Acute inflammation of the intestine. Inflammation of the intestine
- this is a collective name used to refer to disease processes occurring in one or more departments of the mentioned organ. Developing for various reasons, this condition occurs equally often in people of both sexes and all ages. At the same time, due to the complexity of the disease, its treatment should be selected for each individual patient individually, and necessarily by specialists.
What causes inflammation in the large intestine? How does this disease manifest itself? Is it possible to diagnose such a disease on early stage and, most importantly, how and with what to treat it? These and other equally important questions related to inflammatory processes in the intestines will be answered by our article.
Inflammation is the death of mucosal cells.
Before answering this question, you need to understand how this painful process proceeds in general.
From a medical point of view, any inflammation is the death of cells of the mucous membranes, accompanied by an abundant blood supply to the affected area.
This process is accompanied by inevitable disturbances in the work of the “injured” organ and, as a result, pain syndrome.
Of course, other negative factors can serve as the cause of the violation. Among them are:
- autoimmune diseases that entail spontaneous rejection of cells of the mucous membrane of the large intestine;
- genetic predisposition, in other words, inherited deficiency, provoking problems with the digestive tract;
- malnutrition, which provokes chemical and mechanical damage to the mucous membranes of the organs involved in the digestive process (usually through the use of excessively spicy or fatty foods);
- atherosclerotic abnormalities, due to vasoconstriction, inevitably leading to disruption of the blood supply to the intestinal walls.
The following video will tell you about the symptoms and treatment of colitis:
Classification of diseases
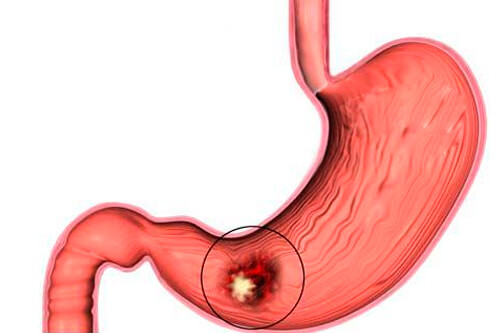
Duodenitis is a disorder of the function of the duodenum.
Depending on the localization of the focus of inflammation, painful processes in the intestines are usually classified as follows:
- . This term refers to inflammation. small intestine(both all at once, and any one of its separate departments).
- . This name means a disorder of the function of the duodenum.
- Mesadenitis. In such diseases, inflammation affects only those located in the intestines. The lymph nodes(the painful process itself, as a rule, is caused by an infection).
- . This generalizing term is usually used to describe inflammatory processes, just in the large intestine. Moreover, both the entire organ and only its lower section can be affected. It is also customary to call colitis inflammation of the mucous membrane of the rest of the intestine.
Typical symptoms
Bloating is a sign of a lack of digestive enzymes.
The symptoms that appear during inflammatory processes in the intestines can vary greatly depending on the localization of the problem.
However, some of the characteristic manifestations of such ailments can be considered common.
It is on them that doctors rely when making a preliminary diagnosis of "inflammation of the intestine." Some of these specific features include:
- pains of a bursting or squeezing nature, it is usually not possible to determine the main source of which, as a rule, is not possible;
- nausea-vomiting syndrome, usually aggravated after eating and weakening after cleansing the stomach;
- and other symptoms that indicate a lack of digestive enzymes;
- unstable stool (from to diarrhea);
- anemia (anemia occurs as a result of iron deficiency, inevitable with intestinal damage);
- fever (a reaction typical of any inflammatory process).
How is intestinal inflammation diagnosed?
A blood test will determine the degree of development of inflammation.
In the case of inflammation of any of the intestines, laboratory diagnosis of the disease is a necessary step before prescribing treatment.
It is she who allows you to establish the focus of the disease process, and therefore - to identify its causes. Without such procedures, the development of an adequate strategy for the treatment of inflammation would simply be impossible.
What examinations will the patient have to undergo if bowel problems are suspected? Today, the following laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods are especially popular (due to their effectiveness):
- bacteriological examination of feces (serves to detect the presence of pathogenic microbes in the body);
- general (allows you to determine the number of active leukocytes in the body, and hence the degree of development of inflammation);
- FEGDS, or video capsule endoscopy (visual examination of the intestines and stomach allows you to accurately identify the focus of inflammation and, moreover, obtain the biomaterial necessary for further laboratory studies, such as biopsy);
- coprogram (a more detailed study of feces is necessary to determine the lack of digestive enzymes).
