postpartum mastitis. Mastitis in newborns Treatment of purulent mastitis
The mammary glands are a "mirror", which indirectly reflects the entire state of the woman's body. The morphology of this organ is a close object of attention of doctors, because in many diseases it is in the chest that the first changes appear.
This is a group of pathologies that are different in terms of reasons and mechanism of development, encrypted by doctors with special numbers.
What do they mean, and how not to get lost in medical encryption in order to have full information about your health?
ICD 10 diagnosis statistics
ICD 10 (No. 60-64) diseases of the mammary glands are subject to careful statistical analysis. This is one of the reasons why the unified classification was introduced. According to the latest data from the World Health Organization, up to 40% of women suffer from mastopathy among the female population of the world, and more than half of all cases (up to 58%) are combined with gynecological disorders. Of particular interest is the fact that many breast diseases are also precancerous conditions. The frequency of morbidity and mortality from breast cancer is increasing every year, even despite the huge advances in medicine in the field of their early diagnosis and effective treatment. The lion's share of cases occurs in developed countries.
The internationally accepted classification of ICD No. 10 is also used in our country. Based on it, there are:
· N 60 - Benign growths of the mammary gland. Mastopathy belongs to this group.
· N 61 - Inflammatory processes. Among them are carbuncle, mastitis, abscess.
· N 62 - Enlargement of the mammary gland.
N 63 - Volumetric processes in the chest, unspecified (knots and nodules).
· N 64 - Other pathologies.
Each of these diseases has its own causes, characteristic clinical picture, methods of diagnosis and treatment. Let's talk about this now.
The definition of the disease was back in 1984 by the experts of the World Health Organization. It characterizes benign dysplasia as a combination of pathological mechanisms, manifested by both regressive and progressive changes in breast tissues with the appearance of abnormal relationships between the epithelium and the connective tissue.
Also, according to the definition, an important sign is the formation of changes in the breast such as fibrosis, cysts and proliferations. But this is not the primary symptom for making a diagnosis, because. it is not always available.
Clinical picture of the diagnosis
The disease can manifest itself in various ways. But the main symptoms can be distinguished:
· Dull pain in the mammary glands, which often tends to increase before the onset of menstruation. After the menstrual bleeding has passed, the pain usually subsides.
Irradiation - the spread of pain outside mammary gland. Often patients complain that pain is given to the shoulder, shoulder blade or arm.
The presence of education in the breast or compaction of its structure. This symptom can be determined by patients who are attentive to their state of health and regularly palpate.
Diagnostics
 The doctor begins the examination with a thorough collection of anamnestic data. The doctor clarifies the patient's onset of menstruation, its nature, cyclicity, soreness, profusion. The gynecological history is also important, which consists in the age of onset of sexual activity, the number of pregnancies, miscarriages, abortions, childbirth. Genealogical data will help to understand whether there were similar diseases in blood relatives in the female line. All this information helps to establish the correct preliminary diagnosis.
The doctor begins the examination with a thorough collection of anamnestic data. The doctor clarifies the patient's onset of menstruation, its nature, cyclicity, soreness, profusion. The gynecological history is also important, which consists in the age of onset of sexual activity, the number of pregnancies, miscarriages, abortions, childbirth. Genealogical data will help to understand whether there were similar diseases in blood relatives in the female line. All this information helps to establish the correct preliminary diagnosis.
An objective examination will help the doctor to identify the asymmetry of the mammary glands, and when they are palpated, to determine the presence or absence of neoplasms. Mammologists pay special attention not only to the consistency and structure of the mammary gland, but also to the color, size and condition of the nipples.
Instrumental methods confirm the correctness of the alleged diagnosis or, conversely, refute it and return the doctor to the beginning of the diagnostic search. Most often resort to mammography and ultrasound of the mammary glands. Additionally, the patient's blood and urine are studied.
Therapy
Treatment of diseases of the mammary glands No. 60 ICD10 is possible in 2 versions. The first is medication, which is used for diffuse growths. A good result can be achieved by hormonal agents, including oral contraceptives.
The second method is surgical, which is indicated for the nodular form. The removed formation is subject to mandatory histological examination to exclude the presence of atypical cancer cells. The prognosis after treatment is favorable.

ICD-10 No. 61 breast diseases included: abscess, carbuncle and mastitis, which is considered the most common pathology in this group.
Mastitis is an inflammatory disease. The defeat of the breast is often unilateral, and only in rare cases (not more than 10%) extends to both mammary glands. The cause of the disease is two main factors that overlap one another:
The first is a violation of the outflow of milk;
The second is the addition of pathogenic or conditionally pathogenic microflora.
Initially, the disease proceeds according to the type of aseptic (sterile) inflammation. However, very quickly, literally in a day, in conditions of stagnation of milk secretion and a favorable temperature, the microflora is activated. Thus begins the stage of bacterial inflammation.
