Symptoms and treatment of acute gastroenterocolitis. Acute and chronic gastroenterocolitis: symptoms and treatment in children and adults.
Acute gastroenterocolitis is a fairly common disease that belongs to the group of toxic infections. The disease is accompanied by inflammatory lesions of the digestive tract, and the foci are mainly localized in the small and large intestine. This is a dangerous condition, as the disease develops extremely rapidly. On the other hand, with proper treatment, the symptoms of the disease disappear already in 3-4 days.
Acute gastroenterocolitis (ICD 10): classification
Of course, patients are interested in additional information about this disease. So where in the international classification of diseases to look for acute gastroenterocolitis? The ICD-10 code looks like K-52.
This group contains almost all types of gastroenteritis and colitis, including toxic, allergic, alimentary, as well as those forms of the disease, the causes of which could not be found out.
Infectious inflammation and its pathogens
According to the ICD, acute gastroenterocolitis is a toxic infection. Pathogens, as well as toxic products of their vital activity, can spread throughout the body both through the digestive system and along with the bloodstream.
Depending on the type of pathogen, acute gastroenterocolitis is divided into several groups.
- The most common form is the bacterial form of lesions. The inflammatory process occurs against the background of the activity of salmonella, ischerichia, E. coli, shigella and other bacteria.
- The disease can be fungal in nature - in most of these cases, yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida act as the causative agent.
- The reasons include the ingestion of viral particles into the body, including rotavirus, ECHO virus, etc.
- Protozoal gastroenterocolitis (acute) develops against the background of penetration into the body of the simplest unicellular organisms, including amoebas, Giardia and Trichomonas.
Pathogenic microorganisms can enter the human digestive system along with contaminated dairy products, canned food, unwashed vegetables and fruits. Sometimes the infection is directly transmitted from an infected animal or person to a healthy one. Also, do not eat pastries with a cream layer, if all the rules for its storage have not been followed.
The main causes of non-infectious forms of the disease
Acute gastroenterocolitis (ICD code K-52) is not always associated with infection of the body. There are a number of other factors that contribute to the onset of the disease.
- Sometimes inflammatory processes in the intestines are the result of an allergic reaction.
- Gastroenterocolitis can occur against the background of alcohol intoxication.
- The development of the disease can lead to the ingestion of poisons, salts of heavy metals, alkalis, acids and other chemically aggressive substances.
- Often during the diagnosis, it is found that toxic damage is associated with uncontrolled medication, in particular an overdose of salicylic acid and diuretin derivatives.
- There is also the so-called alimentary gastroenterocolitis. An acute inflammatory process in this case develops against the background of malnutrition, frequent overeating, eating too spicy, hard or cold food, its irregular intake, and an excess of fiber and fat in the diet.
Types of gastroenterocolitis

Depending on the nature and characteristics of the inflammatory process, it is customary to distinguish several forms of gastroenterocolitis:
- hemorrhagic form - accompanied by the formation of small bleeding erosions on the mucous membrane;
- the catarrhal form is characterized by hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membranes along with the secretion of a large amount of exudate;
- ulcerative gastroenterocolitis (acute) is accompanied by ulcerative lesions of the walls of the digestive tract;
- the phlegmous form is characterized by a purulent lesion, and the gastric mucosa most often suffers;
- the fibrous form is considered quite rare and is accompanied by the formation of fibrinous films on the surface of the lining tissues of the digestive tract.
Symptoms of gastroenterocolitis
Gastroenterocolitis - acute illness which is characterized by rapid progression. As a rule, the disease begins with the onset of soreness, followed by bloating, increased gas formation, and a distinct and frequent rumbling in the abdomen. Many patients complain of severe heartburn, frequent belching, and an unpleasant bitter taste in the mouth.

The disease is characterized by a decrease in appetite. Patients suffer from nausea and severe vomiting, and large undigested pieces of food may be present in the vomit. In the first two days, there may be a delay in stool, which then abruptly turns into diarrhea. Blood streaks and lumps of mucus may be present in the feces.
There is a sharp increase in temperature - up to 38-39 degrees. When examining the patient, one can note the formation of a gray coating on the tongue. The skin of a person becomes paler. As the disease progresses, metabolism is disturbed, the patient quickly loses weight. The list of symptoms includes headaches, muscle weakness, confusion. In severe cases of the disease, fainting is possible.
Acute gastroenterocolitis in children: features of the course of the disease
According to statistics, children are more prone to this toxic infection due to the imperfection of the immune system. Naturally, the clinical picture in a small patient has some features. In particular, the disease begins with a fever - the temperature rises sharply to 38-40 degrees.