Medical measures
Etiotropic therapy involves the systematic use of antibiotics.
After identifying the focus of the disease and making an accurate diagnosis, the doctor can develop an adequate strategy for treating inflammation in the intestines. Typically, such therapy is carried out in several stages, the essence of which is as follows:

With increased acidity, an infusion of chamomile will help.
Medicinal plants are successfully used to combat the symptoms of many serious diseases. Inflammation in the intestines was no exception.
Today, remedies to alleviate the symptoms of this disease can be found in any pharmacy. We list the most effective of them:
- From bloating and to stabilize in equal proportions, the fruits of fennel, cumin and chamomile flowers are mixed. The resulting mass is poured with boiling water. The liquid is filtered and taken after meals (maximum - three times a day).
- With increased acidity in the stomach, a tincture is prepared from pharmacy fees of chamomile, elecampane, valerian, yarrow, cudweed, alder, calendula, licorice and marshmallow. The listed ingredients are mixed, poured with boiling water and sent to a water bath for 5 minutes. The finished liquid is filtered and drunk half a glass at a time before each main one (that is, three times a day).
- With low acidity, other herbs are already used. In this case, the tincture is prepared from linden, marshmallow, chamomile, and elecampane. The ingredients are mixed and placed in boiling water. The liquid is insisted and filtered. They do not drink the drug regularly, but as an anesthetic (in other words, only during exacerbations of the disease).
- Plantain juice and honey will help reduce inflammation in the intestines. The mentioned components are mixed in a ratio of 2 to 1 and drunk three times a day (a tablespoon at least an hour before a solid meal).
- Good help with inflammation and based on a 3% solution of boric acid and calendula. For one session, take a tablespoon of each of the components. It is best to put such an enema before going to bed.
Preventive measures

You should always wash your hands before eating.
Like any disease of the digestive tract, intestinal inflammation can be easily avoided if simple hygiene rules are followed from childhood.
For example, keep your hands clean and wash food before eating. However, in practice, observance of the banal principles of proper nutrition is no less important. What are they?
If the patient is already aware of the tendency of his intestines to inflammation, it will not be superfluous for him to completely revise his own in order to prevent the transition of the disease to the chronic stage. The most rational steps in this sense will be the complete rejection of any exotic food and reasonable restrictions on the use of hot spices.
Noticed an error? Select it and click Ctrl+Enter to let us know.
Tell your friends! Share this article with your friends on your favorite social network using the social buttons. Thanks!
Symptoms of the disease can occur in acute and chronic form, which depends on the type of microorganism that caused the inflammation, and the condition immune system. acute form lends itself fast treatment antibiotics. Chronic runs for years without bright clinical picture which does not allow timely diagnosis.
Symptoms of acute colitis
Acute colitis causes severe swelling of the intestinal mucosa, so the person feels pain in the abdomen, vomiting and nausea. Feces due to the formation of many cracks with bleeding acquires a specific red hue. Inflammatory changes are seen in general analysis blood (increased leukocytes and accelerated erythrocyte sedimentation rate). When the urge to defecate in the abdomen there are painful sensations. In such a situation, a person's appetite decreases, which, with a prolonged existence of the pathology, leads to a decrease in weight.
Symptoms of chronic colitis
Symptoms of chronic inflammation of the intestine are less scarce, but they are more dangerous in terms of prognosis. Against the background of constant inflammation of the mucous membrane, changes occur in the ligamentous-muscular apparatus. Such changes are accompanied by shortening and narrowing of the gastrointestinal tract in the affected area. Expansion of capillaries, the appearance of erosions, ulcers and abscesses further aggravates the symptoms of the disease. Chronic changes lead to the likelihood of polyps in the intestine.
In chronic inflammation of the intestine, there are severe pain, stool disorders, . In fairness, it should be noted that such a condition in humans occurs only a few times a year.
Symptoms of ulcerative colitis
Symptoms of ulcerative colitis occur due to the formation of many erosions, cracks and ulcerative defects in the intestinal wall. Often, pathology is observed in people aged 20 to 40 years. More often, representatives of the beautiful half of humanity fall ill with this form.
The causes of the pathology have not yet been studied. It is believed that the disease occurs more often in individuals with reduced immune system functions. Against this background, severe inflammation occurs in the gastrointestinal tract. Scientists do not exclude even a genetic predisposition to the disease.