Main symptoms

The clinical picture is almost the same in all women. The first symptom is a sharp rise in temperature to high values (38 - 39 ° C). Further, redness of the skin of one of the mammary glands joins, and then severe pain. As time goes by, they only get stronger. With severe inflammation and the absence of timely treatment, sepsis develops very quickly - a deadly complication.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is established on the basis of anamnestic, objective and laboratory data. From the anamnesis it turns out that the woman is breastfeeding. As a rule, the risks increase if you constantly apply the child in the same position. In this case, incomplete emptying of the gland occurs. An objective examination shows hyperemia of the inflamed gland, its slight increase, as well as sharp pain on palpation. A laboratory study in the blood reveals leukocytosis with high values.
Treatment
In the early stages, conservative (drug) treatment is also effective. The main condition is the thorough expression of milk. For these purposes, a breast pump is not the best solution; it is best to do it by hand. The patient can perform the procedure on her own, but often, due to severe pain, it is necessary to turn to specially trained people. Of the drugs resort to the help of broad-spectrum antibiotics. Usually these measures are enough for a complete recovery and further restoration of breastfeeding.
 In severe forms of the disease, before the appointment of an operative method of treatment, attempts are made to temporarily stop lactation with the help of special medicines. If this method was ineffective, then surgeons take up the treatment.
In severe forms of the disease, before the appointment of an operative method of treatment, attempts are made to temporarily stop lactation with the help of special medicines. If this method was ineffective, then surgeons take up the treatment.
Other inflammatory diseases of the breast
Carbuncles and abscesses of the mammary gland also occur in clinical practice, but are now becoming less and less common. Carbuncle of the mammary gland, as in any other part of the skin, is a purulent inflammation of the hair follicle and sebaceous gland. An abscess is a purulent fusion of the mammary gland limited from healthy tissues.
The cause of the disease in carbuncle is a blockage of the sebaceous gland, against which the pathogenic microflora has joined. An abscess can develop as a result of hematogenous or lymphogenous infection from other foci.
Both diseases occur with an increase in temperature, an increase in soreness in one of the mammary glands.
Treatment is often performed surgically. The abscess is opened, freed from purulent contents, treated with an antiseptic solution, and then drainage is established for a while. The patient is prescribed a course of broad-spectrum antibiotics. With timely treatment, the prognosis is always favorable.
In this group, it is customary to single out gynecomastia, which occurs only in men. It is characterized by the growth of breast tissue and, accordingly, its increase. In women, this process is called breast hypertrophy, and also belongs to this group.
The risk of hypertrophy increases the consumption of beer, because. This drink contains plant estrogens. They also stimulate active cell division.
It is worth noting that such a diagnosis is established not only in women, but also in men, but their ratio to each other is 1:18. Mostly women aged 20 to 85 are ill, but it is more common in 40-45 years. Mortality from the disease is 0%.
Causes
The etiology of the disease is not fully understood.
Clinical picture
The first time the disease has no symptoms at all, this is the so-called latent phase of the disease. The duration of this period is individual and can vary from several months to a year or more. The first symptom is periodic pain in the breast, which may increase before the onset of menstruation. Pain, as a rule, subsides immediately after the end of menstruation.

The biggest mistake of patients is that they do not pay attention to changes in their own body and do not go to doctors, attributing ailments to hormonal imbalances, the beginning of a new cycle, or intimacy. menopause. Over time, the pain takes on a constant aching character. With careful self-palpation, the patient can detect a formation in the chest, which often serves as a reason to see a doctor.
Diagnostics
Main research methods:
Collection of complaints
assessment of anamnestic data;
laboratory research methods (general clinical blood test, urinalysis, biochemical blood test or tumor marker test);
instrumental methods (ultrasound, mammography, biopsy).
Treatment
All breast neoplasms are subject to surgical treatment. After removal, the biological material in 100% of cases is sent to histological examination thus establishing an accurate diagnosis and the need for further treatment.
Other diseases of the breast (N64) ICD10
This group includes:

galactocele - a cyst in the thickness of the mammary gland, filled with milk;
involutive change after breastfeeding;
secretion from the nipple outside the lactation period;
Inverted nipple
Mastodynia is a condition that is perceived subjectively. It is characterized by discomfort in the chest. They may be present continuously or intermittently.
Prevention of breast diseases
A priority place in the working tactics among gynecologists and oncologists is propaganda for the prevention of breast diseases. These include social advertising, various medical brochures, preventive conversations with patients at the reception, the increase in the popularity of a healthy lifestyle, as well as the approval of World Breast Cancer Day.