Vomiting is also present - urges occur constantly. The child complains of abdominal pain and diarrhea, and blood is often present in the feces. Due to oxidative processes in the intestines, feces may turn green. A child with similar symptoms should be taken to the hospital immediately, as children's body more prone to dehydration and its attendant unpleasant consequences.
Modern diagnostic methods
First of all, the doctor conducts an examination, finds out all the symptoms, collects an anamnesis. The clinical picture, as a rule, gives reason to suspect gastroenterocolitis. Naturally, additional studies are required, including a blood test (a high number of leukocytes indicates the presence of an inflammatory process). Fecal and vomit masses are also necessarily sent for laboratory research - tests make it possible to determine not only the pathogen, but also its sensitivity to certain drugs.
In addition, it is important to determine what exactly became the source of infection (if there is a suspicion of infectious gastroenterocolitis). Products are also sent for laboratory analysis. This is important, because by discovering exactly how the infection is transmitted, an epidemic can be prevented.
Treatment of gastroenterocolitis

Treatment acute form inflammation is carried out exclusively in a hospital, namely, in the infectious diseases department of the hospital. In most cases, supportive care is needed. If dangerous foods or poisons have been consumed recently, gastric lavage is performed. In addition, patients are prescribed sorbents, as well as drugs that accelerate the elimination of toxic substances from the body (including those that appeared as a result of metabolism). pathogenic microorganisms).
Since gastroenterocolitis is associated with a significant loss of fluid, drinking plenty of water and taking Regidron is indicated - this will help restore the water-salt balance in the body. With profuse vomiting, patients may be prescribed Cerucal, Reglan, or other antiemetics (usually administered intravenously due to constant vomiting spasms). But the use of antidiarrheal drugs is not recommended.
Of course, nutrition is an important part of therapy. Properly formulated diet will help speed up the process of recovery of the patient. Food should be light, but at the same time provide the body with the necessary nutrients. Good on the patient's condition will affect cereals, vegetable and fruit soups.

Be sure to exclude from the diet fried and fatty foods, spicy and smoked foods, spices, sour fruits, in a word, everything that can irritate the intestinal mucosa. It is also worth strictly limiting the amount of black bread, milk, various fruit compotes.
The best option is fractional meals, and you need to eat often (6-7 times a day), but in small portions - this will ensure quick digestion of food. Since acute gastroenterocolitis is associated with dehydration, it is necessary to observe at least 2-3 liters of purified water per day.
All these activities help not only to get rid of the disease, but also to restore the functions of the digestive system.
Pain in the abdomen, accompanied by vomiting, nausea, diarrhea or constipation, indicates that an inflammatory process has begun in the stomach, intestines - acute gastroenterocolitis. If you just take pills that usually help get rid of the ailment, then the pain will subside, the stool will return to normal, but the cause will not be eliminated. And this means that the inflammatory process will go on, the structure of the mucous membrane will be disturbed, ulcers may form that will bleed. The stomach and intestines will no longer cope with their direct duties (digestion, absorption of food), this will lead to exhaustion and disruption of the work of all body systems. Therefore, it is imperative to establish the cause of gastroenterocolitis in order to begin adequate treatment.
Dependence of the treatment of gastroenterocolitis on the cause
A variety of factors can cause an inflammatory process on the mucous membrane. But initially, the disease affects some part of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), and only because of improper treatment does it develop into gastroenterocolitis. Provoke the occurrence:
- intestinal infections;
- malnutrition;
- exposure to allergens;
- diseases of the pancreas and liver;
- nervous tension.
And accordingly, the cause needs to be treated, and gastroenterocolitis is a consequence. So, for example, the disease can be caused by various microorganisms:
Accordingly, it is necessary to treat the disease in different ways. Even antibiotics can only work on one type of bacteria and not cause the slightest harm to another. In this case, an infectious disease specialist should select an adequate therapeutic course.
With psycho-emotional overstrain, it is excited nervus vagus, which innervates the entire gastrointestinal tract, spasm occurs smooth muscle, which in turn causes severe pain and impaired stool. In this case, help:
- sedatives (corvalol, validol);
- antispasmodics (spasmolgon, no-shpa).
Which of them will be more effective, the doctor will advise.
Naturally, if the cause is not eliminated, if concomitant diseases are not cured, especially the liver and pancreas, it will be impossible to restore the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
And over time, this will lead to a violation of the metabolism of all substances. Not to mention that vomiting and diarrhea cause severe dehydration, and in this case acute gastroenterocolitis in children can be fatal.
