacerbation of the disease it is necessary to reduce the amount of carbohydrates and fats), vitamins (ascorbic acid, thiamine, pyridoxine, cyanocobalamin). In case of exacerbation, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed (tetracycline, chloramphenicol, etc.). Or sulfa drugs. Enteroseptol (0.25-0.5 g 3 times a day), intestopan are very effective. Useful colibacterin, bifikol, lactobacterin, bifidumbacterin (6-10 doses per day). To increase the reactivity of the body, aloe extract is used (1 ml 1 time per day, 10-15 injections), peloidin (40-50 ml inside 2 times a day 1-2 hours before going or in enemas, 100 ml 2 times a day). day, 10-15 days). For diarrhea, astringents, enveloping agents (basic bismuth nitrate, kaolin, tansal), infusions and decoctions of plants containing tannins (St. John's wort, blueberries) are used. If diarrhea is caused by secretory insufficiency of the stomach, pancreas, then enzyme preparations (acidin-pepsin, festal, pancreatin) are prescribed. Cholinergic receptors and antispasmodic drugs recommended for spastic colitis. Be sure to treat comorbidities. Physiotherapeutic means: mud applications, diathermy, etc. Spa treatment - Morshyn, Mirgorod, Odessa, Feodosia.Granulomatous colitis (Crohn's disease)
Granulomatous colitis (Crohn's disease) is a necrotizing inflammation of the mucous membrane of the rectum and transverse colon of a non-specific nature.Clinical manifestations of granulomatous colitis (Crohn's disease)
The disease develops gradually. The reason for the patient to see a doctor is rectal bleeding and diarrhea, less often constipation, as well as abdominal pain, depression, and general weakness. In severe forms of the disease, fever, weight loss, vomiting, anemia are observed.Diagnosis of granulomatous colitis (Crohn's disease)
When irrigoscopy shows the alternation of normal and affected areas of the intestinal wall. Biopsy reveals granulomas. With the help of sigmoidoscopy, an uneven thickening of the mucous membrane, its edema, longitudinal and transverse deep ulcers, which often intersect, are determined. There may be a narrowing of the intestinal lumen. If the process is above the examined segment, then it is possible to detect runoff of purulent mucus in the absence of sigmoidoscopy changes.Treatment of granulomatous colitis (Crohn's disease)
Patients are subject to hospitalization. During the period of exacerbation, diet No. 4, 46 is indicated. For anemia, iron preparations are used. In the case of a severe course of the disease, transfusion therapy, corticosteroid hormones (prednisolone, hydrocortisone), sulfa drugs (salazopyrin, sulfasalazine, salazodimethoxine) are indicated. When purulent complications, septic phenomena apply antibiotic therapy (in other cases it is contraindicated). Reasek, codeine phosphate, along with basic bismuth nitrate, and tanalbin are also used to treat diarrhea. Vitamins of group B, vikasol (according to the scheme) are prescribed in 2 weeks, the interval between courses is 1-2 months. A significant role is played by psychotherapy, sedatives (elenium, valerian root infusion, seduxen, small doses of chlorpromazine). Treatment with microclysters is successfully used (phthalazole solution, 0.3% collargol solution, Shostakovsky's balm, dogrose and sea buckthorn oil). According to indications, surgical intervention is performed.Ischemic colitis
Ischemic colitis is a segmental lesion of the large intestine caused by a violation of its blood supply. Allocate reverse and irreversible ischemic colitis. Reverse colitis ends with recovery or progresses with the formation of an ischemic stricture. The course of irreversible colitis is severe, the development of a gangrenous form of the disease is possible.Clinical manifestations of ischemic colitis
Patients complain of pain in the left side of the abdomen, it occurs suddenly and just as quickly passes. Often it is insignificant, may be accompanied by tenesmus. Later, intestinal bleeding appears (however, massive bleeding is against this disease), the blood is dark or bright red. Vomiting, diarrhea, mucus discharge are often observed; in severe cases, fever, tachycardia, leukocytosis. On palpation of the abdomen, sometimes there are symptoms of peritoneal damage, which, as a rule, disappear after a few hours.Diagnosis of ischemic colitis
The diagnosis is confirmed by irrigoscopy, rctoromanoscopy, colonoscopy, and fluoroscopy. Irigoscopy reveals the symptoms of "print thumb"- disgraced or round filling defects, the occurrence of which is due to submucosal hemorrhages in the intestinal wall. A likely sign is their appearance only with tight filling of the colon. With a greater degree of ischemia, the mucous membrane over the site of hemorrhage exfoliates and an ulcer is formed. During sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy reveals submucosal hemorrhages.Treatment of ischemic colitis