To minimize the risk of developing the disease, and also not to miss it on early stage the following rules must be followed:
Refusal to smoke and drink alcohol;
treatment of acute diseases, as well as prolongation of the remission phase in chronic;
passing preventive examinations, especially over the age of 35 years;
Performing self-palpation of the mammary glands at home at least once every 4-6 months.

Benign breast dysplasia according to ICD-10 or mastopathy
Benign breast dysplasia according to ICD-10 or mastopathy is a disease of the mammary glands ( benign tumor). It appears as a result of tissue growth during various hormonal disorders and there are 2 types: nodular (single compaction) anddiffuse mastopathy(with multiple nodes).Mastopathy occurs mainly in women of reproductive age. This phenomenon is easy to explain. Every month in a young body, periodic changes occur under the influence of the hormones estrogen and progesterone, which affect not only menstrual cycle, but also breast tissue (stimulation and inhibition of cell division, respectively). Hormonal imbalance, causing an excess of estrogen, leads to tissue proliferation, i.e. to mastitis.Also, the untimely production of prolactin, the hormone of lactation, can lead to the disease (it normally appears during pregnancy and lactation).The development of mastopathy can provoke vitamin deficiency, trauma, abortion, hereditary predisposition, chronic diseases, etc. You can feel the appearance of mastopathy on your own. It causes pain in the mammary gland, accompanied by breast enlargement, swelling and induration. Sometimes there may be discharge from the nipples. If you find such signs, you should immediately contact a specialist.
ICD-10, (No. 60-No. 64) diseases of the mammary glands according to the International Classification of Diseases

Medical mastopathy is treated with hormonal (gestagens, estrogen inhibitors, antiestrogen, androgens, used according to the International Classification of Diseases, ICD-10) and non-hormonal drugs Mabustin.Surgical intervention is used for nodular mastopathy and is diagnosed in two types: sectoral resection (in this case, the tumor is removed along with the breast area) and enucleation (only the tumor is removed). Surgery is indicated if breast cancer is suspected, the tumor or single cyst rapidly increases.Lifestyle affects the speedy recovery. During the treatment period, it is better to limit the consumption of tea and coffee, include more vegetables and fruits containing vitamins in the diet, give up bad habits, thermal procedures (for example, in a bath or sauna), and wear comfortable underwear. Diagnostics(mammologist) consists of several stages:palpation of the mammary glands in the supine and standing position, examination of the nipples, palpation lymph nodes And thyroid gland;
Mammography - x-ray of the mammary glands;
. Ultrasound to accurately determine the structure and location of the neoplasm in the breast;
. biopsy - examination of tissue for oncogenes;
. hormonal studies, examination of the liver and consultation of specialists (gynecologist, oncologist).

This disease often occurs in the first months of a child's life. It proceeds acutely, with an increase in temperature to high values, swelling of the mammary gland, a change in the color of the skin in the area of the areola, and the development of an abscess. With improper treatment, a generalization of the process may occur with the development of a septic component. The incidence of this disease is similar in girls and boys from birth to three years (according to statistics).
According to ICD10 (International Statistical Classification of Diseases), mastitis in newborns has the code P39.0.
Doctors around the world very often refer to this classification. It helps to display statistical data and answer a number of questions related to the diagnosis, treatment, prognosis of various diseases.
Infectious suppuration of the breast baby occurs frequently. It can occur in children of both sexes of different age groups. However, girls under one month are more susceptible to this pathology.
Very often, the development of mastitis in an infant occurs against the background of physiological mastopathy. The cause may be maternal estrogen hormones. They pass on the 7th month of pregnancy from mother to fetus and infants have an imbalance of hormones. With the right approach and hygiene, the disease can go away on its own within a week. Self-medication can lead to infection. The reason can often be the use of disinfecting ointments, compresses that mothers apply to the gland, and tight bandaging of the breast.

Dr. Komarovsky believes that it is important not to harm in cases where you can just leave the child alone and follow simple hygiene rules.
Often, excessive care can cause infection (rubbing with a washcloth, removing rough areas, squeezing out a secret). Purulent mastitis can develop in a weakened child with reduced immunity. Other reasons are tight, rough or dirty clothes, infrequent bathing of the baby.
In addition to external causes, there may be internal ones leading to this pathology. These are concomitant infectious and inflammatory processes in the child's body. They can spread through the blood or lymph. Their timely treatment can prevent the development of new pathologies.
At this age, it is better to refrain from kissing. The infection can enter through the child's mouth and spread internally. Danger purulent mastitis associated with the possibility of instant development of sepsis. Risk factors also include a burdened obstetric and gynecological history, urogenital diseases, respiratory viral infections mother.
An important place is given today to natural feeding. Breast milk is a powerful immune defense for the child's body. Artificial feeding from the first days, it is often a prerequisite for reducing the defenses of the child's body and the development of a purulent infection.