But the most dangerous and most common cause of gastroenterocolitis is malnutrition. In a child, the disease may occur due to early refusal breastfeeding. In some cases, inflammation occurs due to intolerance to certain foods and even milk. The most harmful for the normal functioning of the digestive tract:
- fast food when food is badly chewed;
- food, anywhere and anytime;
- medicines not prescribed by a doctor (especially aspirin and some antibiotics);
- dry food;
- binge eating.
To prevent infectious inflammation, it is necessary to adhere to the elementary rules of personal hygiene.
Eating a large amount of vegetables and fruits containing coarse fiber can also contribute to inflammation of the mucosa. This does not mean that they should not be eaten at all. You can eat everything, but the main thing is to know when to stop and remember that some foods can only be consumed once in a lifetime (pale toadstool, expired foods, swollen canned food and other foods that cause severe poisoning, even death).
Whatever factor caused the disease, treatment acute gastroenterocolitis needs to start immediately. If you wait for serious complications, when pathological changes all organs are affected, then it will take much longer to be treated, and it is likely that it will not work.
Consequences of the disease
If you do not pay attention to the symptoms of gastroenterocolitis in time, or if you feel pain in the abdomen, nausea, take pills without consulting a doctor, then over time acute inflammation develop into chronic. And this means:
- There will be irreversible pathological changes in the mucosa. Up to necrosis, the appearance of ulcers on it. And over time, the intestines and stomach atrophy, the food will not be digested, instead, the processes of decay will begin.
- Due to the lack of micro and macro elements, metabolic disorders will occur. In turn, this will lead to dystrophy, osteoporosis. Due to the lack of glucose and vitamins, especially group B, there will be malfunctions in the central nervous system.
- Frequent diarrhea and vomiting cause severe dehydration. The skin will become dry, hair brittle, but these are not the worst consequences. Lack of fluid in the body leads to a decrease in the volume of circulating blood. Due to the disturbed water-salt balance, convulsions will occur, and in severe cases - coma.
There is only one effective way to prevent the occurrence of serious consequences - proper treatment gastroenterocolitis. And only a doctor will prescribe it.
How is gastroenterocolitis treated?
![]()
The therapeutic course largely depends on the cause of the disease. But there are drugs that are prescribed in any case. It:
- Painkillers. But they are recommended only for the relief of severe pain.
- Pro- and prebiotics. The inflammatory process in the intestines, taking antibiotics negatively affects the normal microflora. The growth of the necessary lacto- and bifidobacteria is inhibited. And this leads to a deterioration in digestion, contributes to the development of pathogens.
- Sorbents and drugs for detoxification. Especially with intestinal infections, when microorganisms synthesize toxins, persistent poisoning occurs.
- Carry out the correction of metabolism, prevention of anemia and hypovitaminosis.
But the mainstay of treatment for gastroenterocolitis is diet. Recommend table number 4.
What to eat and what not to eat with gastroenterocolitis
- spicy, salty;
- cold or hot;
- rough, tough;
- promote the formation of gases in the intestines;
- containing alcohol.
But this does not mean that only slimy and unappetizing cereals are possible. Large number allowed delicious food, and if they are also decorated (methods to make attractive appearance there are many dishes), then food will contribute not only to the intake of necessary substances into the body, but also to aesthetic pleasure.
With gastroenteritis it is allowed:
- soups with low-fat broth;
- cereals;
- butter;
- grated cottage cheese (fresh milk is strictly prohibited);
- vegetables and fruits, but peeled, without rough skin;
- low-fat meat and fish dishes, it is better if they are steamed;
- soft-boiled egg, steam omelette (no more than 1 per day);
- kissels, jelly;
- compote, weak tea.
- rosehip decoction;
- weak, unsweetened blackcurrant compote.
You can starve for no more than 2 days, and then with very strong diarrhea.
In acute gastroenterocolitis in children, especially young children, with severe diarrhea and vomiting, it is necessary to ensure that there is no dehydration. To do this, constantly restore the lost fluid. The patient is given after each bowel movement to drink warm, boiled water approximately in the volume that was lost.
Diet for gastroenterocolitis should be followed for a long time, even after recovery. After all, this disease easily becomes chronic, especially if you do not eat right.
This is an inflammatory process that simultaneously covers the entire digestive tract, affects the intestines most of all, proceeds in acute and chronic form. Is infectious and non-infectious, including allergic. The cause of gastroenterocolitis of the infectious form is the reproduction in the intestinal tract of pathogens, most often bacteria (Salmonella, E. coli, streptococci, staphylococcal enterotoxins, shigella) and rotavirus. This condition is called food poisoning. The disease is not seasonal, but most cases are recorded in the spring and autumn. Infection of entire groups in kindergartens, schools, families is not uncommon. The causative agents of infection:
- Infected person.