Patients with gangrenous form of colitis are immediately hospitalized in a surgical hospital. Patients with stricture form also require surgical treatment. Therapy of reverse ischemic colitis consists in prescribing a diet, mild laxatives, antispasmodic and anticholinergic drugs. For the purpose of prevention, patients are recommended to take drugs that improve blood circulation (prodectin, anginin, complamin, etc.). Vitamin therapy is important - ascorbic acid, ascorutin, B vitamins, undevit, Gendevit. In case of amplification clinical manifestations diseases, transfusion therapy is indicated, aimed at correcting the water and electrolyte balance, blood transfusions, parenteral nutrition. Corticosteroids are contraindicated. If there is a risk of infection of the necrotic intestinal wall, intensive antibiotic therapy is carried out.Colitis is the most common disease of the gastrointestinal tract. It occurs in the area of the mucous membrane of the large intestine and is inflammatory. The acute form of the disease is accompanied by violent symptoms and fast treatment, while chronic colitis occurs over a long period.
General description and causes of the disease
exist different kinds disease such as colitis. The causes of the development and course of diseases are different, although there are similarities. Accordingly, the large intestine can be affected partially or completely, the disease can be chronic, develop in acute form or have a mild degree of functional impairment.
The reasons for the development of inflammation also include heredity, nervous and physical stress, poor-quality food, and even the wrong daily routine.
Acute colitis and its symptoms
Acute colitis is quite often observed in combination with inflammation of the mucous membrane of the small intestine (enterocolitis). In parallel, the patient can be diagnosed with gastroenterocolitis - inflammation of the stomach.
In acute colitis, a person feels a burning increase in pain, which is spastic or pulling in nature. In addition to pain, other symptoms of the disease also appear:
- loss of appetite;
- strong rumbling in the stomach;
- frequent manifestation of diarrhea;
- liquid stool with mucus;
- dry mouth;
- laying the tongue with a gray coating;
- general weakness and malaise.
When the disease is in a rather severe form, the frequency of watery stools can exceed 20 times per day. There are false urges to defecate (tenesmus). Body temperature rises to 38-39 degrees. There is bloating. With non-stop diarrhea, the stomach, on the contrary, becomes retracted.
Acute colitis of the intestine can have a variety of symptoms, it directly depends on the localization of the focus of inflammation. Severe and burning pains occur when the left side of the colon is affected. Before the act of defecation pain intensify, spreading to the sacrum, perineum. During palpation, the colon area is quite painful, and rumbling is felt in the sigmoid and descending sections. On the walls of the intestine there is mucus, in more severe cases - pus. Hemorrhages, erosions and ulcerations may be observed.
In severe forms of acute colitis, treatment becomes protracted. Due to this disease, a person may develop a number of complications: sepsis, liver abscesses, pyelitis, peritonitis. If acute colitis is mild, the patient's condition improves rapidly.
Chronic form of colitis
With the transition of colitis into a chronic form, in addition to inflammation of the mucous membrane of the rectum, inflammatory processes also occur in the ligamentous-muscular apparatus.
Among the various diseases of the digestive system, colitis chronic form is the most common. It is very important to recognize its signs in time and, in order to avoid serious complications, immediately begin treatment.
Chronic colitis symptoms:
- unstable stool (diarrhea alternating with constipation);
- cramping pains in different parts of the abdomen;
- tenzema when excreting mucus, sometimes with blood;
- flatulence (bloating and heaviness of the abdomen);
- malodorous feces.
In people suffering from chronic colitis, dyspeptic disorders are often observed: nausea, belching, loss of appetite, bitterness in the mouth.
Chronic inflammation allows patients to be in satisfactory shape, but in some cases, irritability, decreased ability to work, general weakness and malaise may be observed.
Ulcerative inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis is one of the forms of a chronic disease of the gastrointestinal tract. The reasons for the development of this disease are not yet reliably identified. Presumable etiological factors are infections (bacteria, viruses), poor nutrition, allergies and hereditary predisposition. Doctors are also inclined to believe that ulcerative colitis develops in people who had some kind of intestinal infection in childhood or were fed with adapted milk mixtures.