The severity of symptoms of ulcerative colitis depends on the stage of pathology. Initially, it causes pain in the abdomen, constipation. A person's temperature rises, soreness in the joints may occur. At the next stage, rectal bleeding can be noticed. There are blood particles in the stool.
The course of the disease consists of alternating periods of remission and exacerbation. During exacerbations, there are pains in the abdomen, diarrhea, he quickly loses weight.
Symptoms of spastic colitis are manifested primarily by bloating and sharp cramping pains. They escalate in stressful situations. Doctors do not consider the pathology to be serious, and its treatment consists in eliminating the symptoms of the disease, taking sedatives.
Symptoms of pseudomembranous colitis are similar to dysbacteriosis, which occurs against the background of reproduction in the intestine conditionally pathogenic microorganisms. According to the severity, mild, moderate and severe forms are distinguished. It can usually be removed antibacterial agents, but in advanced cases, it may be necessary to purify the blood from toxic substances in a hospital setting.
Inflammation can be an independent qualitative disease or appear against the background of other gastroenterological diseases.
Division into classes
- In medicine, there are two classes of the course of the disease and two main types of the origin of the disease.
- The course of the disease
- Acute - severe symptoms that occur along with gastritis and enteritis.
- Chronic - a decrease in the severity of symptoms, with periodic exacerbation.
Origin of the disease
- Ulcerative origin - has an incomprehensible origin. The role of development is played by heredity, infection and the ingestion of autoimmune antibodies.
- Infectious - a disease caused by damage to natural microorganisms in the intestines of the lower section. They can be different and have different specifics, for example, dysentery inflammation, banal and conditionally pathogenic.
Ulcerative origin of the disease
It is referred to as chronic colitis, which occurs when the natural factors of the body and the environment interact.
Irritants of the disease
It is not completely clear where and why this disease appears, but basically they consider a chronic predisposition, viruses and the environment of the body. For example, if relatives have Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis, this greatly increases the chance of developing the disease. Or the use of oral contraceptives, nicotine addiction and/or exposure to various diets may be triggers for the disease.
Inflammation of the large intestine of an ulcerative nature, its symptoms and treatment
Diarrhea or thick stools mixed with blood, pus and mucus, increased pain in the abdomen, fever, weight loss, loss of appetite are all symptoms of colitis. Diagnosing it is usually not difficult. To do this, take clinical and biochemical analyzes blood. Treatment of inflammation takes place on an outpatient basis with the appointment of a special diet, if the disease has a severe exacerbation, then enteral and / or nutrition through a vein is prescribed.

infectious colitis
As we discussed earlier, infectious colitis is different. Dysentery colitis is characterized by general intoxication and symptoms of lesions of the gastrointestinal tract.
The banal include staphylococci, streptococci. Their action is aimed at changing the bacterial space of the intestine, by multiplying external bacteria.
An example of opportunistic changes is Escherichia coli. The impact on the intestinal occurs in the lower part with the help of rod bacteria. They cause severe digestive poisoning.
Common symptoms of inflammation of the colon
Symptoms of the general feeling of the patient have signs of poisoning. But when examining the colon, everything becomes clear to the doctor. The signs are:
- Mucosal edema.
- Thickening or congestion of the walls of the affected area of the intestine with blood.
- Rotting and the appearance of ulcers on the mucosa.
- Small hemorrhage.
Also, if you do not seek help from a specialist in time, the disease will grow and can go into a chronic stage. In the first days, the usual signs of poisoning, but after that feces appear mixed with blood, appetite is lost, and often patients complain of an increase in the abdomen several times in the presence of stools up to 6 times a day.
Signs of transition to a chronic condition
In chronic colitis, there is a change in the condition of the intestine itself. It changes in appearance, shortens, narrows the affected area, disruption of blood supply. The patient himself feels problems with the stool, pain throughout the abdomen with no specific localization, increased formation of gases and constant bloating.
Lower colon treatment
Treatment comes from the severity of the disease and its form. If the inflammation is mild, then it quickly disappears after washing the stomach, taking sorbents, sufficient fluid intake in the body and diet. But if the disease becomes more dangerous, then inpatient treatment is indispensable.