- infected animal.
- Dairy.
- Cream pastry.
- Cottage cheese.
- Canned meat and fish, pates.
- Dirty vegetables and fruits.
Varieties and features of the disease
In some cases, the infection enters the digestive tract with blood flow from other organs, for example, with tuberculosis or typhoid. Persons suffering from anemia, beriberi are more disposed to the disease. A non-infectious form of inflammation develops most often against the background of an unbalanced diet. The rarest - allergic, develops when eating food allergens. Some medications, as well as poisons that enter the body, can also affect the intestines, provoking acute drug-induced gastroenterocolitis. Chronic Cause its development are long-term violations of the digestive system. Gastroenterocolitis of such a course is not completely cured, from time to time the condition worsens, then remission occurs. Deterioration of well-being is associated with a violation of the diet, the ingress of infections into the body, a drop in immunity. If, as a result, inflammation progresses to thin department intestines, the body suffers from poor digestibility of food, the patient weakens and loses weight. Symptoms Infectious and allergic varieties of the disease are characterized by rapid onset and intense course. The latent period of infection development is no more than a few hours. An allergic reaction occurs no longer than an hour after the allergen hit. The first symptoms of gastroenterocolitis:
- Diarrhea with mucus, sometimes blood,
- Vomit,
- paroxysmal pain in the epigastrium,
- lethargy,
- increase in body temperature,
- Fever,
- There is a thick layer of grayish coating on the tongue,
- Headache.
As a rule, they are held for two to three days, after which the weakness remains, but gradually the patient's health returns to normal. The duration of the disease in a mild form is up to seven days. In especially severe cases, the patient's consciousness may be disturbed, the work of the heart and blood vessels, goes into a chronic stage. Diagnosis 1. First of all, the doctor relies on information about the patient's nutrition and well-being and examination data. 2. If an infectious form is suspected, food is examined to detect the pathogen, vomit, feces are taken for analysis. 3. Allergic reaction detected by special tests or blood tests. Treatment in children and adults For the treatment of severe acute gastroenterocolitis of infectious origin, the patient is referred to a hospital. Therapeutic measures:
- gastric lavage,
- Warmer on the stomach
- antimicrobials,
- Antispasmodics (papaverine, atropine),
- Supportive medications (glucose and vitamin drip, heart maintenance medications).
If it proceeds easily, then it is quite possible to get by with the dietary measures described below. Particular attention should be paid to the condition of young patients. A child's body dehydrates faster than an adult, and the consequences of dehydration can be more serious, up to the failure of vital organs: kidneys, liver and heart. Therefore, the drinking regime must be observed! With an increase in body temperature, indomitable vomiting and great weakness must be called immediately ambulance and hospitalize the child! Diet in acute form To alleviate the patient's condition, it is necessary to completely unload the stomach, that is, nothing can be eaten for at least two days from the onset of the first symptoms. However, diarrhea and vomiting dehydrate the body. To make up for the lack of fluids and salts, it is necessary to give the patient to drink infusions of herbs, rose hips, weak tea with lemon and sugar, freshly squeezed juices, half diluted with boiled water. All drinks should be served slightly warm. Drink in small portions, constantly. The daily volume of liquid for children is 1 - 1.3 liters, for adults up to 2.5 liters. Then you can enter into the menu jelly, liquid viscous cereals from oatmeal, rice, curd mass without lumps. Later, you can introduce broths, steam cutlets and boiled meatballs, boiled fish, casseroles and soft-boiled eggs.
The diet for gastroenterocolitis involves only food of a very soft consistency. If the patient is better, from the 4th day of the illness, you can feed him according to the therapeutic diet No. 4, after another week - No. 4B, and after the complete normalization of the intestines - No. 4B.
Nutrition in the chronic form Nutrition should be sparing, easily digestible in order to relieve the inflammatory process in the intestines and stomach, to eliminate toxins from the body. Eat at least five times a day. It is strictly forbidden to eat rough, spicy, acidic foods that irritate the mucous membrane. Prohibited foods: milk, Rye bread, tough meats, canned food, sausages, roasts, pickles and marinades. The basis of the menu is proteins of animal origin: lean poultry meat, cottage cheese, sour-milk products, soft cheeses, low-fat fish only in boiled form, broths. You can use a small amount of well-boiled rice, semolina, oatmeal without milk! Babies should boil pureed vegetable soups and add separately cooked poultry meat to them. Prevention:
- Thorough washing of fruits and vegetables before eating.