Symptoms of mastitis in a child
The clinical picture of purulent mastitis and breasts is similar, and mothers often confuse these diagnoses.
With physiological mastopathy, which develops as a result of hormonal disruptions, there is no infection and high temperature. The child feels quite normal, calm. The only manifestation is an increase in the size of the mammary glands, but the color of the skin over them does not change. It is possible to secrete a certain amount of gray or white secretion, similar to colostrum. With proper care, breasts will often go away on their own without treatment. To do this, mom only needs:
- iron the child's clothes, bed linen well
- use soft cotton fabrics
- bathe your baby regularly
You can, in order to avoid the ingress of bacteria, apply to mammary gland dry clean soft cloth, changing it often. Do not make compresses (cold, hot), use ointments, folk recipes, squeeze out the secret.
If you do not follow the rules of hygiene, do not pay due attention to caring for the child, or, conversely, over-treat, you can introduce an infection. Suppuration of the swollen mammary gland will already lead to a pathological symptom complex - purulent mastitis.
In infants, this disease often begins on the seventh to tenth day after birth with symptoms of intoxication. Heat, sleep disturbance, general state the child is unsatisfactory, appetite decreases, diarrhea may join. In parallel, local symptoms develop.
The mammary gland increases, more often on one side. The skin around the areola is initially hyperemic (blush), then becomes bluish-purple. When touched, the child reacts sharply with screaming and crying. Above the focus, the temperature is increased, later a fluctuation (pulsation) joins - a sign of a formed abscess. When pressed, there may be a release of a small amount of pus, but there is also a spontaneous release of a purulent secret. These symptoms, indicative of a local inflammatory process, develop rapidly, although sequentially. It is necessary to take into account the stage of purulent mastitis in order to choose the right type of treatment.
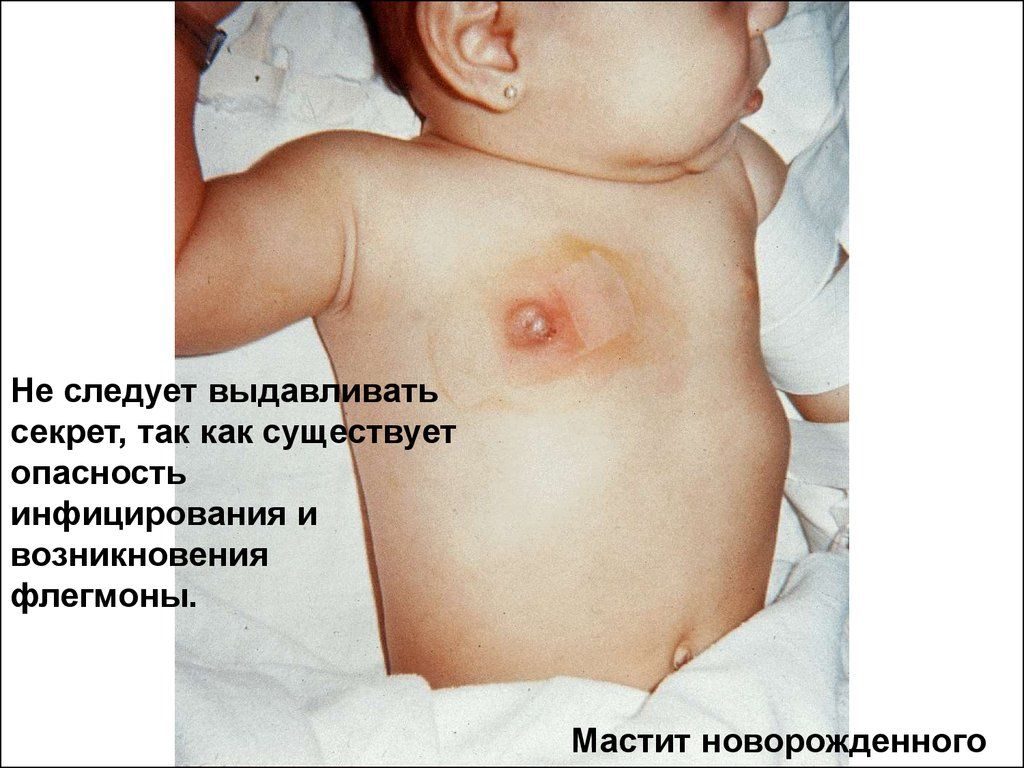
stages
- At the initial stage - serous mastitis, local phenomena are poorly expressed by the accumulation of serous fluid, skin color is often not changed. Characterized by swelling of the mammary gland, deterioration of the general condition of the child, the temperature is low. At this stage, carry out differential diagnosis with physiological mastopathy in order to choose the right treatment tactics.