Inflammation of this form is most often manifested in the age group of people from 20 to 40 years. Cases of the disease are less common in patients older than 60 years.
Symptoms of ulcerative colitis are represented by such deviations in health as:
- frequent liquid stool with an admixture of mucus, blood and pus;
- cramping pains in the abdomen;
- false urge to defecate;
- feeling of incomplete bowel movement;
- bleeding from the anus;
- fever accompanying the inflammatory process;
- weight loss;
- constant fatigue and weakness.
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis should not be left to chance. The disease requires qualified medical intervention. A person diagnosed with ulcerative colitis should follow all doctor's orders. In cases of exacerbation, the patient is subject to hospitalization in a specialized gastroenterological or coloproctological department.
The most common form of colitis

Gastroenterocolitis is an infectious disease with inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterocolitis most severely affects the walls of the large and small intestines.
The culprits of the disease
There are many reasons for the development of gastroenterocolitis. Among them:
- pathogens (rotavirus and enterovirus);
- bacterial infections (, streptococci, salmonella, staphylococcus aureus);
- antibiotics;
- low-quality and very fatty food;
- inflammatory bowel disease (nonspecific ulcerative colitis,);
- extraintestinal infections (sepsis, otitis media);
- alcohol and heavy metals.
Therefore, very often gastroenterocolitis manifests itself in the whole family or team with the joint use of low-quality products. Inflammation easily develops with rotavirus, therefore it carries a great danger not only for adults, but also for children. Gastroenterocolitis is also called food toxin infection, which quite clearly characterizes the causes of its occurrence.
Symptoms of the disease
Gastroenterocolitis is characterized by short incubation period. Symptoms are visible after a few hours. These include:
- flatulence and rumbling in the stomach;
- diarrhea with mucus and blood;
- nausea and vomiting;
- lethargy and weakness in the muscles;
- belching and bitter taste in the mouth;
- fever and fever;
- pale skin and general malaise.
The above symptoms last for about three days, after which the state of health painfully normalizes and only a slight weakness remains. Duration lung disease forms up to 7–8 days. With timely treatment, gastroenterocolitis resolves quickly. If medical treatment and dietary measures are neglected, mild inflammation can lead to undesirable consequences, for example, go into recurrent chronic gastroenterocolitis.
spastic inflammation
One form of inflammation of the colon - chronic colitis - is spastic colitis. Its characteristic is disruption of the intestines, bloating and cramps. In all people, the disease occurs with different symptoms. For some, spastic colitis manifests itself in the form of frequent diarrhea, for others, the disease takes the form of difficult and rare emptying, while others have to experience both diarrhea and constipation.
Spastic inflammation is not a serious disease. Doctors consider it a functional disorder caused by frequent stress, nervous tension and fatigue.
You can't do without a doctor!
The tactics of treating colitis depends on the form of the disease, the age of the patient, the severity of clinical manifestations and the intensity of the course of the disease. An important role in deciding the method of treatment is played by the etiological factor that caused the disease.
It is worth noting that the diagnosis of "colitis" is established only by a doctor, since its symptoms are similar to the manifestation of completely different functional or intestinal diseases. Accordingly, the treatment, which is selected individually for each patient, should be prescribed only by the attending specialist.
The large intestine is the final part of the digestive system in which water is absorbed and feces are formed. It consists of several functional departments. The importance of this organ is often downplayed, and they try not to pay attention to diseases as frivolous, and only after acute attacks of pain do they think that this is an important part of the digestive system. One such disease is acute colitis.
A severe form of intestinal inflammation is accompanied by pain, vomiting, loose stools with blood.
Colitis is an inflammatory disease of the large intestine that can be chronic or acute. With the disease, the intestinal mucosa is inflamed.
Acute colitis develops in parallel with enteritis or gastritis. The manifestation of colitis depends on the location and origin. It is often a symptom of other diseases. In any case, colitis causes problems with stools, pain, fever.
Acute forms of the disease can last up to 14 days. During this time, the patient either recovers or gains chronic illness. With colitis, there is a chance of getting dangerous complications.
Why does acute colitis develop?