- The use of dairy, meat products and eggs, only bought in a store or in authorized markets.
- Compliance with hygiene standards when preparing food at home.
- Washing hands before eating.
- Treatment of infectious diseases under the guidance of a doctor.
- Strengthening immunity.
- Reception vitamin preparations Twice a year.
Gastroenterocolitis is a disease in which inflammation of the mucous membranes of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract occurs. This pathology affects the stomach, thin and colon. Acute gastroenterocolitis most often develops due to food poisoning - poisoning with poor-quality food products infected with pathogenic microorganisms. The causative agent of the disease can be bacteria and viruses. Also, infection of the mucous membranes can occur through the blood. Gastroenterocolitis often develops in children whose immune system is not yet fully formed and is not able to protect the children's body from infection.
Folk remedies are used to treat the disease. Such treatment has an antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory effect, normalizes digestion and envelops the mucosa, contributing to its regeneration. Folk remedies act on the human body gently and do not cause side effects.
Causes of the disease
 Infectious inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract can be bacterial or viral in nature. In the case of a bacterial infection, the pathogen most often enters the digestive tract with food and water. The main causative bacteria of gastroenterocolitis are pathogenic strains of bacteria of the Escherichia coli group: Shigella, Proteus and Escherichia coli itself.
Infectious inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract can be bacterial or viral in nature. In the case of a bacterial infection, the pathogen most often enters the digestive tract with food and water. The main causative bacteria of gastroenterocolitis are pathogenic strains of bacteria of the Escherichia coli group: Shigella, Proteus and Escherichia coli itself.
Viral infection of the mucous membrane is considered more dangerous and more severe. Most often, patients develop intestinal flu- a disease caused by
In some cases, the infection enters the gastrointestinal tract with the bloodstream from other foci of chronic infection. In this case, the pathogen will be the microorganism that causes this infection.
Some patients develop noninfectious gastroenterocolitis. Such a disease can be caused by severe intoxication of the body with heavy metals, alkalis, acids. Sometimes this condition occurs in children who may drink or eat, for example, household chemicals or other toxic substances.
Exacerbation of the chronic form of the disease can be caused by the following factors:
- decreased immunity against the background of hypothermia, intoxication, and other diseases;
- acidification of the body;
- unbalanced diet.
The likelihood of developing gastroenterocolitis is higher in people with mild immune system. Often, such a disease affects children who have not yet fully formed either immunity or the composition of the normal intestinal microbiota. Also, the disease can develop against the background of antibiotic therapy, during which the natural inhabitants of the human intestine die.
Disease classification
The diagnosis "gastroenterocolitis" is a collective name for a number of inflammatory infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Depending on the type of inflammatory process, there are:
- hemorrhagic gastroenterocolitis - develops mainly in small intestine, characterized by the occurrence of erosion and bleeding;
- phlegmonous gastroenterocolitis - purulent inflammation of the mucous membrane, which develops mainly in the stomach
- catarrhal gastroenterocolitis - affects the mucous membranes of the entire gastrointestinal tract, with swelling and redness of the mucous membranes with copious excretion mucus;
- ulcerative gastroenterocolitis - ulcerations form on the mucous membranes of the stomach and intestines;
- fibrous enterocolitis is a rare form of the disease in which fibrin films form on the mucous membranes of the stomach and intestines.
There are also acute and chronic types of diseases. The chronic type is characterized by a long course with intermittent relapses.
Symptoms of the disease
After the pathogen enters the gastrointestinal tract, an incubation period begins, during which the pathogenic microorganism adapts to new conditions and begins to multiply. The duration of this period depends on the nature of the infection. If pathogenic bacteria enter the stomach through the alimentary route (with food or water), then the incubation period is short and lasts only a few hours, but it can last up to 2-3 days.
 After the incubation period, symptoms characteristic of acute gastroenterocolitis occur, and treatment should be started immediately. The diagnosis is made on the basis of the following clinical manifestations:
After the incubation period, symptoms characteristic of acute gastroenterocolitis occur, and treatment should be started immediately. The diagnosis is made on the basis of the following clinical manifestations:
- , bloating and rumbling in the intestines;
- indigestion: which may occur on the first day or a few days after the onset of the pathological process;
- in the feces with diarrhea, there may be mucus and streaks of blood;
- before the onset of diarrhea, constipation is possible;
- pain in the abdomen, the pain may be cramping or pulling;
- symptoms of intoxication: general weakness, headache and dizziness, chills, fever;
- disruption of the stomach: heartburn, belching, bitterness in the mouth;
- nausea and vomiting;
- a sharp decrease in appetite, with a long course of infection, a strong weight loss is possible.