- The stage of infiltration occurs when the process passes to neighboring tissues, the formation of a diffuse focus, which is accompanied by reddening of the skin, pain and high temperature.
- Then the foci of infiltration merge, leukocytes accumulate in large numbers, which fight the infection, pus is formed. Often the process can move to the underlying tissues with the formation of phlegmon and gangrene - a purulent stage.
- Complications and consequences. At this stage, mastitis in children is dangerous, as it can develop at lightning speed and turn into sepsis. It is necessary to start treatment as soon as possible, and if necessary, on the recommendation of a doctor, agree to a surgical operation. Although such an operation would have undesirable consequences for future mother, but it is carried out according to vital indications and is not discussed.
Diagnostics
For later life, mastitis in girls is more dangerous than in boys because the milk ducts can become blocked, and in the future, asymmetry of the mammary glands can be observed. In adolescence, there are also undesirable consequences: when a girl grows up, becomes a mother, she may have problems with lactation. Then these women will be included in the risk group for oncology, mastopathy.
Of the additional methods of examination, it is sufficient to determine general clinical tests. General analysis the child's blood often shows high leukocytosis with a stab shift, an increase in ESR. However, due to immaturity immune system, pronounced changes may not be in the blood picture. But this does not exclude an acute infectious process.

Treatment
The tactics of therapeutic measures depends on the stage and prevalence of the process.
On the early stages- serous and infiltrative - treatment is often limited to only conservative methods. Bed rest is established for the child, cold is applied to the mammary gland. Do bacteriological examination, and prescribe an antibiotic, taking into account the sensitivity of the bacterial flora. In parallel, antipyretic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out. These are usually medicines active substance paracetamol acts - it can be used from the first days of a child's life. In addition, drugs are used local application- water-soluble ointments with analgesic, antibacterial action, while simultaneously promoting healing.
With the formation of phlegmon and abscess of the baby, they immediately operate. The affected areas of the gland are opened, washed and drained. Antibiotic treatment of the child is continued at the discretion of the doctor.

Complementary Therapy
Use funds traditional medicine with the application of various ointments, tinctures, camphor oil often not recommended by doctors. All this can lead to sad consequences, because there is a danger of infection and allergens entering the child's body. Therefore, it is better to strictly follow the recommendations of the doctor and not engage in amateur activities.
Restorative, physiotherapeutic treatment is often prescribed during the recovery period. prescribing vitamins, mineral complexes, as well as proper balanced nutrition will help the child recover faster, get stronger.
These are the consequences that can be as a result of an inattentive attitude and neglect of the simple rules of hygiene for a baby, and the “golden rule of medicine” - prevention of a disease is easier than treatment!
But this opinion is erroneous, since it can also appear in women who have never given birth to children, as well as in men and even in newborn babies.
What is mastitis (ICD code 10), what it is and what are the causes of the development of the disease - let's talk about it.
In contact with
signs
 This disease is characterized by inflammation of one, and in some cases both mammary glands.
This disease is characterized by inflammation of one, and in some cases both mammary glands.
At the same time, a person experiences pain, the chest becomes heterogeneous, seals appear in it, it roughens, the skin turns red, the body temperature rises, and sometimes unusual discharge (pus) appears.
When the first signs of this disease appear, you should consult a specialist, especially when it comes to a nursing mother. .
It's important to know: continue breast-feeding it is impossible with a purulent form of mastitis, as this can harm the health of a newborn baby.
 Based clinical course mastitis disease can be:
Based clinical course mastitis disease can be:
- Acute - a form of the disease in which the inflammatory process affects the breast tissue. In most cases, they suffer from women who have become mothers for the first time, whose children are breastfed;
- Chronic - a form of the disease observed for a long time, and sometimes for a lifetime. One of its varieties is plasmacytic mastitis, which occurs mainly in older women.
Causes of lactational mastitis:
- Insufficient expression of milk, resulting in stagnation. Which can be fought with the help of careful decanting with your hands or with a breast pump. Otherwise, such stagnation can lead to the formation of mastitis;
- The defeat of the mammary glands by infections through wounds and cracks that arose as a result of improper attachment of the child to the breast. A prime example is Staphylococcus aureus.
Doctor's comment: various thyroid diseases, hypertension also contribute to the development of mastitis.
Causes of non-lactational mastitis:
- Infection of the mammary glands;
- Impaired health in adults or the perinatal period in newborns.
What is the main purpose of classification
 There is an international classification of absolutely all diseases, the main purpose of which is to assign a class and code to each specific human condition.
There is an international classification of absolutely all diseases, the main purpose of which is to assign a class and code to each specific human condition.
Knowing him, another doctor, scientist or relative can find out what kind of disease the patient has and draw appropriate conclusions about his health. This document is periodically updated, supplemented and each time a revision number is given.