There are many factors that can provoke the development of an acute form of colitis. Among them:
- exposure to radiation;
- use of antibiotics for a long time;
- infections;
- food or chemical poisoning;
- diseases caused by bacteria;
- blood flow disorders, etc.
Most often, colitis develops against the background of bacteriological infection, for example, against the background of salmonellosis or dysentery. Sometimes a food allergy can be the cause of acute colitis.
Symptoms
Symptoms of acute colitis may include:
- cramping pain in the abdominal cavity, mainly below or in the side;
- pain becomes stronger after eating;
- after defecation, the pain decreases;
- constipation (may last several days) and diarrhea;
- the stool may have blood impurities;
- there is mucus in the feces;
- false urge to defecate;
- nausea;
- gagging;
- increase in body temperature;
- weakness;
- loss of strength, etc.
The symptoms associated with acute colitis can vary, as the causes of the disease are varied.
Diagnostic methods
If signs of colitis are found, you should not delay going to the doctor or self-medicate. To identify the etiology of the disease and make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor conducts diagnostics according to the following scheme:
- conversation, history taking, palpation;
- general blood analysis;
- stool analysis;
- endoscopic examination - colonoscopy;
- biopsy and histological analysis of the removed material;
- rectomanoscopy, in which puffiness is visible, the presence of pus in the intestines and;
- irrigoscopy.
Sometimes additional diagnostic methods are used.
Treatment
If the doctor found an acute form of colitis in a patient, he immediately hospitalizes him, while if the disease is caused by an infection, the patient is placed in the infectious diseases department.
The acute form of the disease is not complete without the use of astringent medications in therapy that envelop the intestines. Enzymatic agents and anticholinergics are shown. During therapy or after it, the patient is recommended to use probiotics to normalize the intestinal microflora. You may need to instill with dehydration products.
If the disease is caused by the fact that the patient has been drinking medicines for a long time, they are canceled or replaced with others. Often, intestinal motility regulators and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. Sometimes glucocorticoid hormone therapy is needed.
For the treatment of acute colitis, the patient needs bed rest and a sparing diet. The first day after the attack, food is prohibited. The patient needs to drink a lot. To do this, it is better to use warm, clean water or tea without sugar. You need to drink in small sips so as not to swallow air at the same time. On the second day, the patient is allowed to eat. The patient's diet depends on what causes colitis and how it manifests itself.
For constipation, it is recommended to eat soup-puree from vegetables, meat and fish of low-fat varieties, steamed or boiled, vegetables in raw or thermally processed form. Vegetables such as beets, carrots, cauliflower are useful for the digestive organs. The menu can include berries and sour-milk low-fat products. You can't eat fresh bread.
In acute colitis with diarrhea, the menu can include sour-milk products, grated cereals cooked in water (except millet and barley), mashed soups, steamed omelettes. It is useful to eat jelly.
If a patient has an attack of an acute peptic ulcer, a starvation diet is forbidden to him. Food is allowed, as in other types of illness. It should be remembered that citrus fruits, tomatoes and milk in this case should not be consumed.
The diet is developed for each patient individually. The basic principle is that food should be healthy and rich in essential substances. Physiotherapeutic procedures or psychotherapy can be useful for the patient. In case of bowel diseases, spa treatment is recommended.
Possible Complications
The risk of developing complications in the disease is high, so timely treatment for diagnosis and treatment is so important. The disease can provoke the following negative consequences:
- peritonitis - an inflammatory process in the abdominal cavity and its membrane;
- sepsis - systemic inflammation that develops throughout the body due to the ingress of infectious pathogens into the blood;
- liver abscess - purulent inflammation of the tissues of the organ;
- pyelitis is an inflammatory process in the renal pelvis.
Prevention
Any disease is better to prevent than to treat later. For the prevention of acute colitis, proper nutrition is recommended, which is gentle on the organs of the gastrointestinal tract. It is necessary to monitor the quality of food, their expiration date. You need to choose fresh produce. It is important to set the power supply.
It is important to lead a healthy lifestyle, move more. It is recommended to play sports or at least do general strengthening physical exercises.
It is also important to adhere to personal hygiene: thoroughly wash your hands, vegetables and fruits. It is necessary to monitor the health of the teeth, clean them well, treat them in time. It is advisable to have a scheduled check-up with a dentist. It is necessary to monitor health, not to delay the treatment of diseases, especially if they concern the digestive organs.