In acute gastroenterocolitis, the symptoms appear abruptly, and the patient's condition deteriorates rapidly. The infection spreads to all organs of the gastrointestinal tract. With the development of an acute form of the disease, it is very important to start immediately complex treatment. If this is not done, there is a high probability that gastroenterocolitis will become chronic. In the chronic course of the disease, the symptoms are less pronounced, and appear periodically during periods of exacerbation. This disease can last for years.
Diagnosis of pathology
The diagnosis is made on the basis of clinical manifestations. But it is important to accurately identify the source of infection. For this, whenever possible, bacteriological examination suspicious food samples. A bacterial culture of the patient's feces is also done on differential diagnostic microbiological media.
Treatment of gastroenterocolitis
 The first aid in the development of acute gastroenterocolitis is gastric lavage. The patient must be induced to vomit. For these purposes, they give him to drink about a liter of boiled water. cold water in one gulp. Pressing the fingers on the root of the tongue can cause vomiting. It is necessary to wash the stomach until food particles disappear from the vomit.
The first aid in the development of acute gastroenterocolitis is gastric lavage. The patient must be induced to vomit. For these purposes, they give him to drink about a liter of boiled water. cold water in one gulp. Pressing the fingers on the root of the tongue can cause vomiting. It is necessary to wash the stomach until food particles disappear from the vomit.
With the development of gastroenterocolitis, treatment consists in taking antimicrobial agents that suppress the reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms. Exist folk methods treatment of gastrointestinal infections based on the intake of drugs based on medicinal plants. Such therapy has a complex effect on the patient's body: it inhibits the development of pathogenic microorganisms, helps in the removal of toxins from the body and helps to restore the damaged mucosa.
Folk recipes:

Treatment of gastroenterocolitis also includes temporary dieting and restoration of water-salt balance. The fact is that with vomiting and diarrhea, the human body loses a large amount of fluid with mineral salts dissolved in it. To combat dehydration, it is necessary to drink saline solutions, for example, saline (9 g of common salt per 1 liter of water) or still mineral water.
In the first days of the disease, a person is only shown to drink plenty of water, since the body cannot absorb any food anyway. You can drink mineral water. It is also useful to drink a decoction of various cereals.
 After a few days, when there is some relief, you can gradually introduce some foods into the diet. Boiled mashed food is recommended, protein is best. It is necessary to exclude from the diet fried, spicy, salty foods, poorly cooked meals, fatty foods, as well as vegetables and fruits that contain a lot of fiber and can irritate damaged mucous membranes.
After a few days, when there is some relief, you can gradually introduce some foods into the diet. Boiled mashed food is recommended, protein is best. It is necessary to exclude from the diet fried, spicy, salty foods, poorly cooked meals, fatty foods, as well as vegetables and fruits that contain a lot of fiber and can irritate damaged mucous membranes.
Prevention of gastroenterocolitis
Prevention of the disease is primarily the observance of personal hygiene measures.
It is necessary to wash hands before eating, thoroughly wash vegetables and fruits. Products must be of high quality. It is better not to trust food prepared by someone else, do not buy it in the ready-made food department, since such food is often made from stale products.
It is important to carry out high-quality heat treatment of food, not to eat half-baked dishes. During heat treatment, most bacteria die.
Most often, the bacteria that cause gastroenterocolitis enter the human body with meat and fish dishes, sausages, and canned food. When choosing these foods, you need to be especially careful.
Write in the comments about your experience in the treatment of diseases, help other readers of the site!
Share the material on social networks and help your friends and family!
Gastroenterocolitis - the course of the inflammatory process simultaneously in the stomach, large and small intestines. It is a serious condition because it can cause severe dehydration of the body. The disease is characterized by spontaneous onset and rapid course. The disease can occur in acute or chronic form, and can also be caused by infectious and non-infectious causes. It equally affects men and women, and is also often diagnosed in children.
The reasons for the formation of such a disorder can be: irrational nutrition or pathological effects of certain microorganisms. In addition, the disease can be contracted from another person or provoked by prolonged use of antibiotics.
The degree of intensity of manifestation of symptoms depends on the stage of gastroenterocolitis. Often there are such clinical manifestations, as an increase in body temperature, diarrhea, bouts of nausea with profuse vomiting, bloating and increased gas formation, as well as pain in the abdomen and loss of appetite. Symptoms and treatment of gastroenterocolitis in children and adults are somewhat different.