The number 10 is the number of the last revision, it is they who should be guided by specialists in their practice.
Disease code
 Diseases of the mammary gland are characterized by a disease class from N60 - N64, mastitis corresponds to N 61. Next comes a block of codes from 085 to 092, which describes the main complications that arose after a standard birth.
Diseases of the mammary gland are characterized by a disease class from N60 - N64, mastitis corresponds to N 61. Next comes a block of codes from 085 to 092, which describes the main complications that arose after a standard birth.
In accordance with the international classification of diseases of the 10th revision (ICD 10), the following codes correspond to mastitis 091-092:
- Mastitis, the appearance of which is due to the birth of a child - 091;
- Purulent - 091.1;
- Nonpurulent - 091.2.
- The causes of the disease can be determined by the following code:
- Sore or fissure of the nipple - 092.1;
- Violation of unspecified nature 092.2;
- Violations resulting in initially little or no milk 092.3;
- Reduced breast milk production 092.4;
- Lack of milk production or its production in insufficient quantities after normal feeding, sometimes associated with the state of health of the mother 092.5;
- Disorders associated with excessive milk production, and sometimes the development of lactostasis. Codes 092.6 and 092.7 respectively.
Disease code in children
 The block of codes P00-P96 characterizes the condition of newborns. Mastitis in newborns is classified under code P39.0.
The block of codes P00-P96 characterizes the condition of newborns. Mastitis in newborns is classified under code P39.0.
It occurs in infants as a result of an increased level of hormones that have passed to them with the mother's blood. Treatment in this case is not required, since the disease resolves within a few weeks from the moment the child is born without the intervention of specialists.
Take note: a child who has this disease is most vulnerable, so it is necessary to make special demands on cleanliness in the house, as well as to monitor compliance with the hygiene rules of all family members.
Using the codes of this classification of diseases, doctors summarize information from around the world about the number of cases, the most effective ways and methods of care, as well as the analysis of the patient's condition.
Watch the following video about the features of a disease such as mastitis:
Most women probably know what mastitis is, because indirectly or directly, but most of us have experienced breastfeeding problems.
Mastitis is usually called one or another degree of severity, one form or another, inflammation of the mammary gland.
At the same time, not all women understand what the international statistical classification of diseases or other problems directly related to our health is (ICD 10). And even more so, not everyone knows what is the significance of this classification on a global scale or, for example, what is the code (in this classification) of such a common female disease as mastitis. We propose to deal with these issues slowly and strictly in order.
What is ICD 10
The abbreviation ICD means - International Classification of Diseases (from the English version - International Statistical Classification of Diseases).
The concept of ICD refers to a certain international document that is used as a leading, both statistical and classification basis in world health.
Naturally, medical science never stands still, which means that this classification document should be updated at certain intervals. World scientists and physicians considered that this document should be updated at least once every 10 years.
In such an update, the document is revised, analyzed and modified, under the direct guidance of the so-called WHO or the World Health Organization. Today, it is a unique regulatory document of its kind.
ICD 10 is designed to provide some unity of all world methodological approaches to understanding and treatment various diseases, and is also designed to ensure international comparability (and even compatibility) obtained from different countries medical materials.
Probably, someone will ask why the international classification of diseases is 10, and not 5 or, say, 15. And this also has its own direct explanation.

Note that at present, it is precisely this form that is fully operational.
international classification of diseases or conditions associated with human health, which was adopted after its tenth revision, and again after its tenth update (the familiar abbreviation ICD10, or the English version of ICD-10).
The sole and main purpose of this international classification is to create comfortable conditions for the permanent conduct of:
- Fully systematized registration of medical data from all over the world.
- Conditions for conducting a full-fledged analysis of medical data received from all over the world.
- Absolutely correct interpretation and adequate comparison of data received from all over the world on mortality, incidence and successful outcomes of treatment of diseases.
In addition, this international classification document can be used to fully transform the verbal formulations of diagnoses (dramatically different in different countries) of various diseases into a code that will be understandable to physicians anywhere in the world.
As a rule, it is the alphanumeric code that provides the greatest convenience for storing information, the convenience of its extraction and subsequent analysis. After all, data about certain diseases come from completely different countries or regions, in different periods of time.
It must be said that the international classification of diseases could become a generally accepted world (standard) diagnostic classification, convenient and useful for general epidemiological purposes.
Doctors got the opportunity to fully analyze the overall health situation in certain groups of the population. By means of this document (using a specific disease code), a full calculation of the frequency of occurrence and prevalence of a variety of diseases occurs, and in their direct relationship with a variety of external factors.
What is the place of mastitis in the international classification of diseases 10
Recall that the international classification of diseases of the tenth revision consists of three separate volumes:

- The first of which contains the entire basic classification of diseases.