Improper or lack of treatment can lead to various diseases that are dangerous to the life of the human body. Various treatments are prescribed for treatment, such as diet, enemas, some exercises, pharmaceutical treatment, and sometimes even surgery.
Proper nutrition for colitis contains liquid or semi-liquid products that are not able to form fermentation and putrefaction in the colon. With such a diet, fatty, salty, spicy, fried, sour, spicy, sweet foods are excluded. All of them cause irritation of the intestinal mucosa. Also, this diet lacks fruits, berries and vegetables. This diet should be followed throughout the treatment of the disease.
Therapeutic enemas are prescribed only by a doctor, if necessary, rinse the intestines from infectious antibodies and contents. Sometimes various additives are made into the enema in the form sea buckthorn oil to improve healing or chamomile infusion, which help reduce swelling and soothe the mucous membranes.
Exercises during colitis include exercises sufficient for the body, if they are not done, stagnation begins in the intestine, which reduces blood circulation, causes constipation. But it is worth remembering that with such a disease, prolonged sedentary movements are prohibited.
Treatment with medicines begins only after full information about the disease, its form and origin.
- Antibacterial and antiviral drugs. They are prescribed only after the detection of irritants of viruses, infections, worms, microflora of the entire colon.
- To suppress the feeling of spasms and heaviness in the abdomen, noshpu or drotaverine is prescribed.
- In case of poisoning or intoxication, enterosorbents are prescribed, such as Polyphepan, Enterosgel.
- To relieve constipation and tension of the intestinal walls, you can drink antihistamines but only after a doctor's prescription.
- With dehydration, a solution of table salt is injected into the body.
- With a severe course of the disease, doctors prescribe glucocorticosteroids.
- For the recovery process of the intestine, the intake of probiotics is recommended.
The process of life after the disease
The first time is to continue to engage in proper nutrition. You can not starve or overeat, eat in small portions, but often, up to six times a day. It is necessary to completely abandon alcoholic beverages, energy drinks, smoking. Start exercising, within reason. More often to be in the fresh air, nature.
Surgical intervention
It is necessary for dying and complicating processes. The most common reasons for surgery are discussed below.
Lack of necessary results after drug treatment. Ulcerative colitis is often treatable with pharmaceuticals, but sometimes the patient may experience repeated outbreaks of the disease with severe symptoms, then it is worth considering the need for surgery.
Urgent cases. Surgical intervention, at times, is required for patients with acute progressions of the disease. For example, with severe diarrhea, dehydration, fever. These symptoms are not always drug treatment and requires intervention in the course of treatment.
Advantages of the operation
- The patient gets rid of the pain associated with colitis.
- Absence of symptoms interfering with life.
- Opportunity to refuse drug treatment.
- Rehabilitation after surgery and impact on daily life
After the hospital, the patient returns home weakened and tired, at first he will not have the strength to do ordinary things. But gradually strength will return to him, the desire to pursue his hobbies. But this period differs for everyone both in time and in the course of the recovery itself. This is played by various factors, such as age, organism, heredity, conditions and many others.
The intestine is part of the human gastrointestinal tract. It consists of the duodenum, small intestine and large intestine. Its main function is the digestion of food with the help of digestive enzymes to simpler compounds and their absorption into the blood. Various factors can lead to dysfunction of the intestinal mucosa and its inflammation. 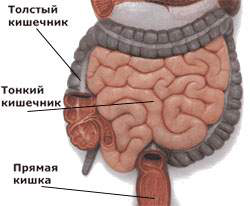 is a collective term that characterizes the presence of an inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of one or more sections of the intestine. In terms of frequency, this condition ranks second among all diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, with the same frequency it occurs in people of both sexes and all age categories.
is a collective term that characterizes the presence of an inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of one or more sections of the intestine. In terms of frequency, this condition ranks second among all diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, with the same frequency it occurs in people of both sexes and all age categories.
Causes
Inflammation in the intestines can develop as a result of many different causes, for convenience they are all divided into several main groups:
The mechanism of development of inflammation is associated with the fact that as a result of exposure to a damaging factor, the cells of the mucous membrane die, the blood supply to the site increases (hyperemia), pain and dysfunction occur (cells inflamed area do not secrete enzymes, absorption stops nutrients).
Classification
Inflammation of the intestine is divided into several types, depending on the localization of inflammation, the duration of the process and the causes.