In the diagnosis, an important role is played by the study by a specialist of the medical history and anamnesis of the patient's life. Additionally, several instrumental and laboratory studies are used. The disease can be treated with medication and diet therapy. Surgical operations for this disorder are not provided.
Etiology
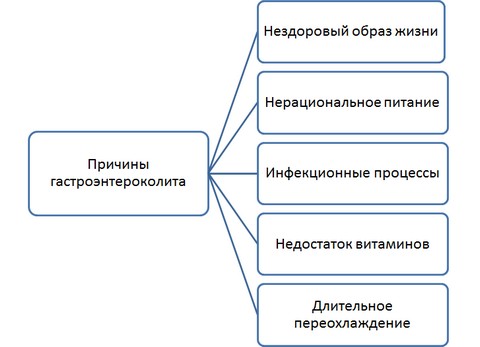
There are several predisposing factors, the totality of which can serve as the formation of such an ailment in both an adult and a child. The main causes of gastroenterocolitis are:
- maintaining an unhealthy lifestyle;
- the course of infectious processes in the organs of the digestive system;
- poor nutrition, frequent episodes of overeating, eating low-quality food, as well as addiction to excessively fatty and spicy foods;
- penetration into the body and reproduction of salmonella, E. coli, staphylococcus and other microorganisms, as well as rotavirus or enterovirus infection;
- the presence of a disease such as ulcerative colitis;
- prolonged use of some medicines eg antibiotics;
- individual intolerance to a particular food product;
- harmful working conditions under which a person is forced to come into contact with chemical poisons and toxins, which is why their entry into the body is not excluded;
- deficiency in the body of one or a group of vitamins;
- prolonged hypothermia of the body;
- non-observance of hygiene rules before eating;
- consumption of unwashed vegetables and fruits.
Due to the fact that the disease can be infectious in nature, the possibility of infection from one person to another is not excluded, which is one of the main reasons for the formation of gastroenterocolitis in children.
Varieties
There are several classifications of the disease. Depending on the nature of the manifestation of symptoms, the disease is divided into:
- acute form of leakage The incubation period ranges from several hours to three days. During this time, a large number of characteristic features illness;
- chronic gastroenterocolitis - the manifestation of symptoms is not as pronounced as in the previous form. Differs in the recurrent nature of the course.
Depending on the causes of the disease, gastroenterocolitis is infectious and non-infectious. Infectious type of illness, in turn, can be:
- bacterial- the most common form of the disease, which is caused by various bacteria;
- viral- due to the ingestion of a virus into the body;
- fungal- caused by fungi from the genus Candida;
- protozoan- the formation is facilitated by the presence in the human body of the simplest unicellular organisms, including Giardia and Trichomonas.
By the nature of the course of the inflammatory process, the disease is:
- hemorrhagic- due to erosive lesions of the mucosa;
- catarrhal- characterized by severe redness and swelling of the membrane, as well as increased production of exudate;
- phlegmonous- in the diagnosis, a purulent lesion of the organ is observed. The severity of the course depends on the area of the lesion;
- ulcerative- the formation of ulcers on the mucous membrane of the digestive tract;
- fibrinous- a dense fibrinous film is formed on top of the mucous membrane. This form of the disease is extremely rare.
Regardless of the variety, the treatment of gastroenterocolitis consists in prescribing medications and diet therapy.
Symptoms
In the acute course of the disease, the clinical picture is expressed suddenly and develops rapidly. The main symptoms of the disease are:
- a decrease or complete lack of appetite, against which a person loses weight;
- bouts of nausea, which quite often end in profuse vomiting;
- severe headaches and dizziness;
- increased fatigue and weakness, in severe cases up to loss of consciousness;
- stool retention for several days, after which the feces take the form of diarrhea. The feces may contain particles of blood and mucus;
- soreness in the abdomen, which has a pulling or cramping character;
- increase in body temperature;
- belching and heartburn;
- the appearance of an unpleasant aftertaste in oral cavity;
- significant bloating;
- increased gas emission;
- muscle weakness;
- impairment and confusion.
In addition, there may be signs of general intoxication of the body.
In children, the onset of the disease is caused by an incompletely formed immune system, which is why the symptoms of the disease may differ somewhat from the manifestation of the disease in adults. Thus, the symptoms of gastroenterocolitis in children are:
- a feverish state that does not subside for three days, after which the temperature drops slightly and lasts for about seven days;
- nausea, vomiting is temporary;
- diarrhea with a fetid odor, as well as impurities of blood and mucus;
- the formation of a dark green shade of feces.