- The second volume is filled with instructions for use intended for different users of the classification.
- In the third volume, users will find a complete alphabetical index, for the convenience of using the classification.
The classification itself is standardly divided into twenty-one classes. Always the first sign of a disease in the international classification of diseases is a letter that corresponds to a strictly defined class.
At the same time, the first seventeen classes belong to certain diseases ( pathological conditions), and here, the eighteenth grade is reserved for injuries, or poisoning, as well as other consequences, from the influence of certain external factors. Note that all remaining classes cover a number of modern concepts that are associated with diagnostic data.
So, such a disease as mastitis should be sought in several classes.
Firstly, this is class XIV, which includes various diseases genitourinary system, and secondly, this is class XV, which includes all conditions associated with pregnancy and childbirth, as well as the postpartum period.
The code for such a disease as mastitis also varies. For example, in class XIV, mastitis should be searched under the code N61, which includes all inflammatory diseases of the mammary gland. But, in class XV, mastitis will have several encodings depending on its forms. This is first of all:

E. Malysheva: Recently, I have been receiving many letters from my regular spectators about breast problems: MASTI, LACTOSTASIS, FIBROADENOMA. To completely get rid of these problems, I advise you to familiarize yourself with my new method based on natural ingredients...
- Code O91.2, meaning information about non-purulent forms of mastitis associated with childbearing.
- Code P39.0 describing neonatal but infectious mastitis.
- And of course P83.4, representing swelling of the mammary glands that occurs directly in newborns.
In general, it is really extremely difficult to overestimate the importance and significance of the international classification of diseases and conditions related to health, its necessity for physicians from all over the world. Although it is almost impossible to use this classification for ordinary patients, without a medical education.
Do you still think that it is completely impossible to cure your body?
How can they be identified?
- nervousness, sleep disturbance and appetite;
- allergies (watery eyes, rashes, runny nose);
- frequent headaches, constipation or diarrhea;
- frequent colds, sore throat, nasal congestion;
- pain in the joints and muscles;
- chronic fatigue(You get tired quickly, no matter what you do);
- dark circles, bags under the eyes.
MASTITIS honey.
Mastitis is an inflammation of the mammary gland. Dominant age
Mastitis of newborns occurs in the first days of life as a result of infection of hyperplastic glandular elements.
postpartum mastitis- during breastfeeding
Periductal mastitis (plasmocytic) - more often during menopause.
Predominant gender
Mostly women are affected
Juvenile mastitis - in adolescents of both sexes during puberty.
Classification
With the flowAcute: serous, purulent (phlegmonous, gangrenous, abscessing: subareolar, intramammary, retromammary)
Chronic: purulent, non-purulent
By localization - intracanalicular (galactophoritis), periductal (plasmacytic), infiltrative, spilled.
Etiology
Lactational (see)carcinomatous
Bacterial (streptococci, staphylococci, pneumococci, gonococci, often combined with other coccal flora, Escherichia coli, Proteus).
Risk factors
Lactation period: violation of the outflow of milk through the milk ducts, cracks in the nipples and areola, improper care of the nipples, violations of personal hygienePurulent diseases of the breast skin
Mammary cancer
Diabetes
Rheumatoid arthritis
Silicone/paraffin breast implants
Taking glucocorticoids
Removal of a breast tumor followed by radiotherapy
Long history of smoking.
Pathomorphology
Squamous metaplasia of the epithelium of the ducts of the mammary glandsIntraductal epithelial hyperplasia
Fat necrosis
Expansion of the ducts of the mammary glands.
Clinical picture
Acute serous mastitis (may progress with the development of purulent mastitis)sudden onset
Fever (up to 39-40 ° C)
severe pain in the mammary gland
The gland is enlarged, tense, the skin over the focus is hyperemic, on palpation - a painful infiltrate with fuzzy boundaries
Lymphangitis, regional lymphadenitis.
Acute purulent phlegmonous mastitis
Severe general condition, fever
The mammary gland is sharply enlarged, painful, pasty, the infiltrate without sharp boundaries occupies almost the entire gland, the skin over the infiltrate is hyperemic, has a bluish tint
Lymphangitis.
Acute purulent abscess mastitis
Fever, chills
Pain in the gland
Mammary gland: reddening of the skin over the lesion, retraction of the nipple and skin of the mammary gland, severe pain on palpation, softening of the infiltrate with the formation of an abscess
Regional lymphadenitis.
Laboratory research
Leukocytosis, increased ESRA bacteriological study is required to determine the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics.
Special Studies
ultrasoundMammography (breast cancer cannot be completely ruled out)
Thermal Imaging Research
Biopsy of the breast.