According to the localization of the process, intestinal inflammation is divided into the following types:
- inflammation of the duodenum (duodenitis) - the process develops in the initial section of the small intestine, inflammation of the duodenal bulb (the place where the stomach passes into the small intestine) is isolated separately;
- inflammation of the small intestine (enteritis) - there may be inflammation in a limited area, but more often it occurs throughout the entire small intestine;
- inflammation of the large intestine (colitis) - occurs both in infections and in autoimmune processes, inflammation usually occurs throughout the entire large intestine.
According to the duration of the process, there are:
- acute inflammation - the period of time during which inflammation develops does not exceed 1 month;
- chronic inflammation - the process lasts from six months or longer.
According to the causative factor, all inflammatory processes in the intestine are divided into 2 groups:
- infectious - the cause is any infectious agent (most often bacteria), these inflammatory processes are also called acute intestinal infections;
- non-infectious - all other causative factors (autoimmune processes, hereditary genetic factors, dietary errors, etc.).
Symptoms of inflammation of the intestine
For inflammatory diseases intestines are characterized by a series common symptoms, which do not depend on the localization of the process and the causes of occurrence:
- abdominal pain - the character is pressing or bursting, without a clear localization, the occurrence of pain is associated with spasm of the smooth muscles of the intestinal walls;
- nausea - indicates inflammation of the small intestine or duodenum, occurs after eating;
- vomiting - happens with inflammation in the upper intestines after eating, usually vomiting brings relief;
- bloating - due to increased formation of gases due to insufficiency of digestive enzymes during inflammation in the small intestine;
- unstable stool - there may be a loosening of the stool, up to the development of diarrhea (acute intestinal infection), inflammation of the large intestine is often accompanied by a tendency to constipation;
- weight loss is the result of insufficient absorption of nutrients from the small intestine;
- anemia (anemia) - a decrease in hemoglobin in the blood due to insufficient intake of iron into the body from an inflamed intestine.
Diagnosis of diseases
Diagnosis is carried out to clarify the diagnosis, cause and localization of inflammation. For this, the following additional methods of laboratory and instrumental examination are used:
- a clinical blood test - an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and the number of leukocytes makes it possible to suspect the presence of an inflammatory process in the body;
- coprogram - a laboratory study of feces makes it possible to assess the function of the intestine, to identify the insufficiency of digestive enzymes (by undigested dietary fiber residues);
- bacteriological examination of feces - examination of feces for the presence of bacteria, their identification and determination of sensitivity to antibiotics to select adequate treatment;
- fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy (FEGDS) - endoscopic examination of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum using a fiber optic tube with a camera and lighting, if necessary, it is possible to take a piece of the mucous membrane for histological examination(biopsy);
- colonoscopy - the principle is the same as FEGDS, only the sensor is inserted not through the mouth, but through anus, examined colon, the condition of the mucous membrane, the localization of inflammation is assessed;
- video capsule endoscopy modern method examination of the intestine, in which the patient swallows a capsule with lighting and a camera, the capsule passes through all parts of the intestine during the day, the information is transmitted via radio waves to a computer, allows you to assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the entire intestine.
What and how to treat inflammation of the intestine?
Treatment of intestinal inflammation is complex and includes several areas of therapy:
- aimed at eliminating the cause of inflammation. Antibiotics are used to kill bacteria. Immunosuppressants (drugs that reduce the activity of the immune system) are needed for autoimmune inflammation. For the destruction of helminths, antihelminthic drugs are taken - piperazine, albendazole.
- with intestinal inflammation is a fundamental factor in successful treatment, a menu is used that minimizes the load on the inflamed mucosa. Recommended products are lean meats, chicken, vegetables and fruits, black bread, low-fat dairy products. All dishes are steamed or boiled, they must not be fried, smoked or cooked over an open fire.
- used to relieve inflammation, anti-inflammatory drugs and sorbents are used that bind toxins in the intestinal lumen. To reduce the load on the intestines and create functional rest, enzyme preparations are used that contain digestive enzymes - pancreatin, mezim.
- helps to alleviate the patient's condition, relieve pain with the help of antispasmodics (drugs that relieve intestinal spasm - no-shpa), painkillers. To reduce bloating, take defoamers - espumizan.
It should be remembered that in most cases, chronic inflammation of the small intestine can be caused by dietary errors, so dietary recommendations are useful not only for the treatment, but also for the prevention of intestinal inflammation.