With timely treatment, all signs of the disease will disappear in a week.
![]()
Diagnostics
Determining the correct diagnosis from an experienced specialist in the field of gastroenterology is not difficult. To do this, the doctor needs to get acquainted with the patient's medical history and anamnesis, as well as conduct a thorough examination, which must necessarily include palpation of the abdomen. Such events will help the specialist to detect the causes of the formation of the disease, as well as to find out the presence and degree of intensity of the symptoms.
To determine the severity and form of the course of this disease, additional instrumental and laboratory studies will be required. The second consists of holding a general and biochemical analysis blood, which will help to detect concomitant diseases. In addition, bacteriological studies of feces and vomit are carried out. In some cases, an allergic examination of the patient is necessary.
Instrumental diagnostic methods include:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- FEGDS - examination of the mucous membrane of the digestive tract;
- sigmoidoscopy - a procedure aimed at detecting pathologies of the membrane;
- biopsies;
- X-rays - with or without a contrast agent.
After confirming the diagnosis and studying the results of the examinations, the attending physician may prescribe an individual tactic for the treatment of gastroenterocolitis.
Treatment
With a mild and moderate course of the disease, therapeutic measures can be carried out at home, with a severe course, as well as when diagnosing a similar ailment in children, treatment is performed only in a medical institution.
Elimination of the disease consists of several stages:
- gastric lavage;
- therapeutic fasting for one or two days;
- detoxification of the body by taking individually prescribed substances. The duration of such treatment is approximately one week;
- taking antibiotics;
- the use of antispasmodics and laxatives.
In addition, to eliminate the disease, you must follow proper nutrition. The diet for gastroenterocolitis is to drink plenty of fluids, eat small meals, five times a day. At the same time, it is necessary to completely abandon fatty and spicy dishes, smoked meats and dairy products.
Timely drug therapy and proper nutrition will make it possible to completely get rid of such a disease in just seven days.
Preventive measures for gastroenterocolitis include thorough hand washing before eating, eating only high-quality foods, enriching the diet vitamin complexes, taking medications only as prescribed by a doctor, as well as following nutritional recommendations. If symptoms are ignored, the disease can lead to severe dehydration, which is a dangerous condition, especially for children.
Similar content
Acute gastroenterocolitis is a disease that entails the occurrence of an inflammatory process mainly in the small or large intestine. This disorder is characterized by a sudden onset and a rapid course. For this reason, it poses a serious danger to human life. But it is often found at a stage that is quite easily treatable, which is why after four days a significant improvement in a person’s condition occurs.
Esophageal diverticula are a pathological process characterized by deformation of the esophageal wall and protrusion of all its layers in the form of a sac towards the mediastinum. In the medical literature, the esophageal diverticulum also has another name - esophageal diverticulum. In gastroenterology, it is precisely this localization of the saccular protrusion that accounts for about forty percent of cases. Most often, pathology is diagnosed in males who have crossed the fifty-year milestone. But it is also worth noting that usually such individuals have one or more predisposing factors - peptic ulcer stomach, cholecystitis and others. ICD code 10 - acquired type K22.5, esophageal diverticulum - Q39.6.
Achalasia cardia is a chronic disorder of the esophagus, which is characterized by a violation of the swallowing process. At this point, relaxation of the lower sphincter is observed. As a result of such a violation, food particles accumulate directly in the esophagus, which is why there is an expansion of the upper sections of this organ. This disorder is quite common. Almost equally affects both sexes. In addition, cases of detection of the disease in children have been recorded. In the international classification of diseases - ICD 10, such a pathology has its own code - K 22.0.
Distal esophagitis is a pathological condition that is characterized by the progression of the inflammatory process in the lower part of the esophageal tube (located closer to the stomach). Such a disease can occur in both acute and chronic forms, and is often not the main, but a concomitant pathological condition. Acute or chronic distal esophagitis can develop in any person - neither the age category nor gender play a role. Medical statistics are such that more often the pathology progresses in people working age as well as in the elderly.
Candida esophagitis is a pathological condition in which the walls of this organ are damaged by fungi from the genus Candida. Most often, they first affect the oral mucosa (the initial section of the digestive system), after which they penetrate the esophagus, where they begin to actively multiply, thereby provoking the manifestation of a characteristic clinical picture. Neither gender nor age category affects development pathological condition. Symptoms of candidal esophagitis can occur in both young children and adults from the middle and older age groups.