Differential Diagnosis
Carcinoma (inflammatory stage)Infiltrative breast cancer
Tuberculosis (may be associated with HIV infection)
Actinomycosis
Sarcoid
Syphilis
Hydatid cyst
Sebaceous cyst.
Treatment:
Conservative therapyIsolation of mother and child from other mothers and newborns
Stopping breastfeeding with the development of purulent mastitis
Bandage that suspends the mammary gland
Dry heat on the affected mammary gland
Expression of milk from the affected gland in order to reduce its engorgement
If pumping is not possible, to suppress lactation, bromocriptine is prescribed at 0.005 g 2 r / day for 4-8 days
Antimicrobial therapy: erythromycin 250-500 mg 4 r / day, cephalexin 500 mg 2 r / day, cefaclor 250 mg 3 r / day, amoxicillin-clavulanate (Augmentin) 250 mg 3 r / day, clindamycin 300 mg 3 r / day (if anaerobic microflora is suspected)
NSAIDs
Retromammary novocaine blockade.
Surgery
Aspiration of contents under ultrasound guidanceOpening and drainage of the abscess with careful separation of all ligaments
Operational incisions
With subareolar abscess - along the edge of the peripapillary field
Intramammary abscess - radial
Retromammary - along the submammary fold
At small sizes an abscess, it is possible to excise it with adjacent inflammatory tissues according to the type of sectoral resection with active drainage of the wound with a double-lumen tube and suturing tightly
Opening of all fistulous passages
With the progression of the process - removal of the gland (mastectomy).
Complications
Fistula formationSepsis
Subpectoral phlegmon.
The course and prognosis are favorable
Full recovery occurs within 8-10 days with adequate drainage
After operations, scars remain, disfiguring and deforming the mammary gland.
Prevention
Careful breast careCompliance with feeding hygiene
Use of emollient creams
Expression of milk.
Synonyms
Mastitissee also
ICD
N61 Inflammatory diseases of the mammary glandDisease Handbook. 2012 .
Synonyms:See what "MASTITIS" is in other dictionaries:
Mastitis- ICD 10 N61.61. ICD 9 611.0611.0 DiseasesDB ... Wikipedia
MASTITIS- (thorax) inflammation of the mammary gland. Mastitis usually occurs as a result of penetration (through nipple cracks) of pyogenic microbes into the mammary gland. Most often it occurs in lactating women and pregnant women. With mastitis, it suddenly rises ... ... The Concise Encyclopedia of the Household
mastitis- breast Dictionary of Russian synonyms. mastitis n. chest Dictionary of Russian synonyms. Context 5.0 Informatics. 2012. mastitis ... Synonym dictionary
MASTITIS- MASTITIS, breast, mastitis, mammitis, mas tadenitis (from Greek mastos female breast), inflammation of the mammary gland. Distinguish sharp and hron. inflammatory processes. Acute inflammation mammary glands can occur at all periods of life, but more often ... ... Big Medical Encyclopedia
mastitis- a, m. mastite mastos breast, nipple. Inflammation of the mammary gland. Krysin 1998. Lex. Michelson 1866: mastitis; BASS 1: suits / t ... Historical Dictionary of Gallicisms of the Russian Language
mastitis- MASTITIS, colloquial. reduced chest ... Dictionary-thesaurus of synonyms of Russian speech
MASTITIS- (from the Greek mastos nipple chest) (breast), inflammatory disease mammary gland in humans and animals, usually as a result of infection through nipple cracks; occurs more often in the postpartum period ... Big Encyclopedic Dictionary
MASTITIS- MASTITIS, husband. Inflammation of the mammary gland. | adj. venerable, oh, oh. Explanatory dictionary of Ozhegov. S.I. Ozhegov, N.Yu. Shvedova. 1949 1992 ... Explanatory dictionary of Ozhegov
Mastitis- (from the Greek mastos nipple, chest) (breast), an inflammatory disease of the mammary gland in humans and animals, usually as a result of infection through the cracks in the nipples; occurs more often in the postpartum period. … Illustrated Encyclopedic Dictionary
Mastitis- I Mastitis (mastitis; Greek mastos chest + itis; synonymous with breast) inflammation of the parenchyma and interstitial tissue of the mammary gland. There are acute and chronic mastitis. Depending on the functional state of the mammary gland (Mammary gland) (the presence of ... Medical Encyclopedia
MASTITIS- (breast), acute or chronic inflammation of the mammary gland, usually associated with its infection during lactation. MASTITIS IN HUMANS Mastitis usually occurs in women, although occasionally cystic mastopathy observed in men. Spicy… … Collier Encyclopedia
Books
- Acute purulent lactational mastitis, A. P. Chadaev, A. A. Zverev. The book covers the issues of etiology and pathogenesis, clinic, prevention and treatment of acute purulent lactational mastitis, as well as the principles of surgical treatment, depending on various forms ...