The intestine is the most important part of the digestive system, in which the breakdown of fats and proteins to monocompounds, the absorption of nutrients and biologically active substances into the blood. In addition, throughout its entire length, the intestines are inhabited by microorganisms that synthesize B vitamins and some humoral factors of the body's defense system. In view of this, intestinal inflammation should not be perceived as a disease of one organ, but as a serious pathology throughout the body.
Depending on the location of the lesion, inflammatory processes in the intestine are divided into local and total. Enteritis is especially distinguished - an inflammation that covers only thin department, and colitis - processes affecting the large intestine.
Causes of inflammatory processes in the intestines
Acute inflammatory processes in the intestines are not uncommon and can be observed even in children. An example of this is lactase deficiency, in which the baby's body is not able to absorb milk sugar - a rapid growth of putrefactive and gas-forming microflora is observed, which leads to acute enterocolitis. An equally common cause of intestinal inflammation in children is dysbacteriosis - colonization of the intestines by pathogenic microbes due to the absence of colonies of bifidus and lactobacilli.
The development of enteritis and colitis in adults are the most various diseases, infectious and non-infectious nature:
- Gastritis, in which inflammation often extends first to duodenum and then to the entire small intestine.
- Coprostasis is a difficulty in moving food masses through the intestines, which can be observed due to the lack of peristalsis and volvulus. At the same time, Escherichia coli, Proteus, putrefactive microflora intensively multiply in the stagnant masses of chyme. It should be remembered that volvulus poses a serious threat and needs urgent surgical intervention, so an appeal to a specialist is necessary.
- Infectious hepatitis is almost always accompanied by enteritis.
- Local inflammatory processes in the intestine can also be observed against the background of taking medicines such as diclofenac.
- Unreasonable fasting can cause enteritis due to the high aggressiveness of digestive juices.
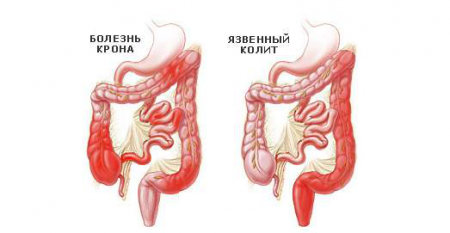
- Chronic ulcerative colitis is a disease of unknown etiology that occurs with a frequency of 1-2 people out of a thousand. In the mucous membrane of the large intestine, ulcerative foci are formed, regularly bleeding and non-healing.
- Crohn's disease. It is generally accepted that the disease is hereditary, and autoimmune processes are involved in its pathogenesis. The disease affects not only the mucous membrane, but also the own layer of the intestine, and changes can be observed throughout the entire digestive tract.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of acute intestinal inflammation is quite pronounced - sharp pains in the abdomen, painful urge to defecate and diarrhea with a lot of mucus often occur against the background of an increase in body temperature to 37.5-38 degrees. Blood may also be present in the feces, and enteritis is characterized by the presence of latent blood - the black color of feces, and for colitis - explicit, in the form of streaks or redness in the feces.
Chronic intestinal inflammation has an undulating course, with periods of exacerbations and remissions. In addition to abdominal pain and defecation disorders, deterioration is observed general condition- lethargy, drowsiness, apathy. In view of the violation of the synthesis of B vitamins, diseases of the skin and hair, dysfunction of the nervous system are noted.
With ulcerative chronic colitis and Crohn's disease, due to a long course, skin lesions often take on the form of an independent pathology - phlegmon appears, pyoderma develops on the legs and arms, and even gangrene of the extremities is recorded. Decreased appetite and exacerbation of soreness after eating lead to a decrease in the patient's body weight.
Treatment
The course of treatment for inflammatory bowel disease must be prescribed by a qualified specialist. The very first point in the intensive treatment of intestinal inflammation is the diet - it is strictly forbidden to eat smoked and salty foods, fried foods, most vegetables and fruits - all these foods can increase the secretion of digestive juices and have an irritating effect. The first few days after the diagnosis is recommended fasting with a plentiful drinking regime, if this is not possible, then it is allowed to eat a small amount of rice and oatmeal.
At acute inflammation small intestine good healing effect have adsorbents, astringents and mucous decoctions. Flax seed, oak bark - generally recognized folk remedies. As anti-inflammatory drugs from folk therapy, you can use galangal tincture, propolis extract, chamomile decoction.
